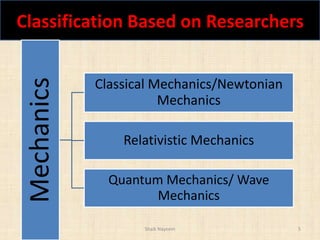
This document provides an introduction to engineering mechanics and its classifications. Engineering mechanics can be classified based on researchers into classical mechanics, relativistic mechanics, and quantum mechanics. It can also be classified based on the type of body into mechanics of rigid bodies, deformable bodies, and fluids. Additionally, engineering mechanics is divided into statics and dynamics. Statics deals with bodies at rest while dynamics considers bodies in motion, and can be further broken down into kinetics and kinematics.