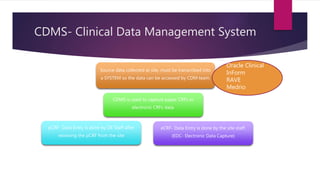
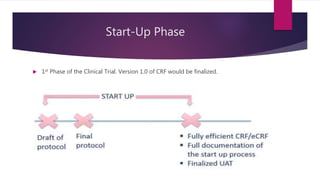
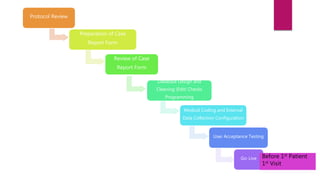
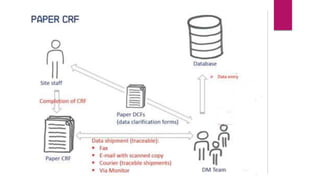
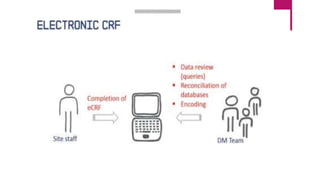
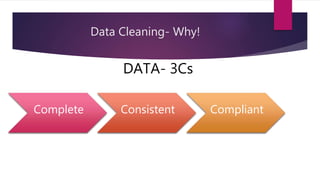
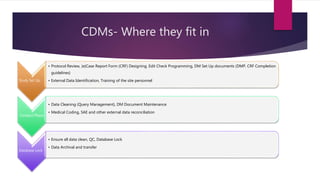
Clinical data management (CDM) involves collecting, validating, and cleaning patient data from clinical trials to ensure it is complete, consistent, and compliant. A CDM team typically includes clinical data managers, programmers, and data entry associates. They are involved in all stages from study setup to completion. Key CDM activities include designing case report forms, programming data validation checks, overseeing data entry into clinical data management systems, manually and electronically cleaning the data, reconciling safety data with external sources, and locking the database once the trial is complete and the data is ready for analysis. The goal is to generate high-quality clinical trial data that can be analyzed to advance drug development timelines.