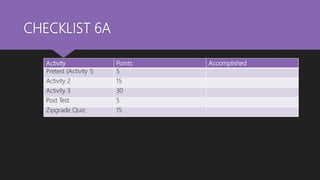
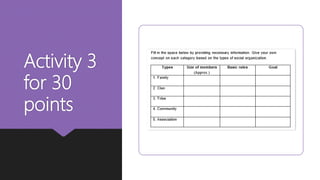
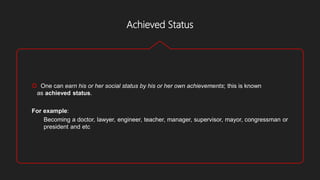
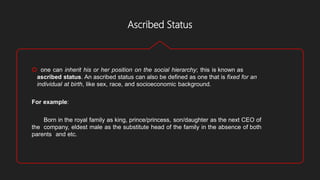
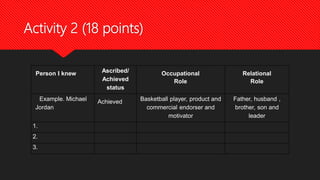
Social organization refers to how individuals associate and depend on one another to form formal social groups. Family is the most basic social organization, with members extending to clans, communities, tribes and nations. There are two types of social organizations - kinship which includes family, clan and tribe, and voluntary which includes community and association. Social structure refers to the network of roles and hierarchy of statuses that define expectations within a social unit. Social status can be achieved, through one's own accomplishments, or ascribed, inherited at birth. Roles are norms that function as plans for expected behavior.