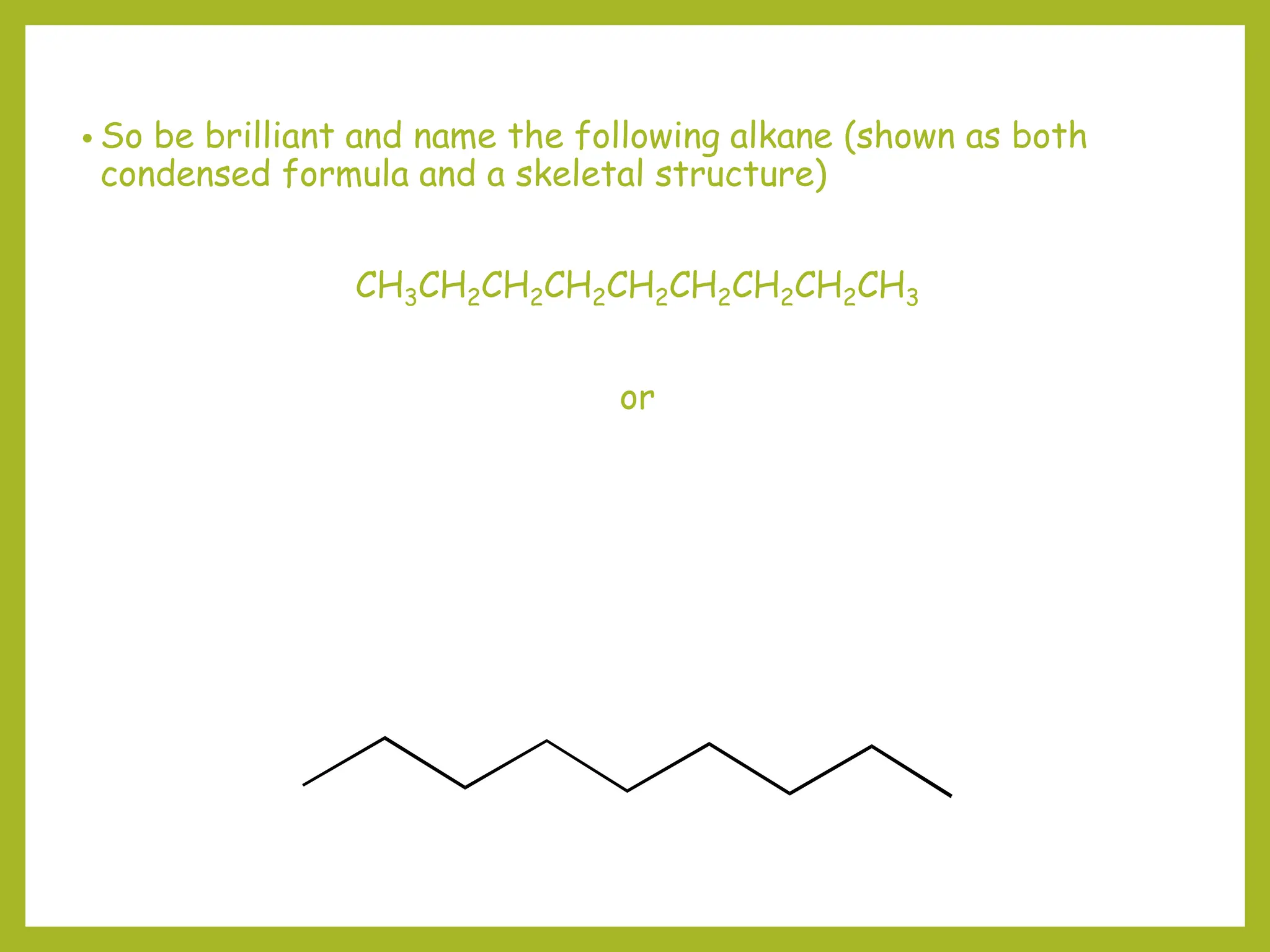
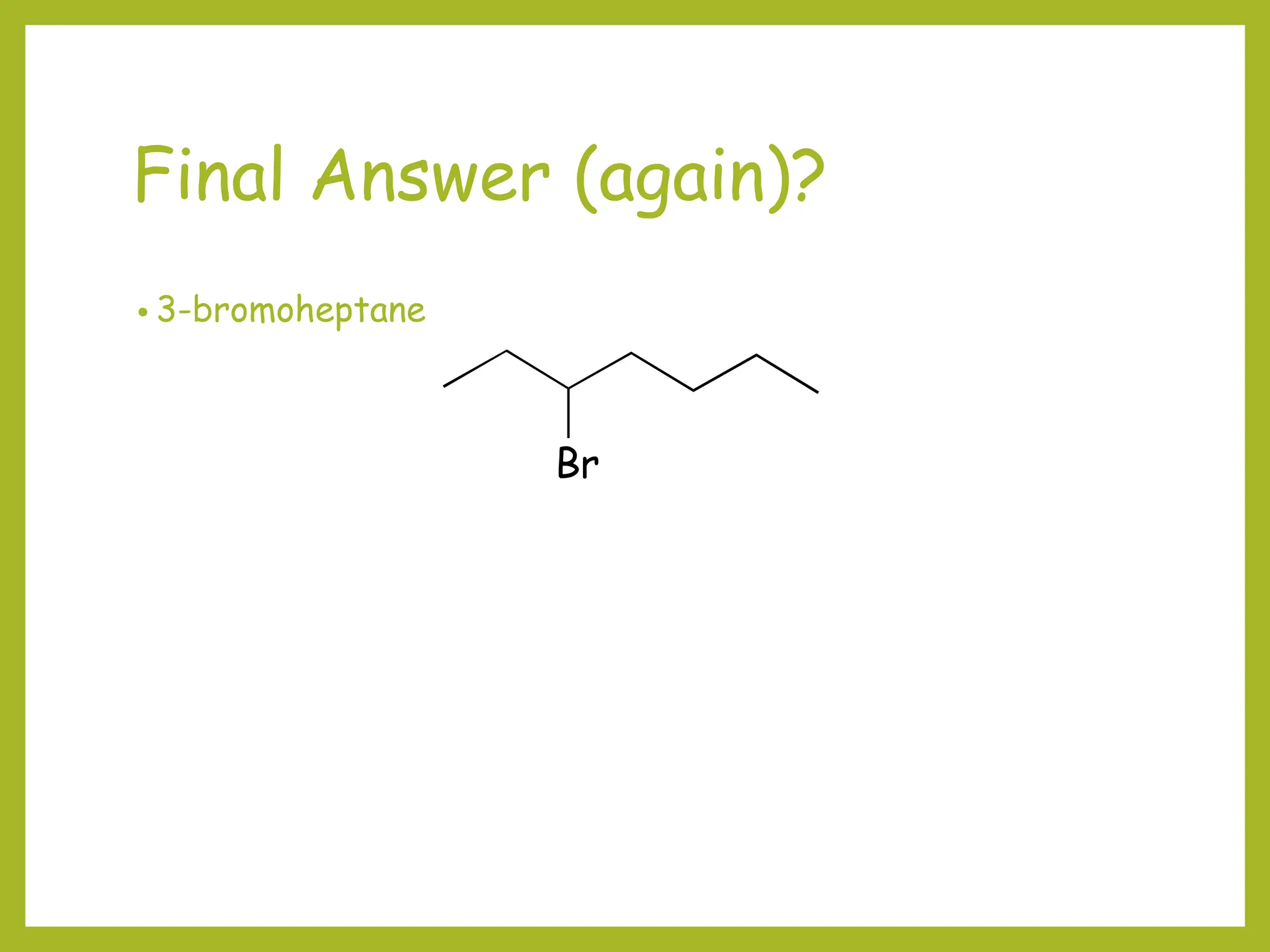
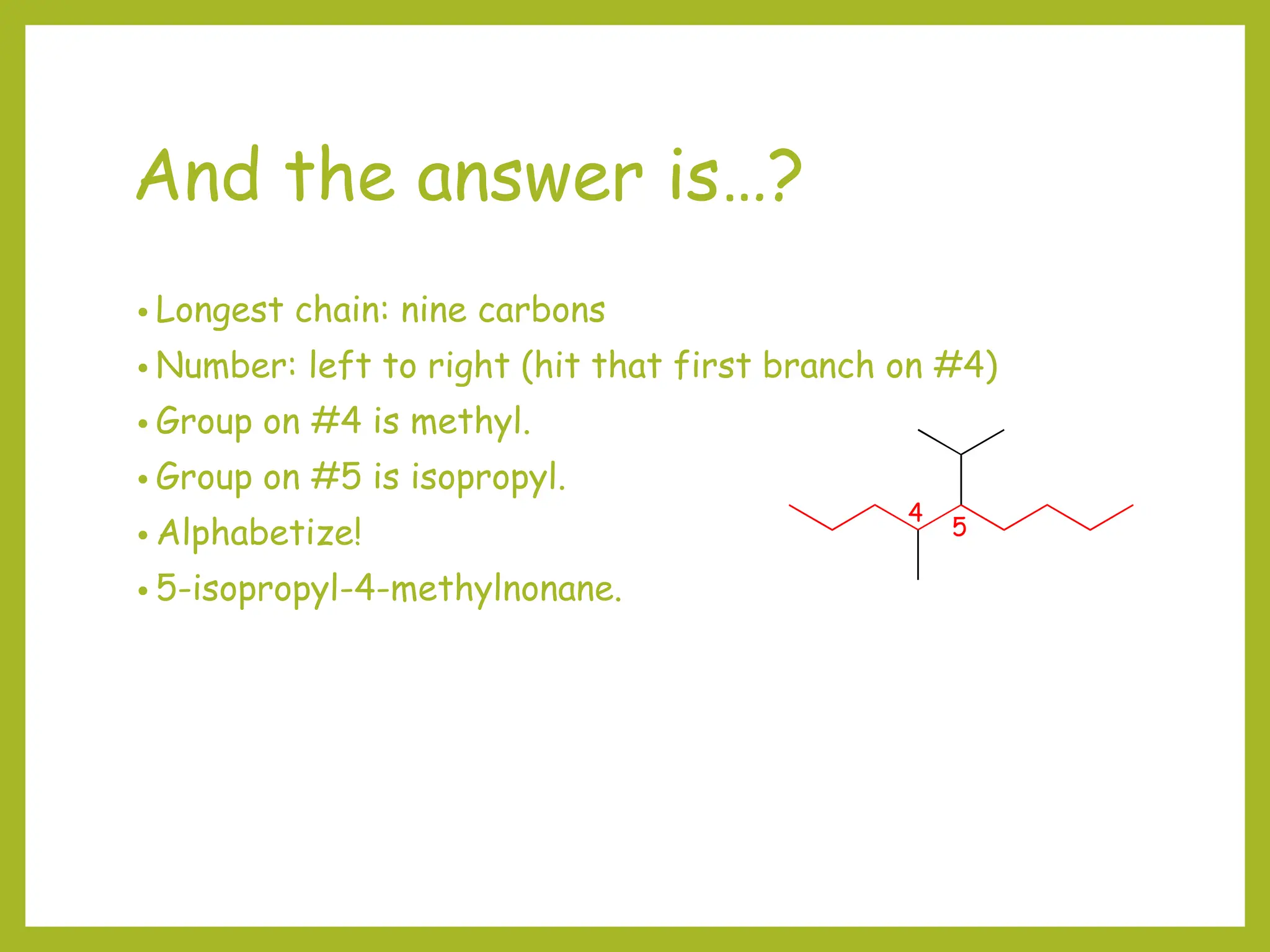
1) Organic molecules are named using a prefix-parent-suffix system. The parent is the longest carbon chain or ring and the suffix indicates the molecule family (e.g. -ane for alkanes).
