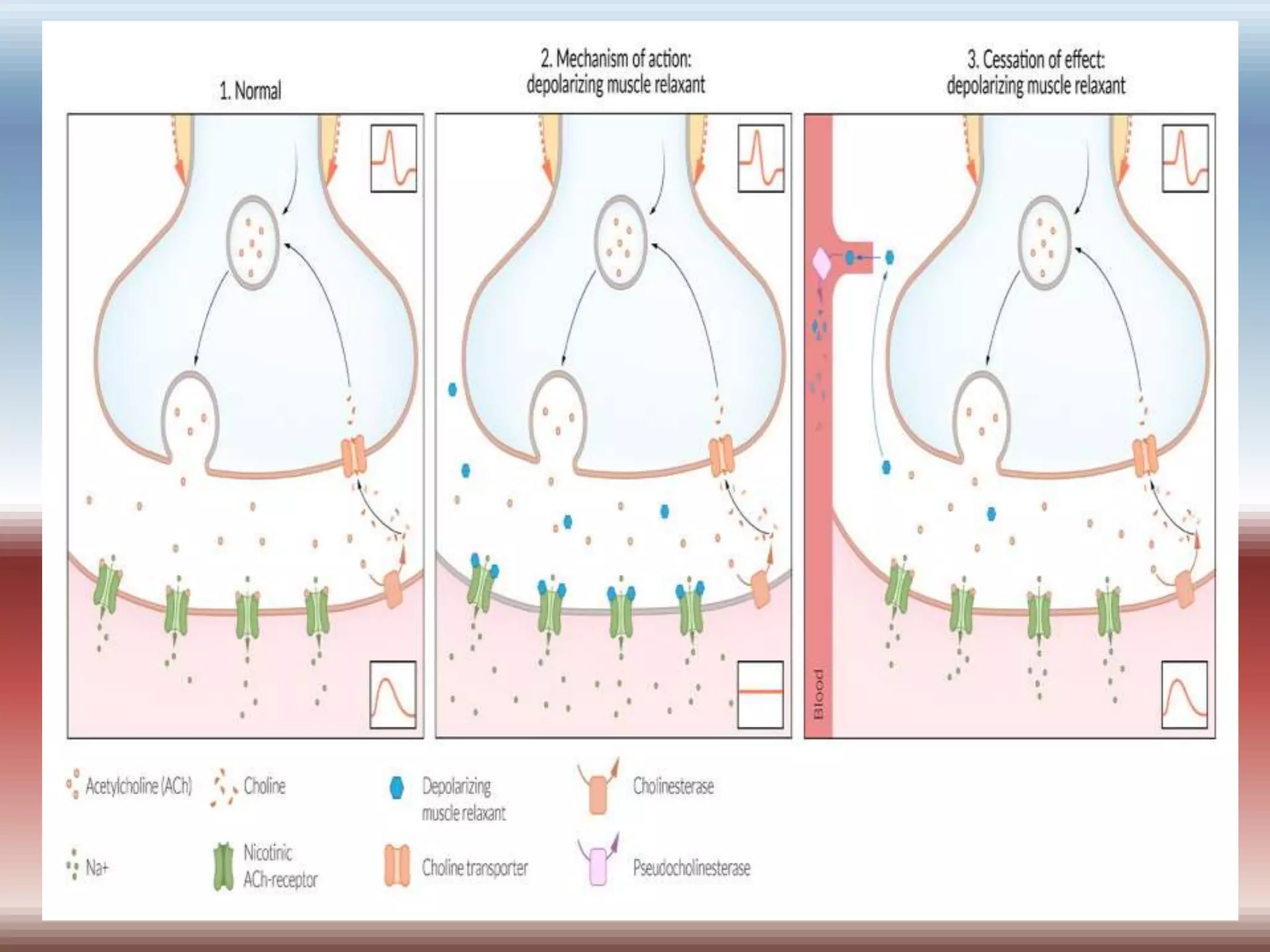
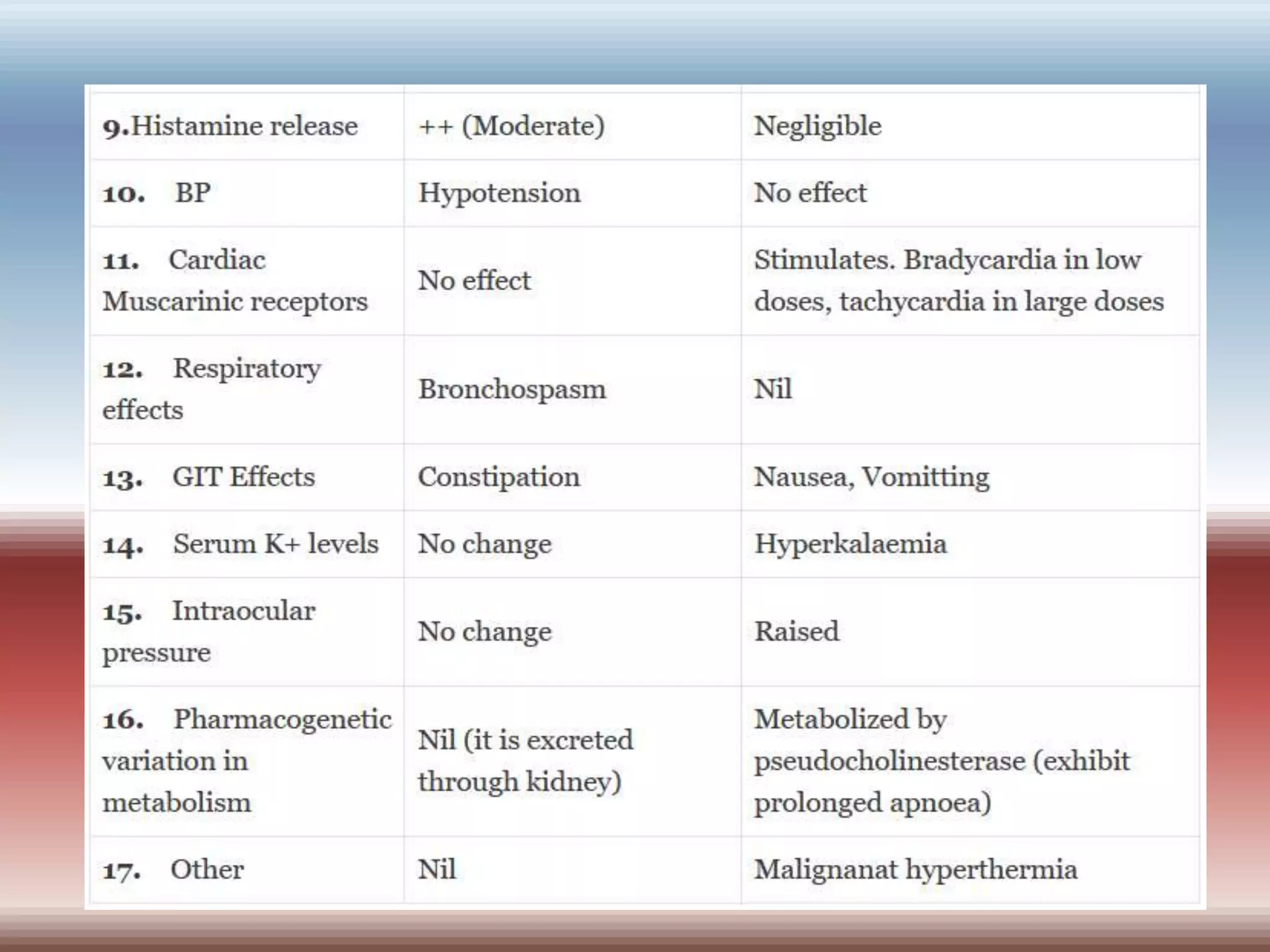
Skeletal muscle relaxants can be categorized into peripheral and central acting drugs, with peripheral acting agents primarily used during surgery and central acting agents for muscle spasms. Neuromuscular blocking agents include nondepolarizing and depolarizing blockers, while centrally acting relaxants selectively modulate spinal reflexes without affecting consciousness. Key uses include general anesthesia, assisted ventilation, and treatment of spasms and convulsions.