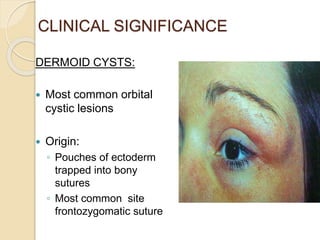
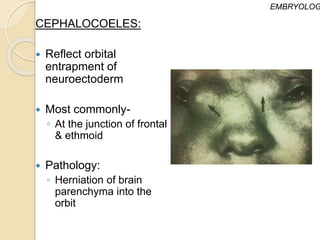
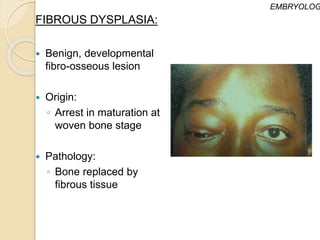
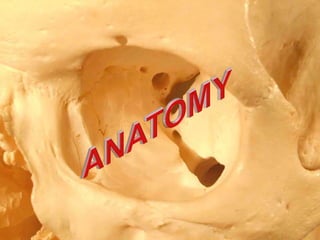
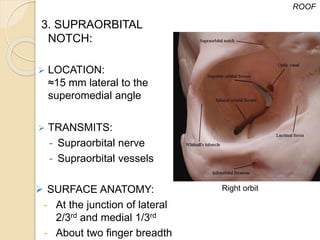
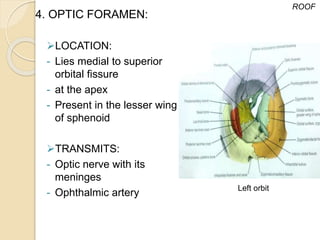
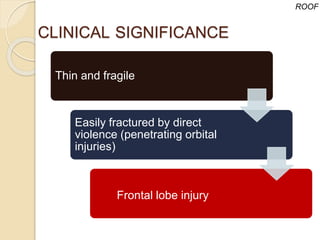
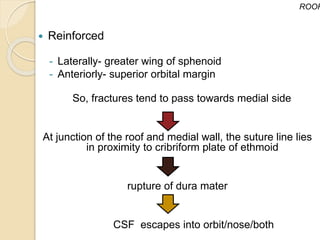
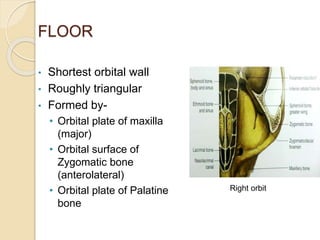
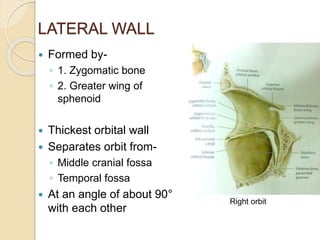
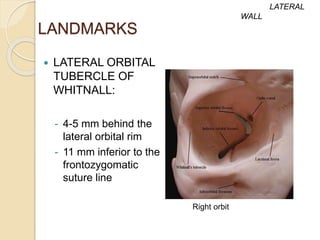
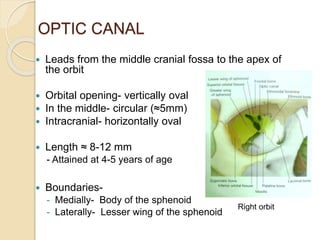
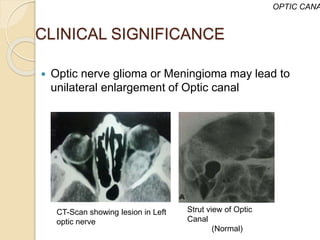
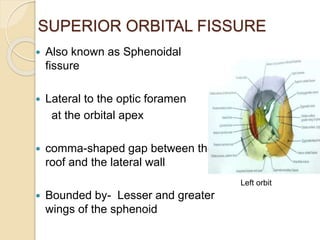
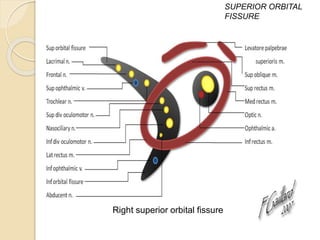
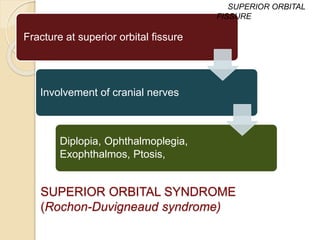
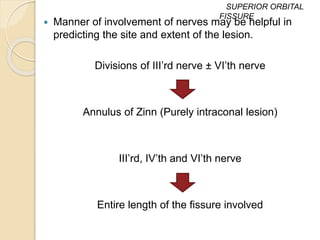
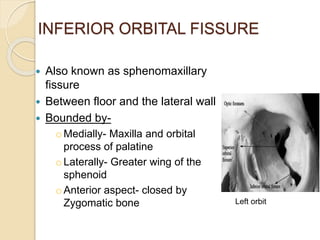
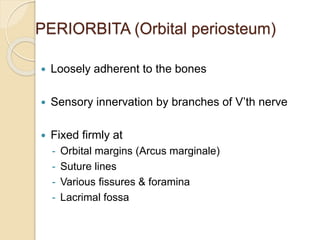
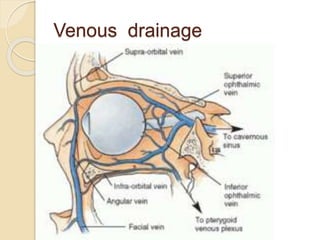
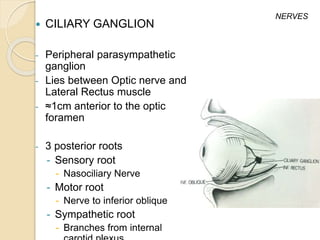
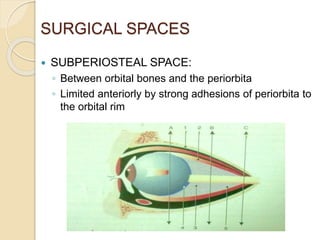
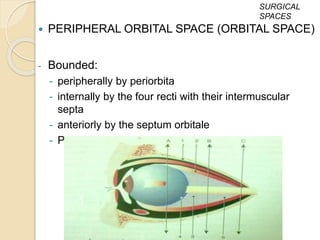