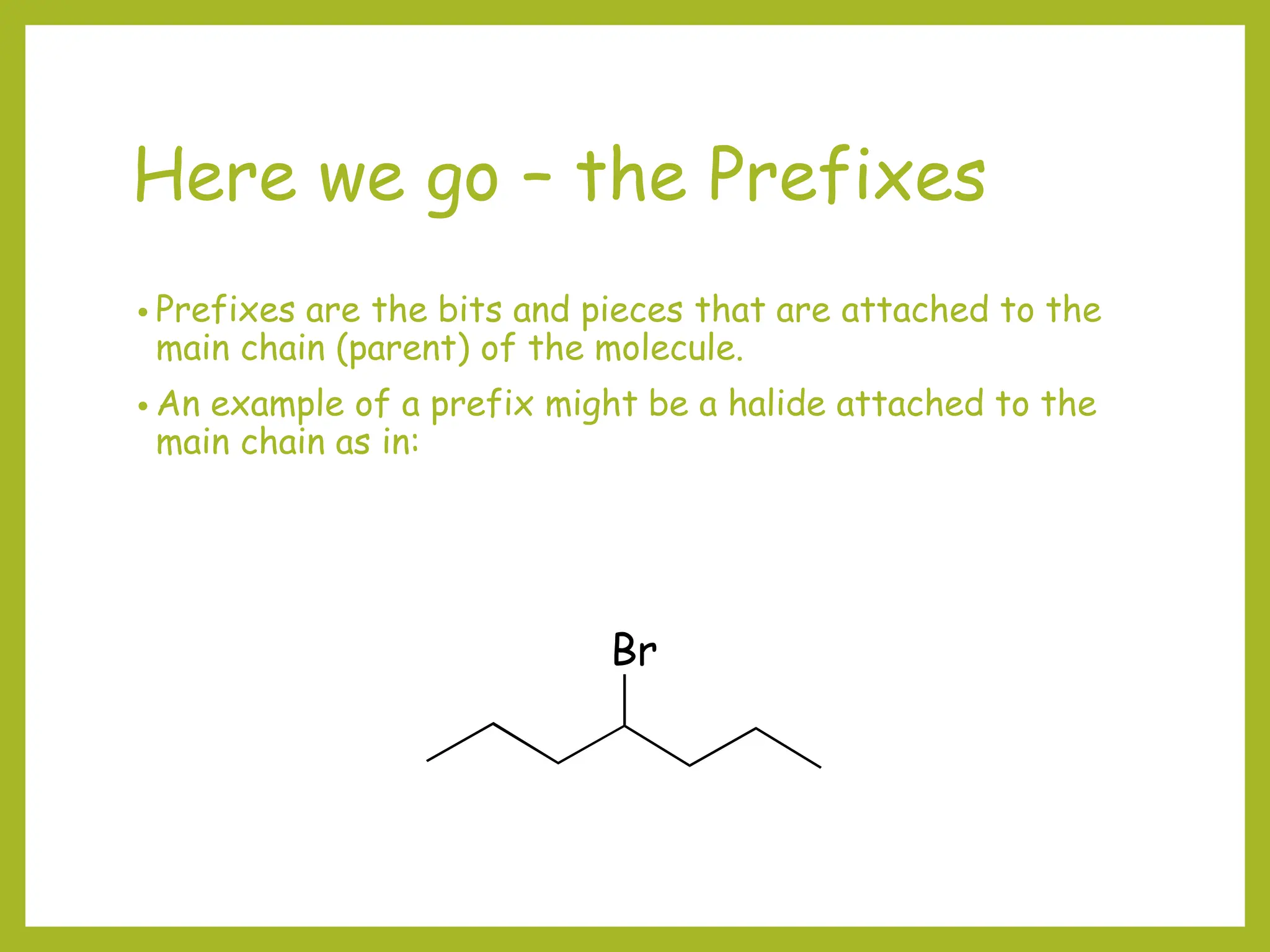
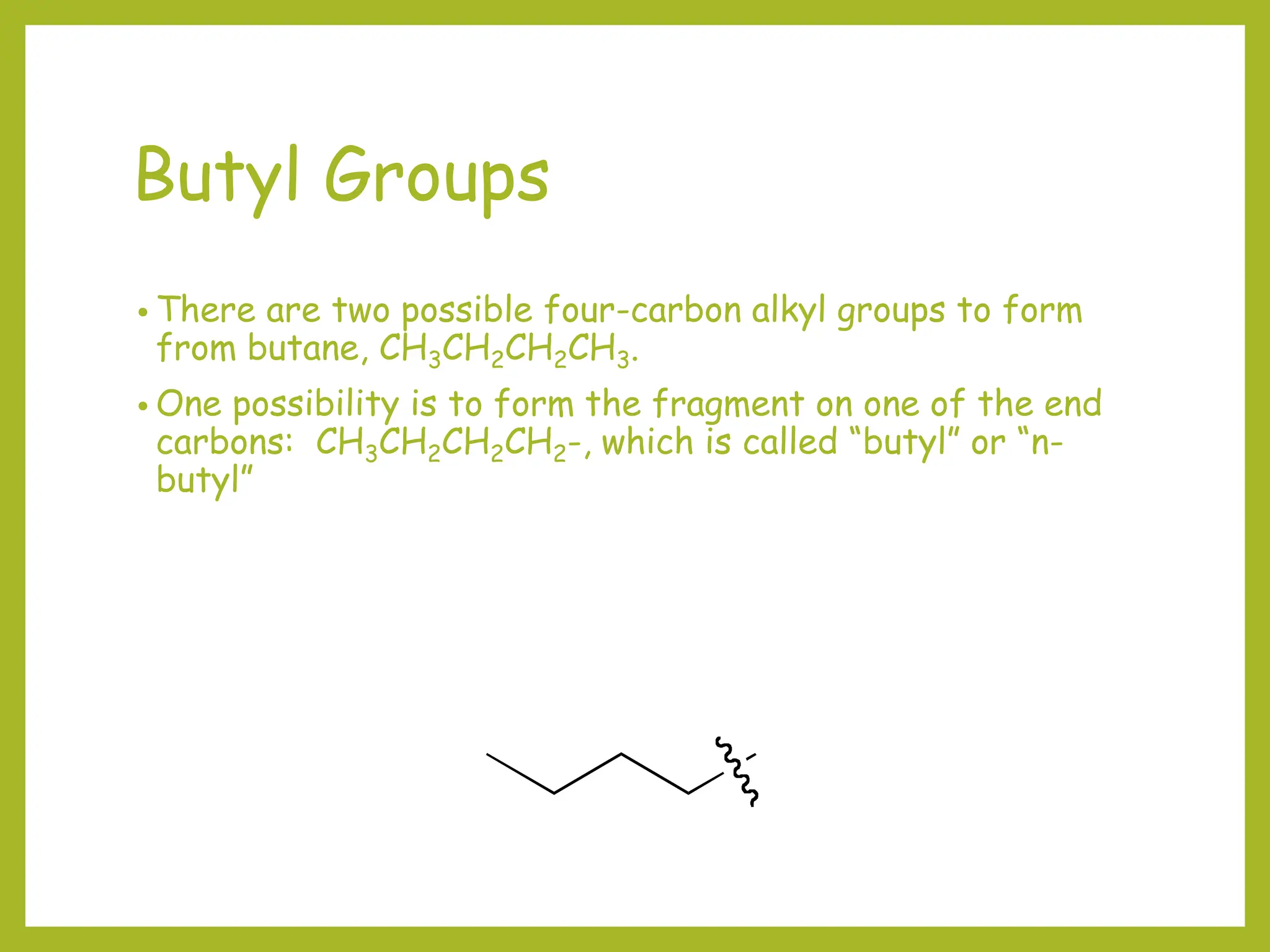
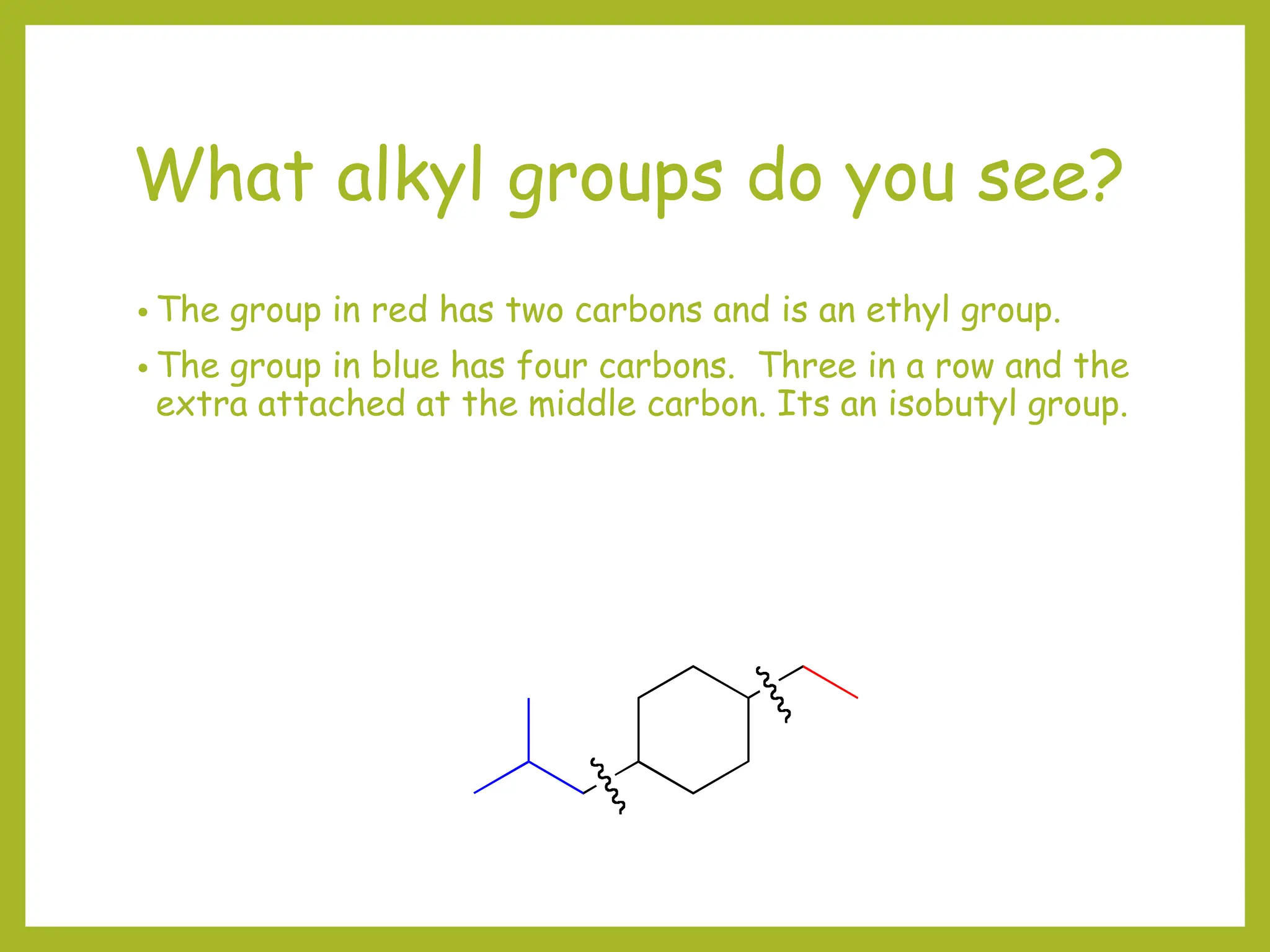
2) Prefixes like methyl, ethyl, and propyl indicate substituents on the parent chain or ring. Prefixes are alphabetized and include position numbers.
