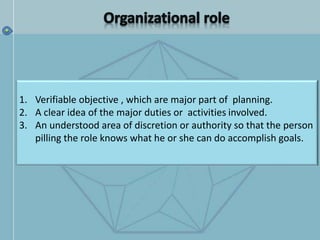
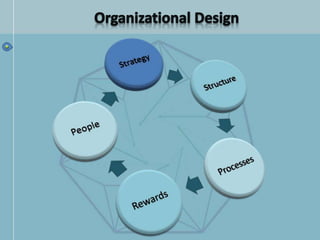
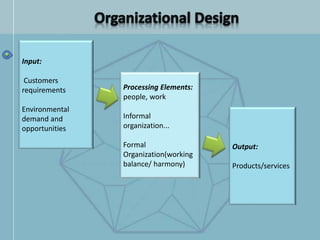
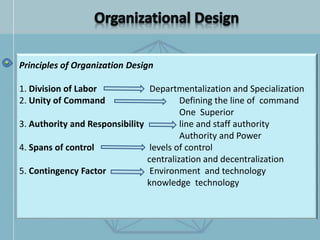
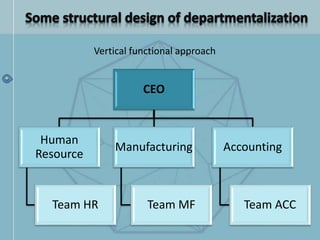
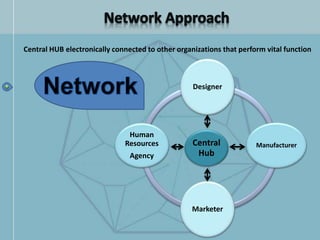
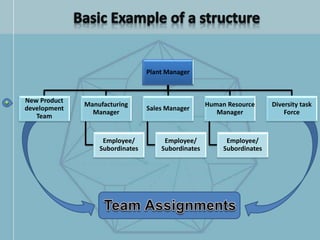
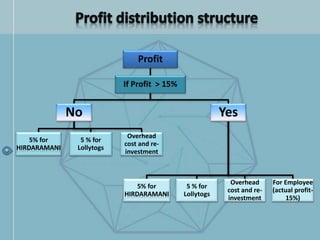
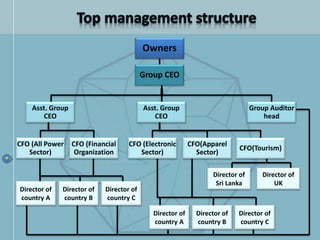
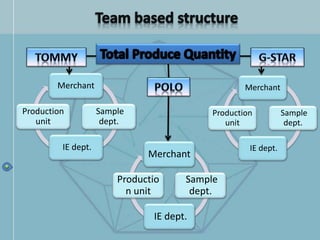
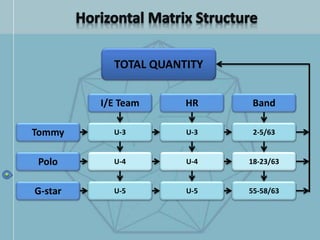
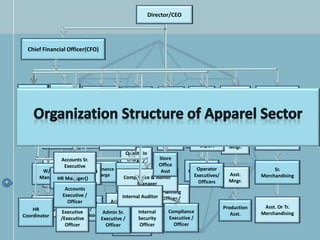
The document discusses organizational structure and design. It begins by outlining the key topics to be covered, including departmentalization, establishing reporting relationships, allocating authority, and coordinating activities. Several principles of organization design are then explained, such as division of labor, unity of command, and spans of control. Different approaches to departmentalization are described, including functional, product, and matrix structures. The document also includes organizational charts for the Hirdaramani Group, a large conglomerate operating in multiple industries and countries. Some challenges of the current structure are noted.