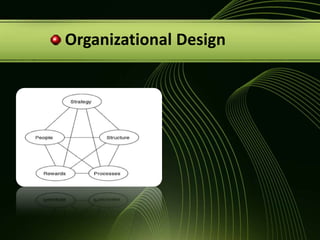
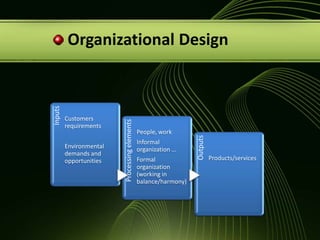
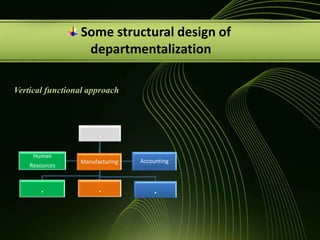
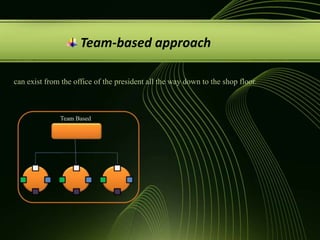
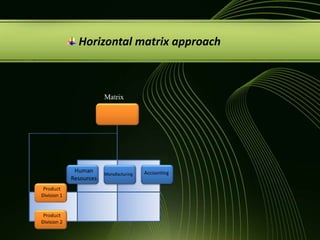
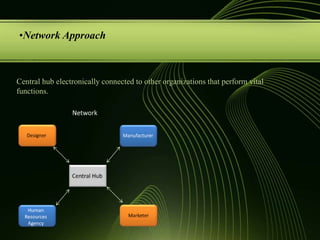
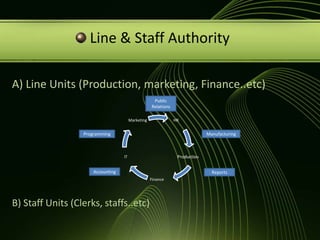
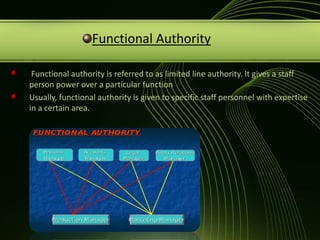
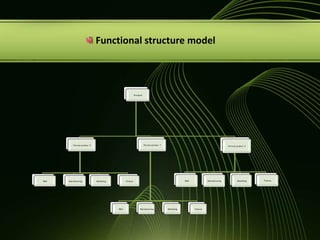
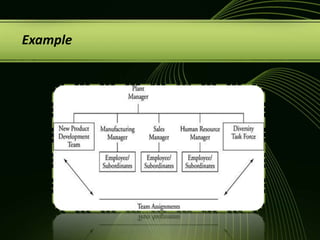
The document discusses various concepts related to organizational structure and design including departmentalization, establishing reporting relationships, allocating authority, coordination activities, and basic forms of organizational design. It provides examples of different departmentalization approaches like functional, team-based, matrix, and network. It also outlines principles of organizational design such as division of labor, unity of command, and spans of control. Current issues organizations face include adapting to a changing environment and addressing workforce diversity and ethics.