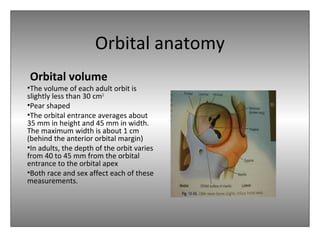
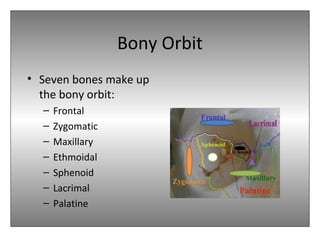
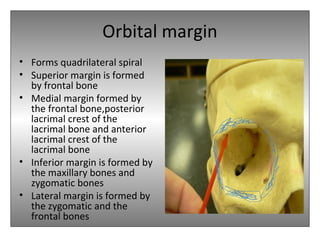
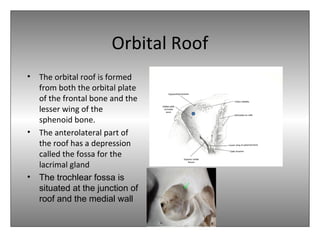
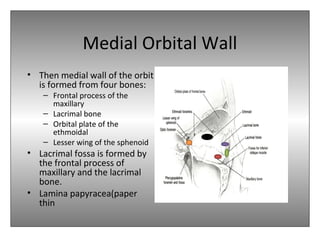
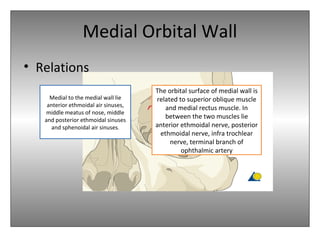
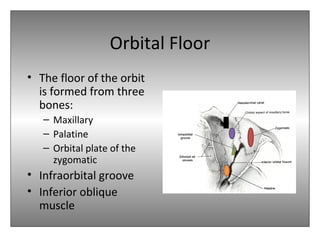
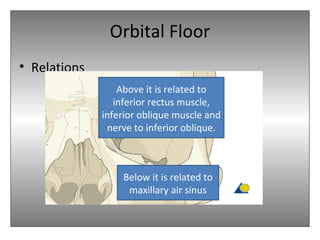
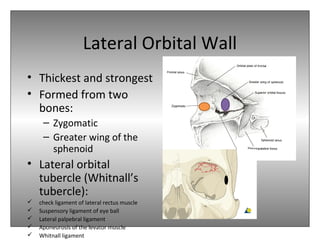
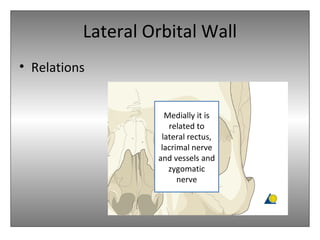
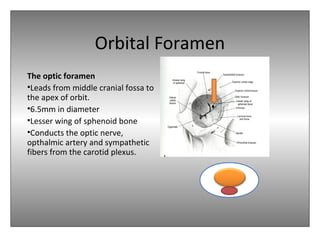
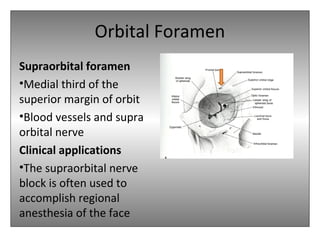
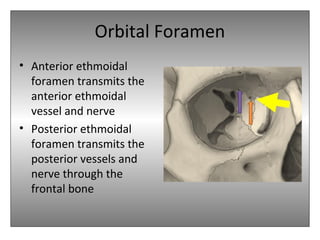
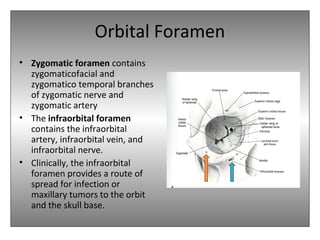
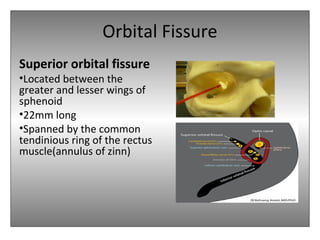
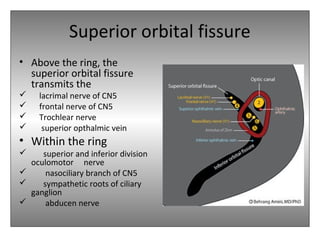
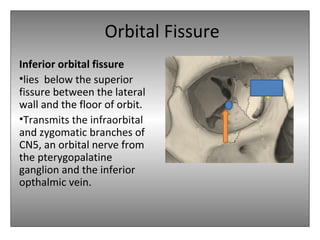
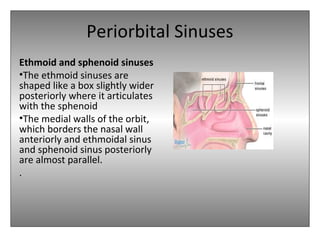
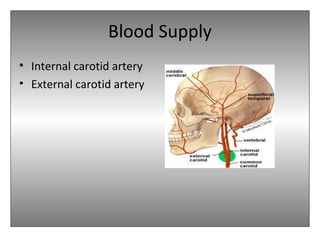
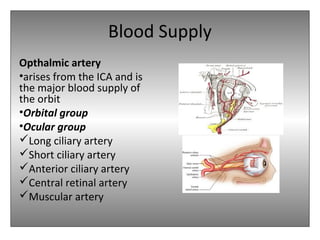
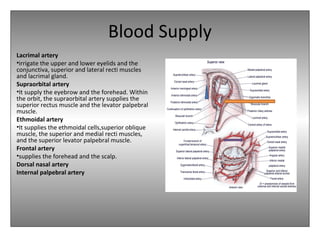
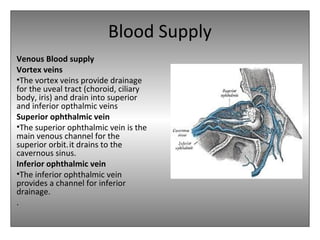
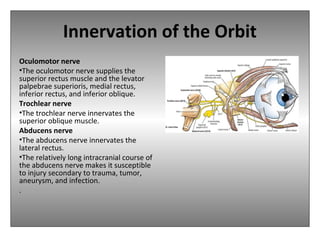
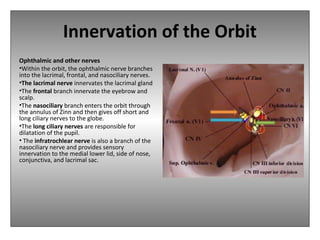
The document provides an overview of the anatomy of the eye and orbit. It describes the seven bones that make up the bony orbit, including the frontal, zygomatic, maxillary, ethmoidal, sphenoid, lacrimal and palatine bones. It details the structures forming each wall of the orbit, such as the medial orbital wall formed by the frontal process of maxillary, lacrimal bone, orbital plate of ethmoid and lesser wing of sphenoid. Key orbital foramina and fissures transmitting nerves and vessels are also outlined, along with the blood supply and venous drainage pathways. Sinuses related to the orbit including the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid and maxillary sinuses