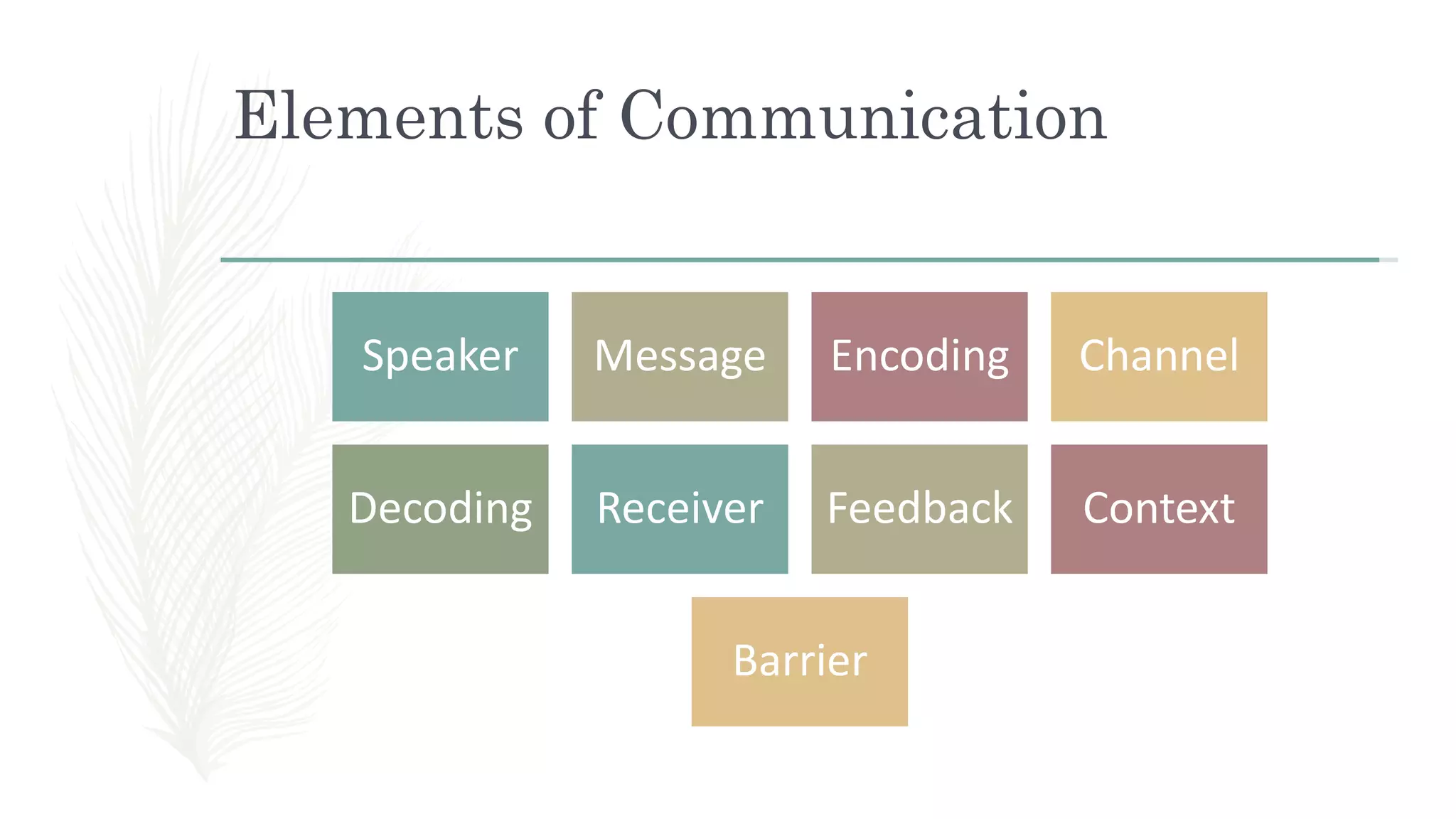
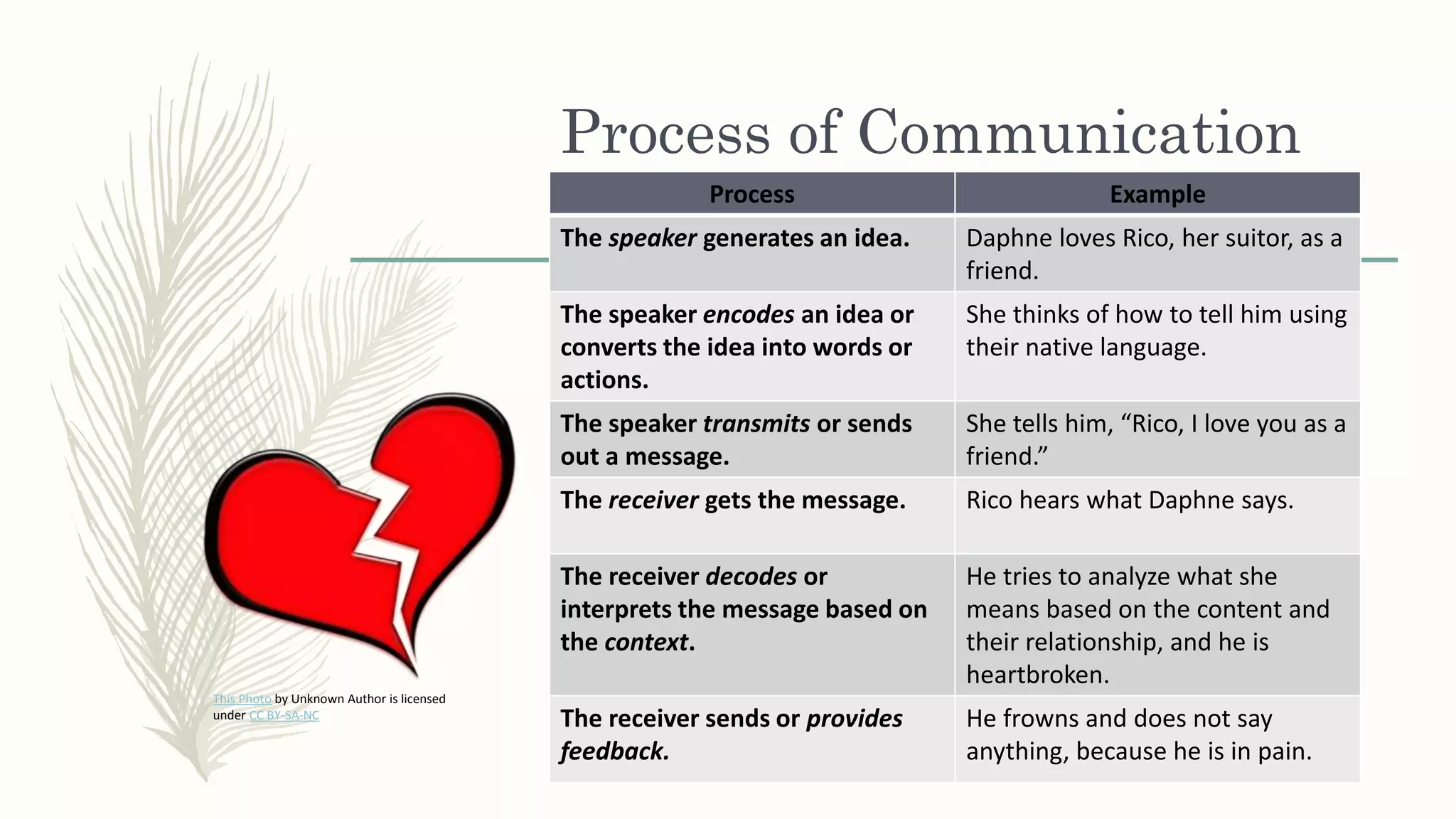
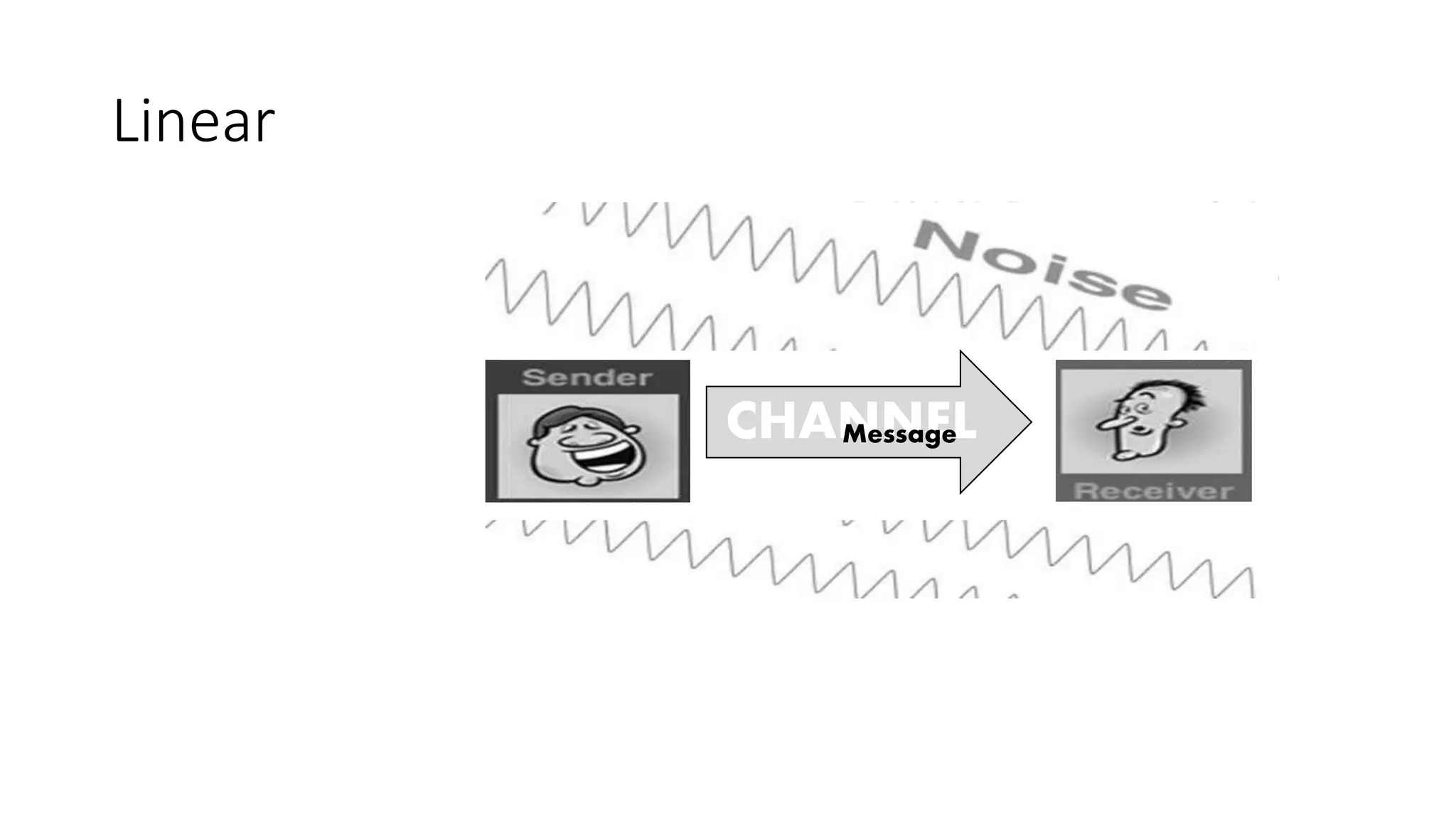
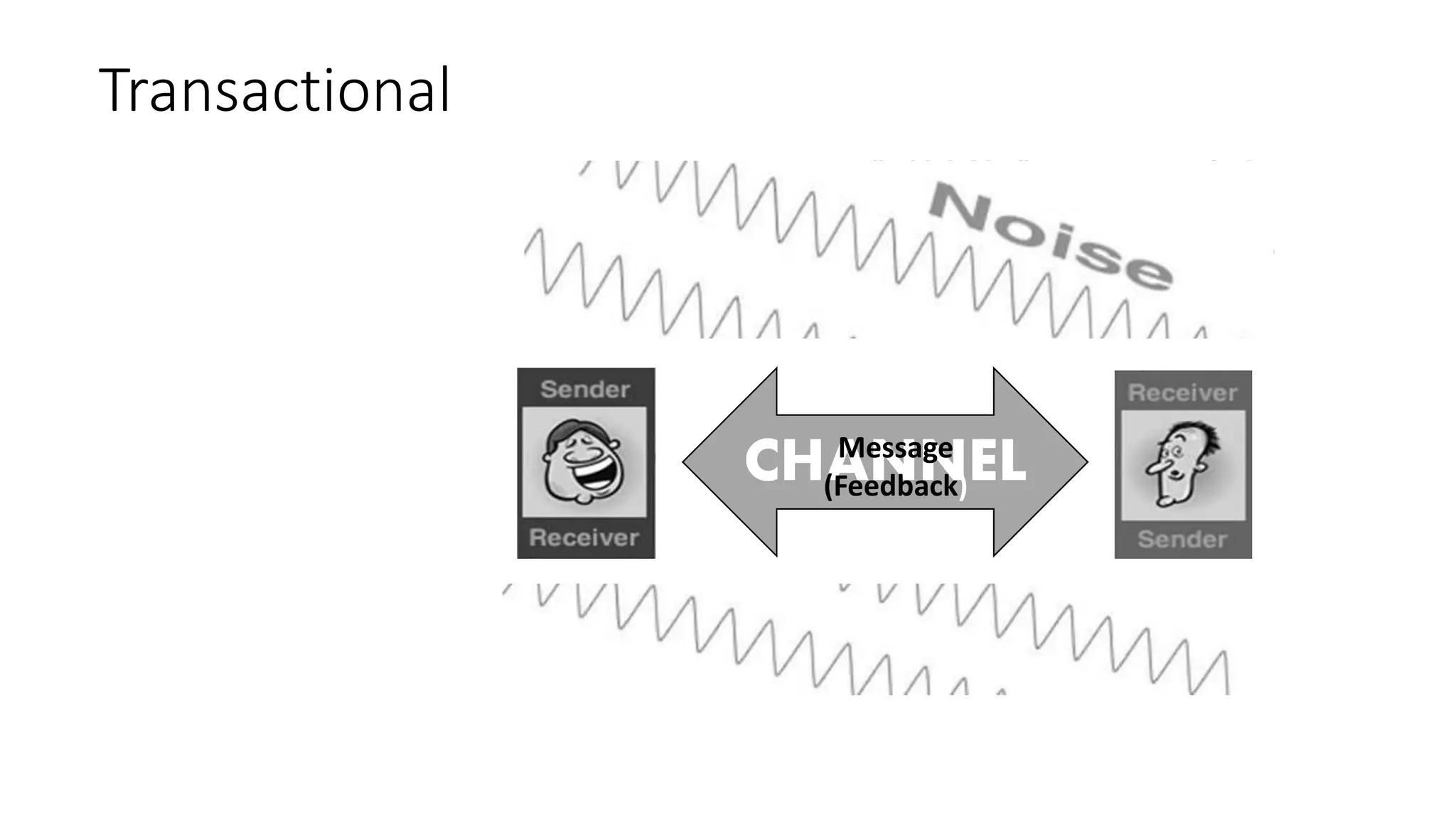
This document provides an overview of oral communication and the nature of communication. It discusses key aspects of communication including its definition, process, elements, forms, and models. The main points covered are that communication is the exchange of information between individuals using symbols or behaviors, it is a process that occurs between a sender and receiver through a channel, and elements of communication include a speaker, message, encoding, decoding, receiver, feedback, context and barriers. Communication can take different forms like face-to-face, group discussions and calls. Models of communication include linear, interactive and transactional. The document aims to explain the functions, nature and process of communication.