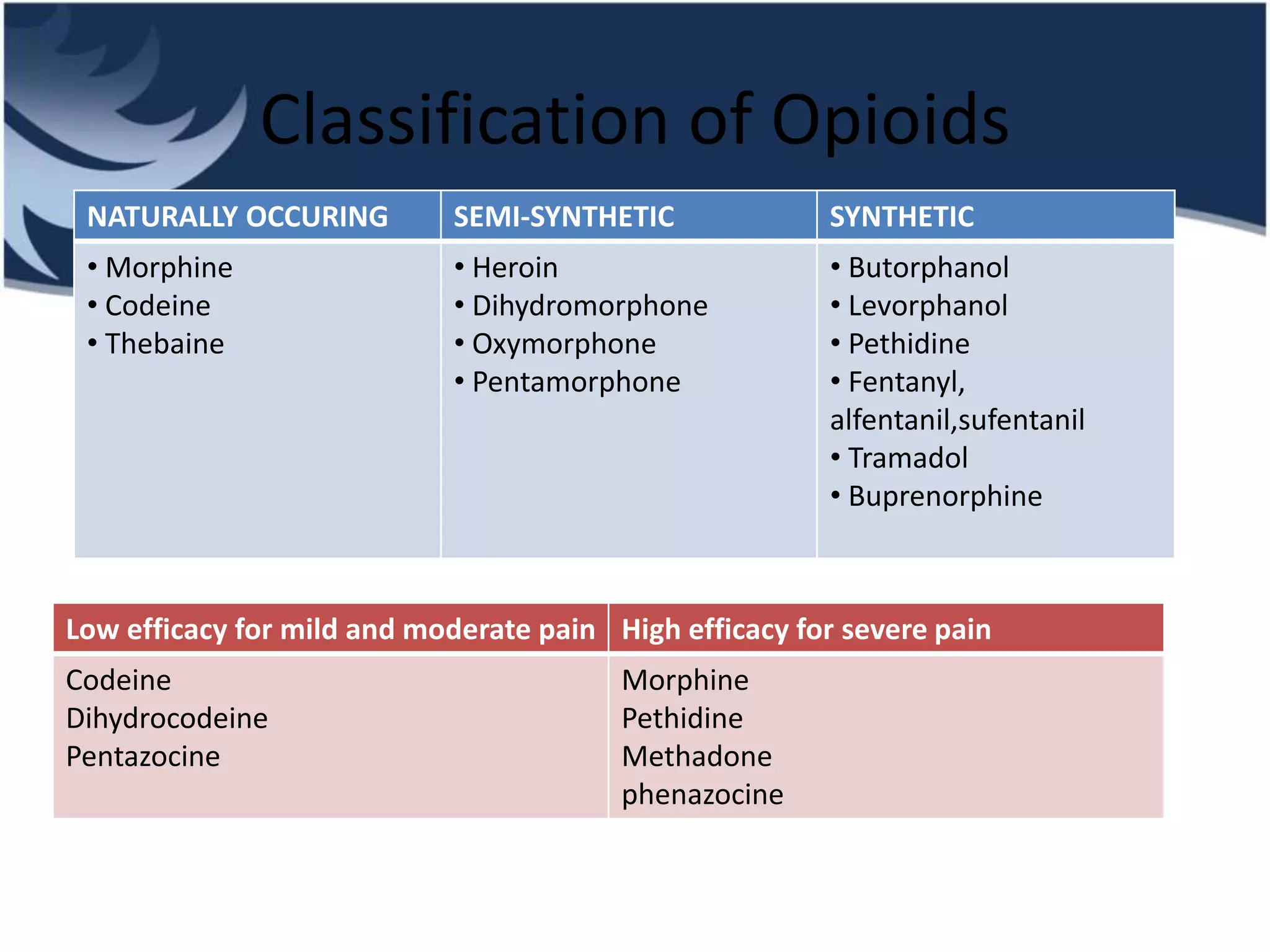