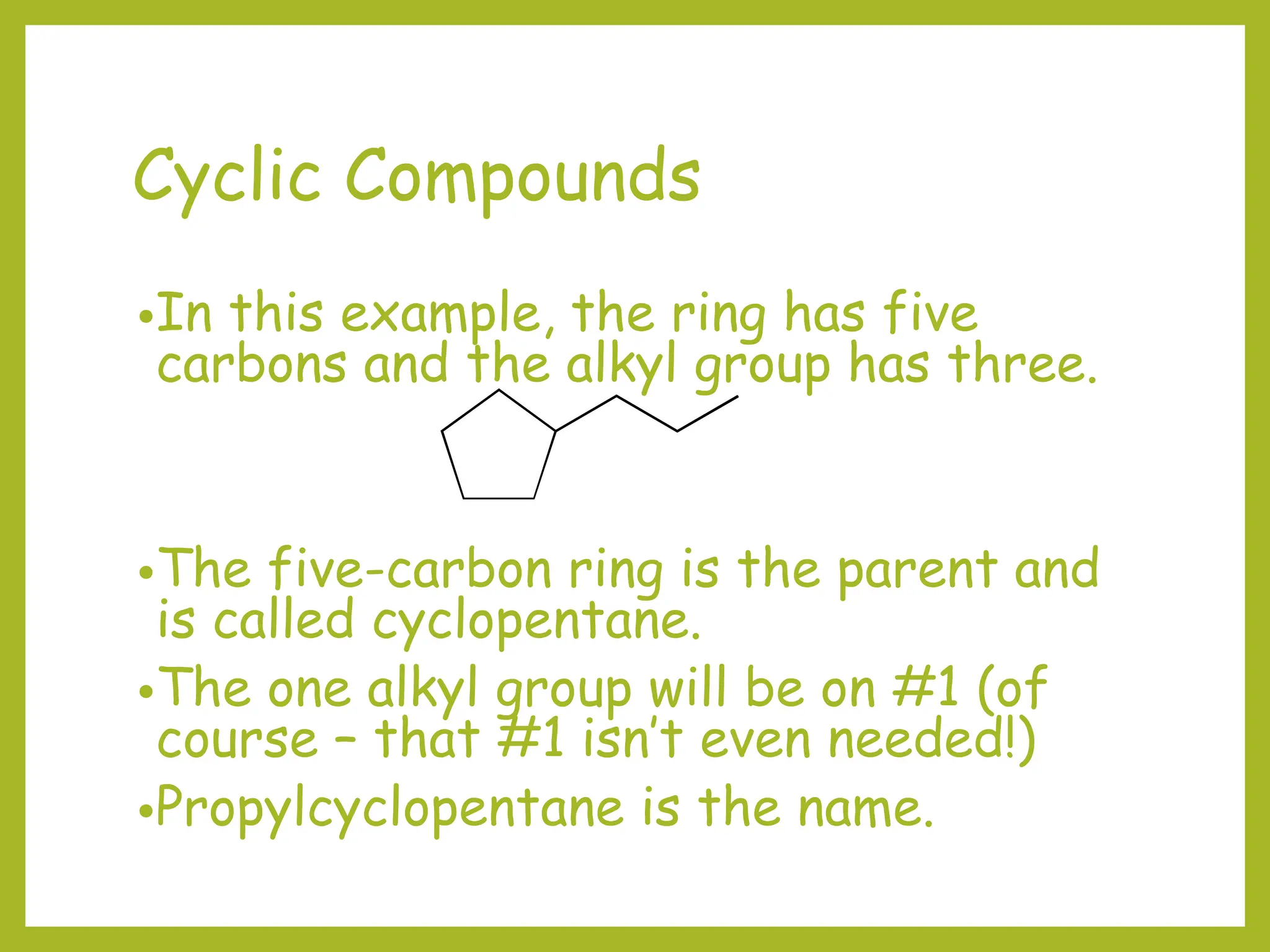
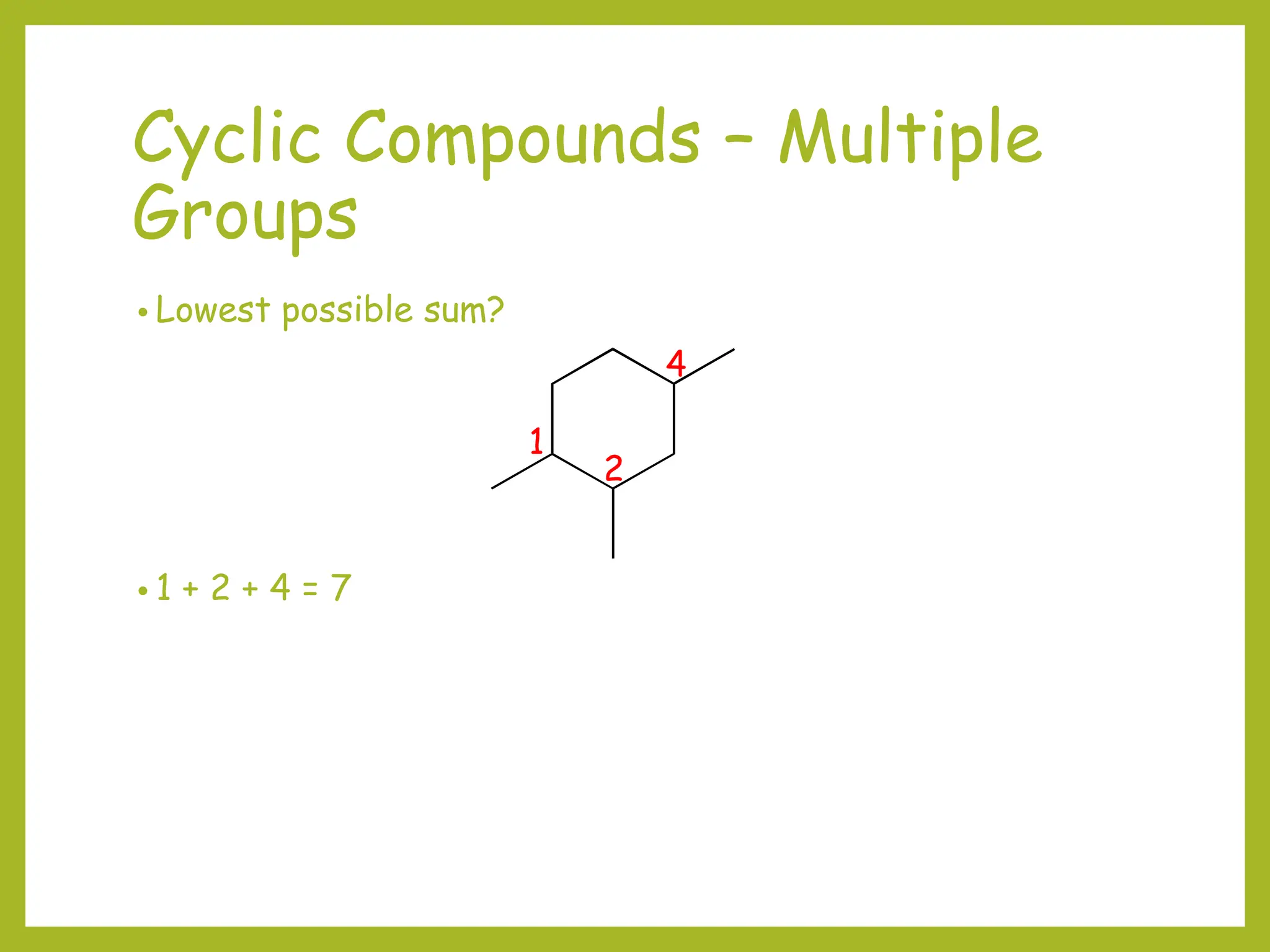
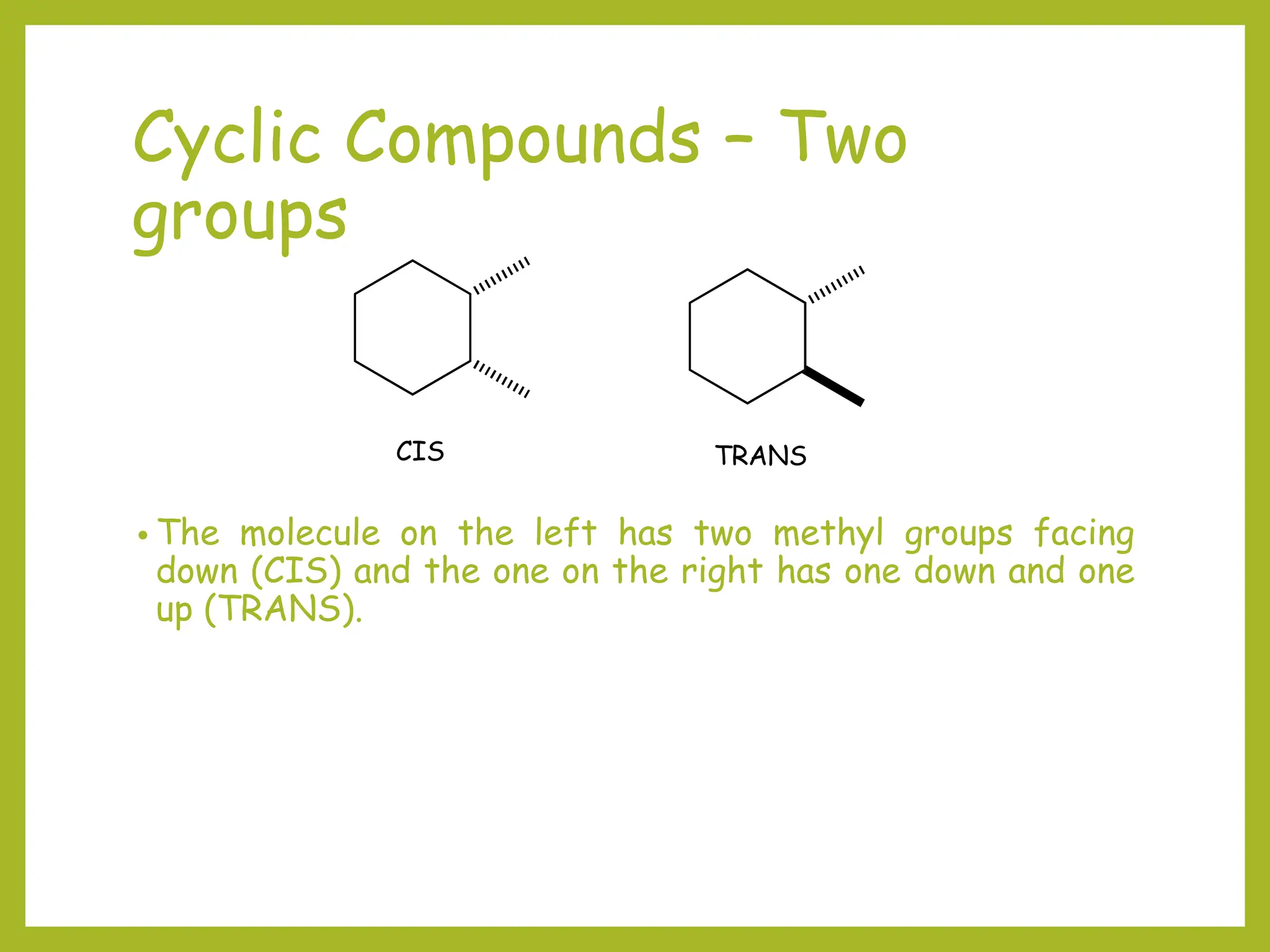
