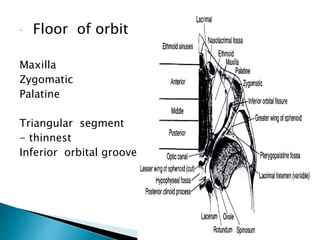
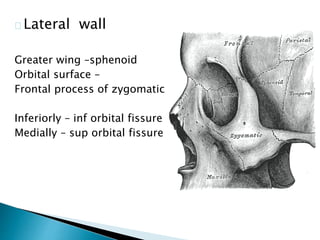
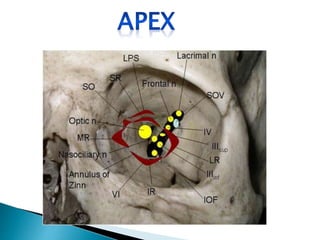
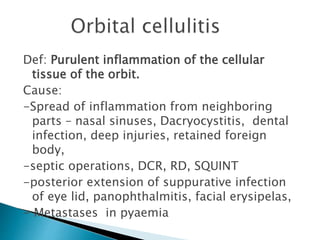
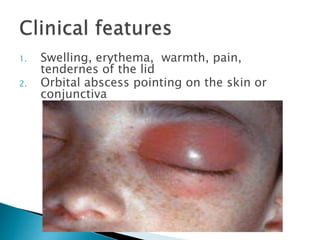
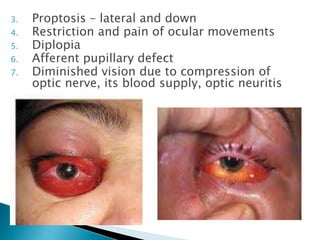
This document describes orbital cellulitis, including its causes, symptoms, potential complications, diagnostic tests, and treatment. Orbital cellulitis is a purulent inflammation of the orbital connective tissue that can be caused by the spread of infection from nearby areas like sinuses or injuries. Symptoms include swelling, eye pain, and vision issues. Without treatment, complications can include abscesses, vision loss, and spread to nearby areas like the brain. Diagnosis involves tests like CT scans and cultures. Treatment consists of broad-spectrum antibiotics, monitoring by multiple specialists, and sometimes surgical drainage or decompression.


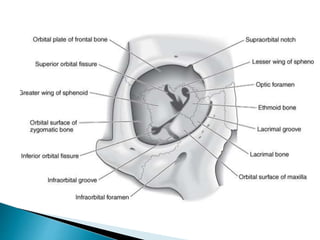

![Roof of orbit
Frontal bone [Orbital plate] & lesser wing of sphenoid
Separated from frontal sinus and anterior
cranial fossa above
Lacrimal gland fossa and trochlear fossa
behind orbital rim](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orbit-tina-141021000448-conversion-gate01/85/ORBIT-Anatomy-5-320.jpg)
![Medial wall
Body of sphenoid
Ethmoid
Lacrimal
Maxilla[frontal
process]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/orbit-tina-141021000448-conversion-gate01/85/ORBIT-Anatomy-6-320.jpg)