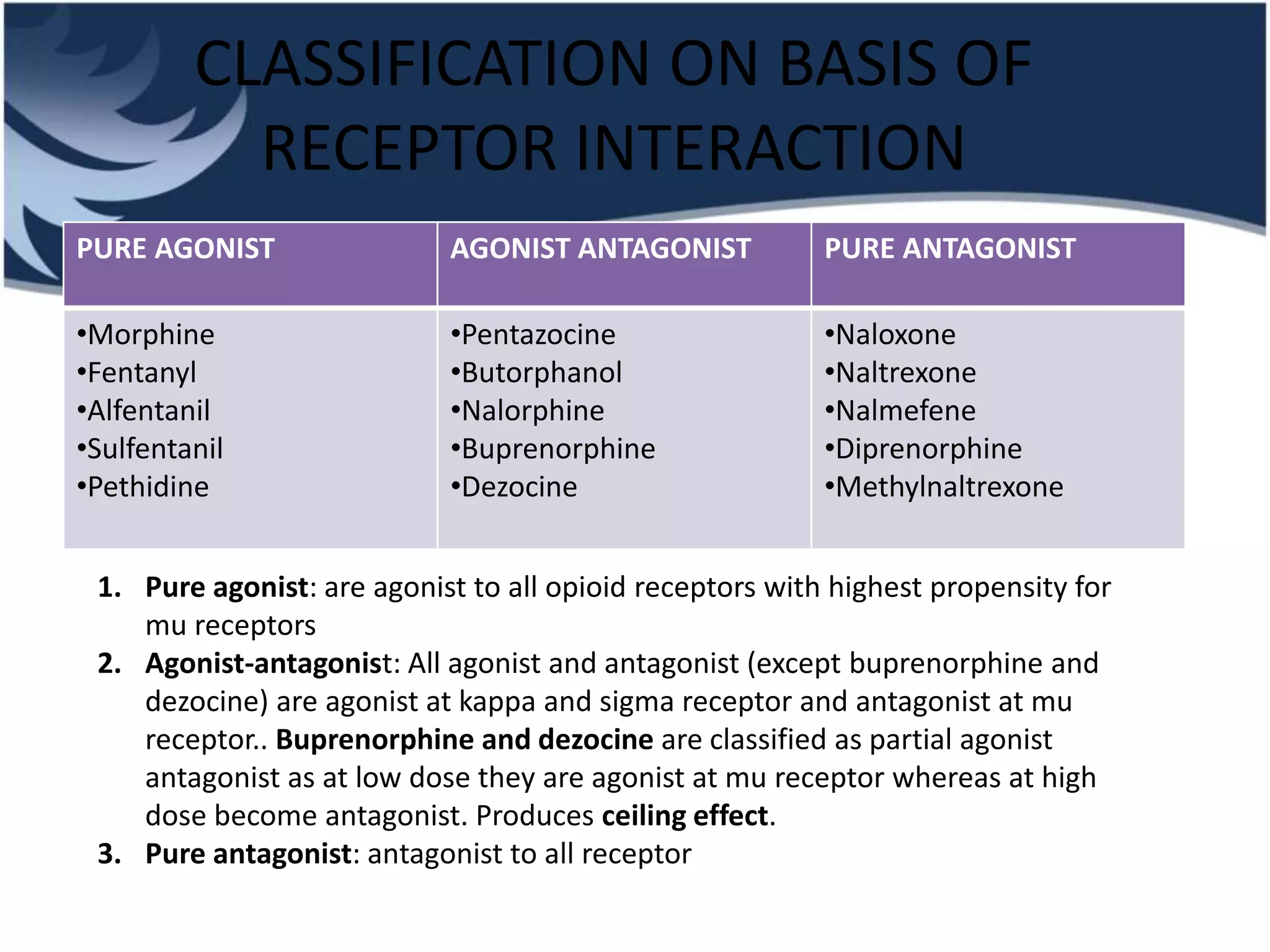