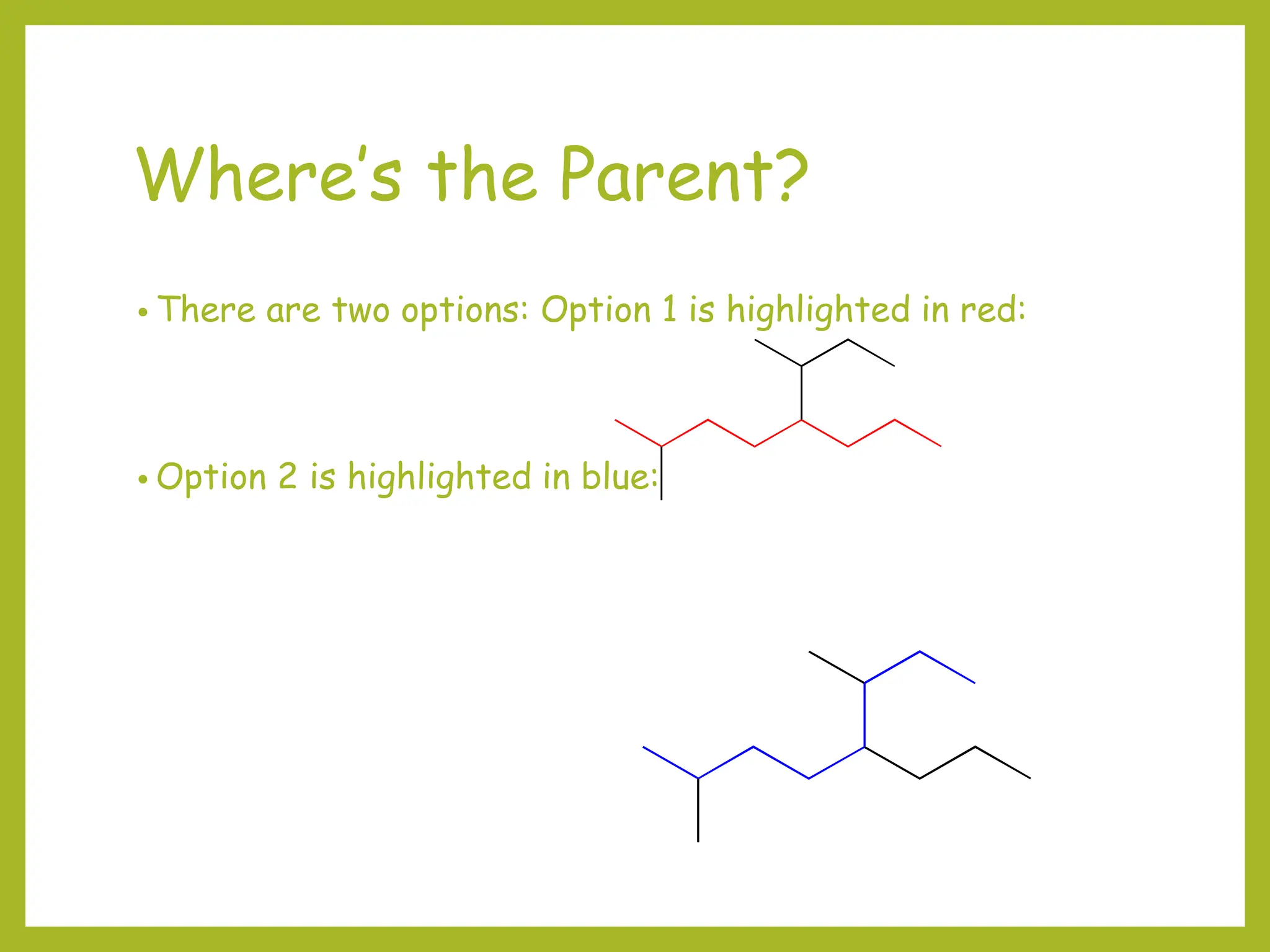
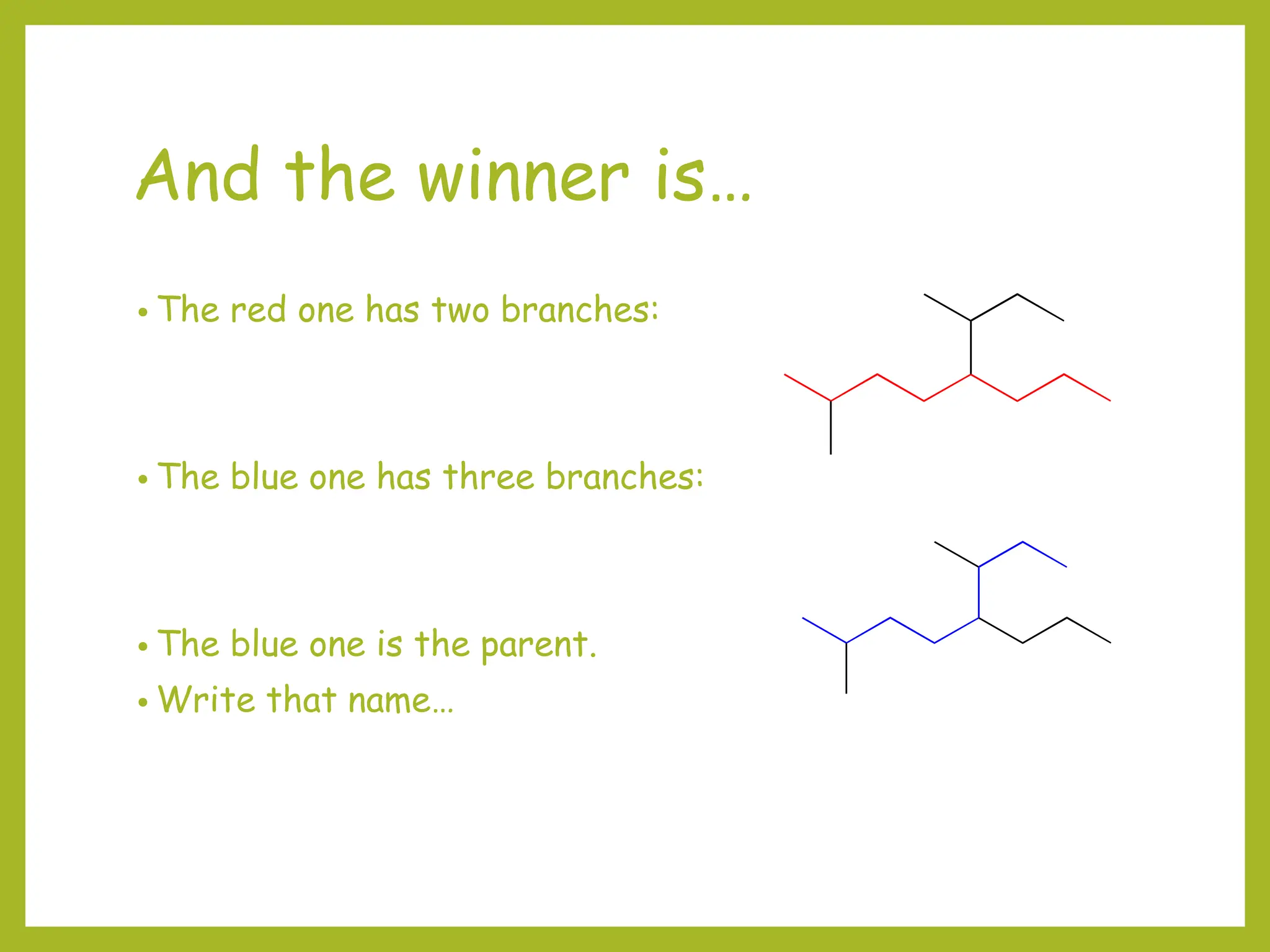
3) Cyclic compounds can have the ring or longest carbon chain as the parent. Multiple substituents are numbered to minimize the sum of their positions.
























