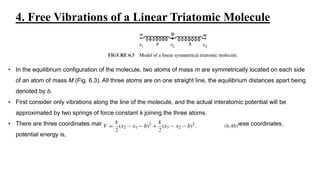
This lecture discusses oscillations in linear systems near equilibrium. It introduces the formulation of the eigenvalue equation to determine the normal modes and frequencies of free vibration. As an example, it analyzes the free vibrations of a linear triatomic molecule, modeling it as three masses connected by springs. Solving the eigenvalue equation yields three normal mode frequencies, one of which is zero corresponding to the center of mass motion.