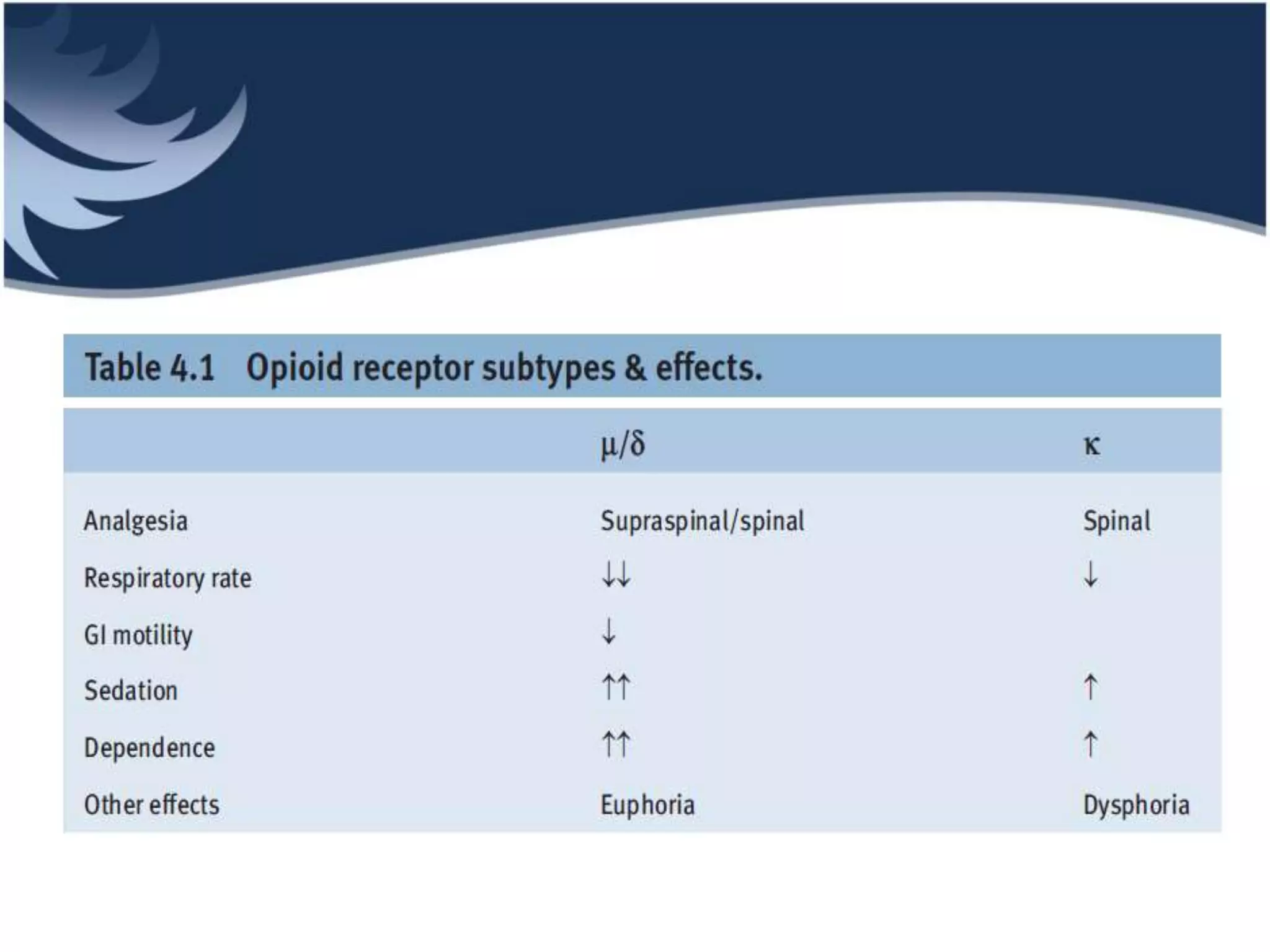