![Sec-Butyl Groups
• The other possibility is to form the fragment one of the
central carbons: CH3CHCH2CH3, which is called “sec-
butyl”. [Note that the carbon second from the left only
has three bonds – so that’s where its bonding to the main
chain]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nomenclature-240218164212-2e83c0d6/75/Nomenclature-AND-IUPAC-naming-of-alkanes-30-2048.jpg)















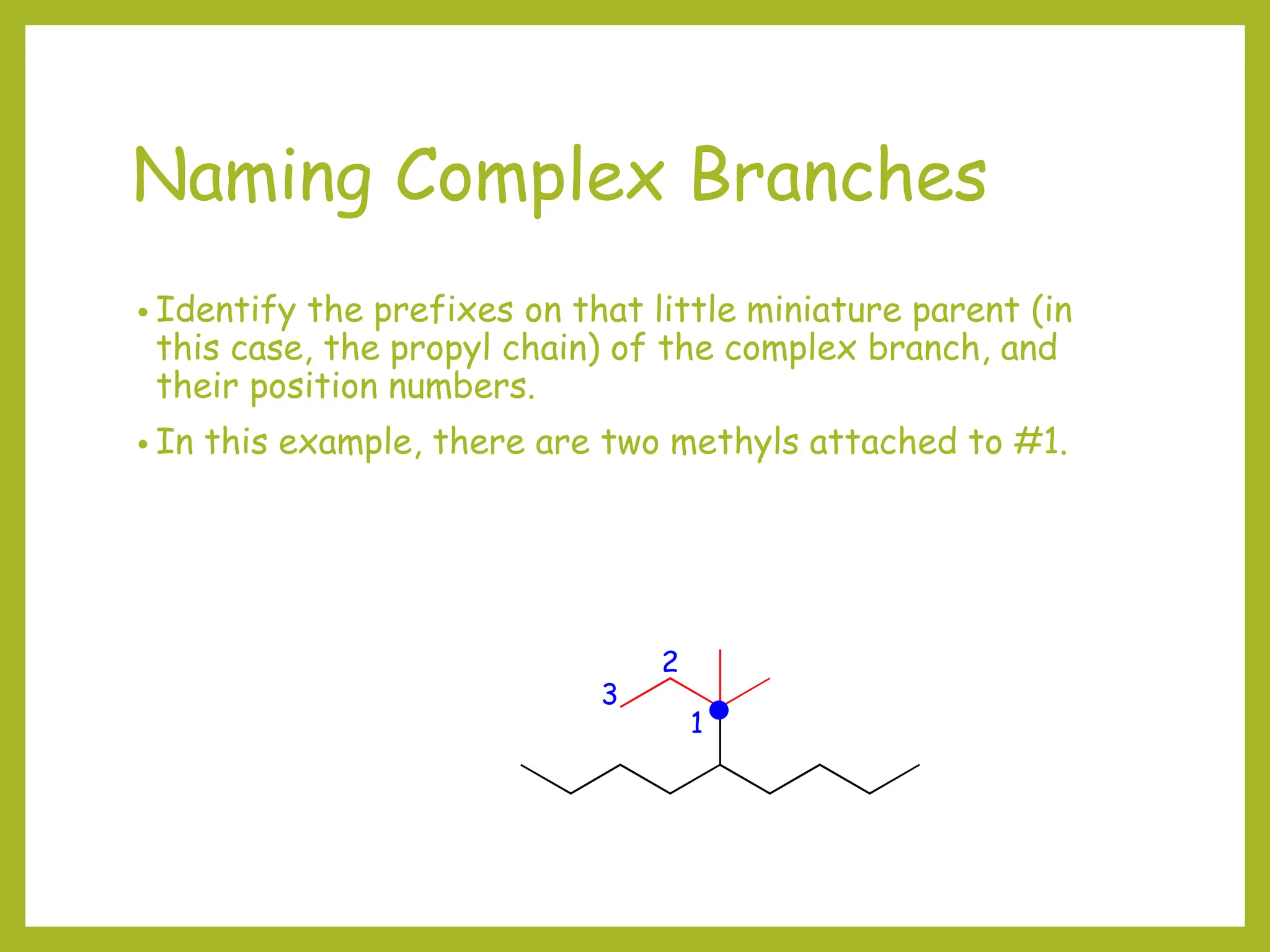
![Naming Complex Branches
• Write the full name, placing the complex branch inside
brackets. This complex branch is attached to #5 of the
original main chain so:
• 5-[1,1-dimethylpropyl]nonane is the name.
1
2
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nomenclature-240218164212-2e83c0d6/75/Nomenclature-AND-IUPAC-naming-of-alkanes-51-2048.jpg)