The document discusses the anatomy of the orbit, including its embryology, dimensions, boundaries, and clinical significance. It can be summarized as follows:
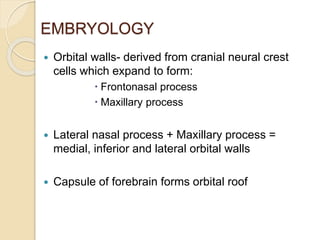
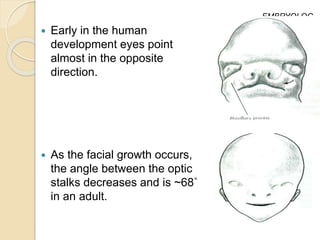
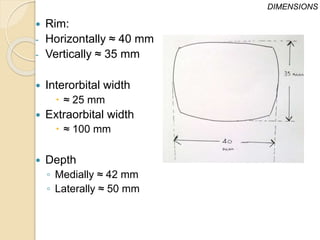
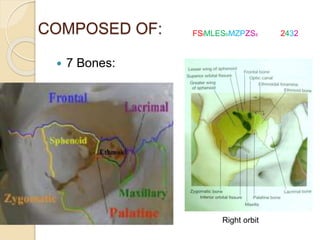
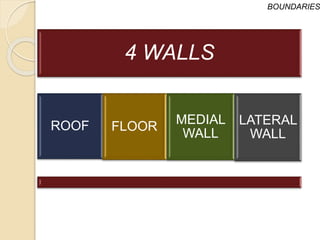
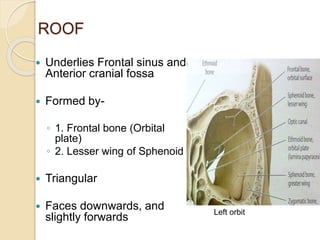
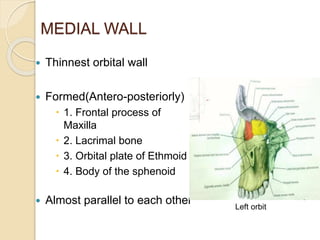
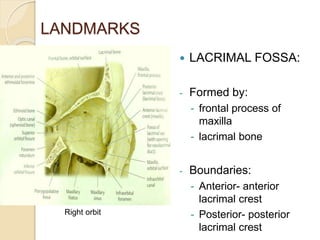
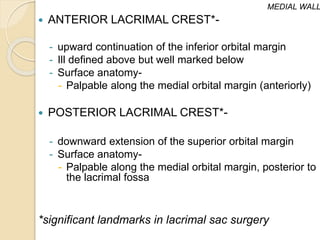
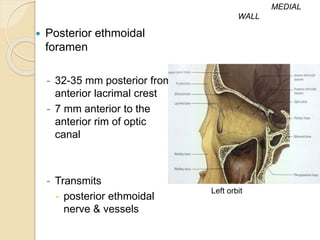
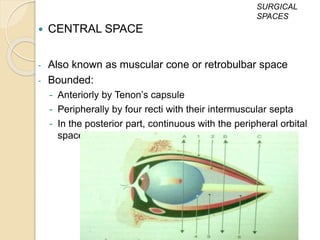
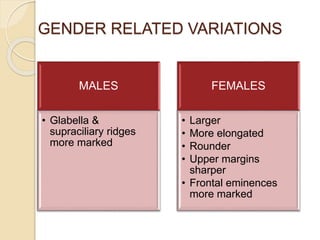
The orbit is a pyramid-shaped space bounded by seven bones and containing the eye. It develops from the frontal process, maxillary process, and lateral nasal process in embryology. The thin medial wall and floor are most prone to fractures. Landmarks like the lacrimal fossa and infraorbital foramen have clinical importance. Fractures of the orbit can damage surrounding structures and cause diplopia or sensory changes.