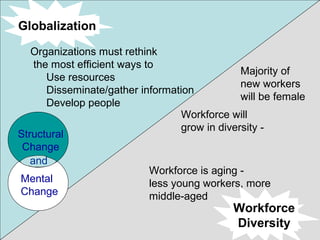
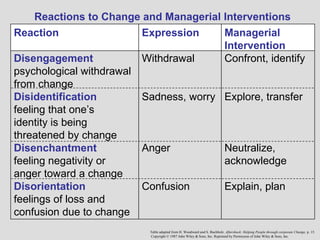
1) Managing change involves dealing with both planned and unplanned changes in organizations. Planned changes result from deliberate decisions while unplanned changes are often imposed and unforeseen.
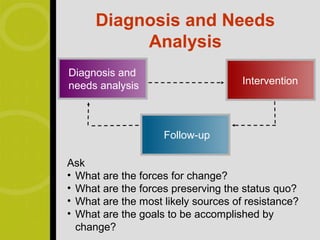
2) Organizational development is a systematic approach to organizational improvement that applies behavioral science to increase individual and organizational effectiveness. It involves diagnosis, intervention, and follow up.
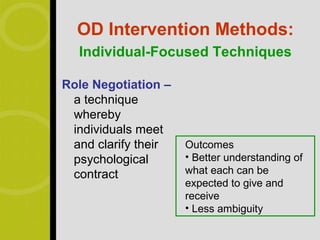
3) Common intervention methods include survey feedback, management by objectives, team building, and process consultation at the group level as well as skills training, leadership development, and job redesign at the individual level.