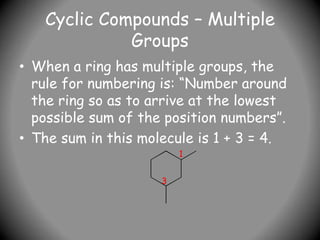
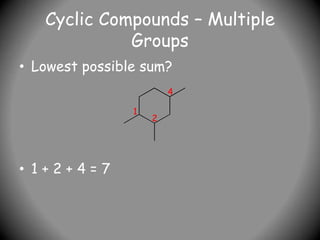
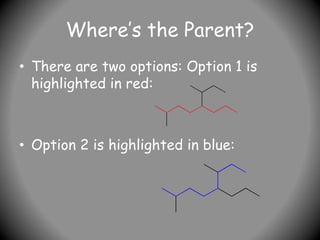
1) IUPAC nomenclature provides systematic names for organic compounds based on their structure. Names specify the parent chain, substituents, and their positions.
2) Names have three parts - prefixes, the parent name indicating chain length, and a suffix denoting compound class (e.g. -ane for alkanes).
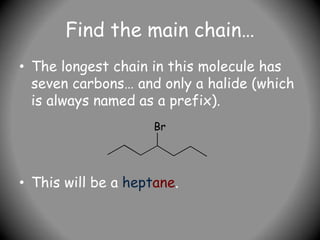
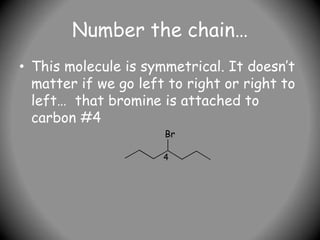
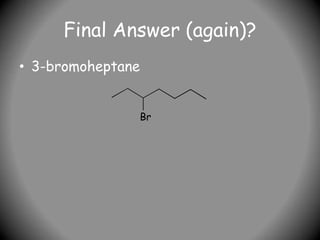
3) Prefixes include alkyl groups like methyl or ethyl, and halides named as prefixes with position numbers (e.g. 3-bromoheptane). More complex prefixes are in brackets.










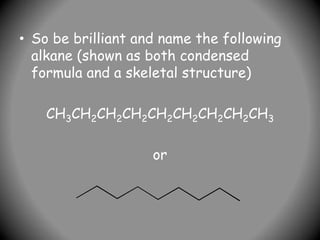




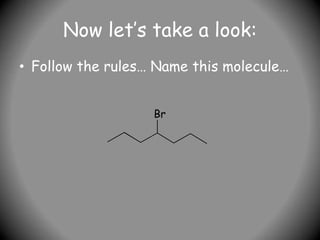










![Sec-Butyl Groups
• The other possibility is to form the
fragment one of the central carbons:
CH3CHCH2CH3, which is called “sec-
butyl”. [Note that the carbon second
from the left only has three bonds – so
that’s where its bonding to the main
chain]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nomenclature-230920030146-c4ff5b23/85/nomenclature-ppt-30-320.jpg)















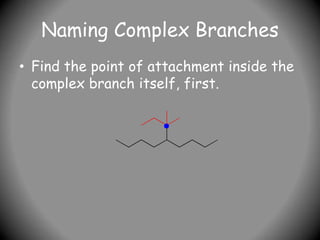
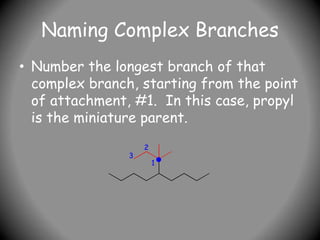
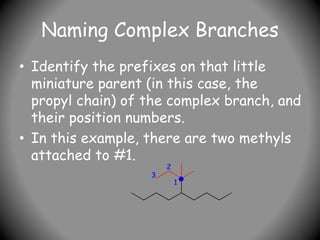
![Naming Complex Branches
• Write the full name, placing the
complex branch inside brackets. This
complex branch is attached to #5 of
the original main chain so:
• 5-[1,1-dimethylpropyl]nonane is the
name.
1
2
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nomenclature-230920030146-c4ff5b23/85/nomenclature-ppt-51-320.jpg)