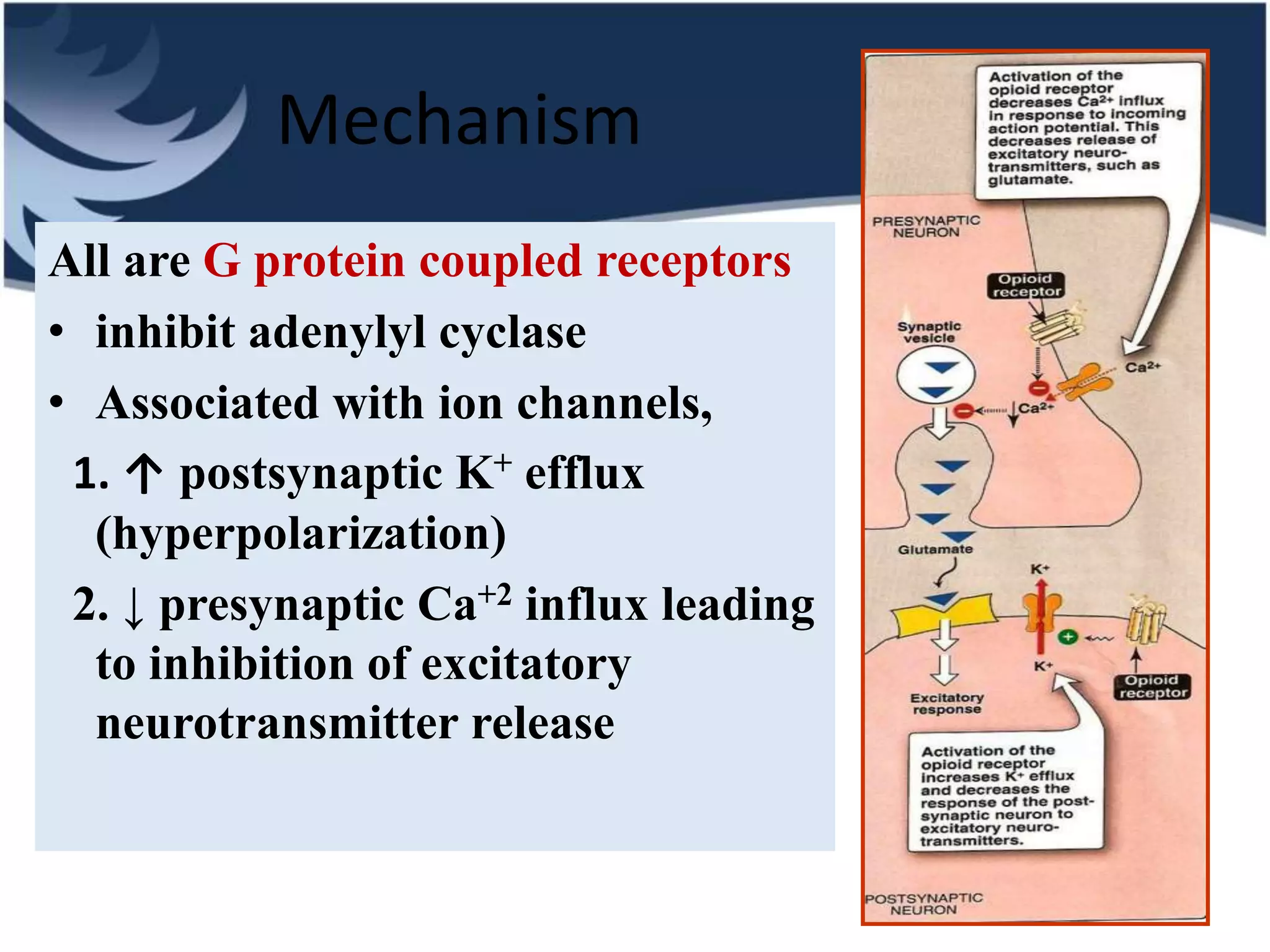
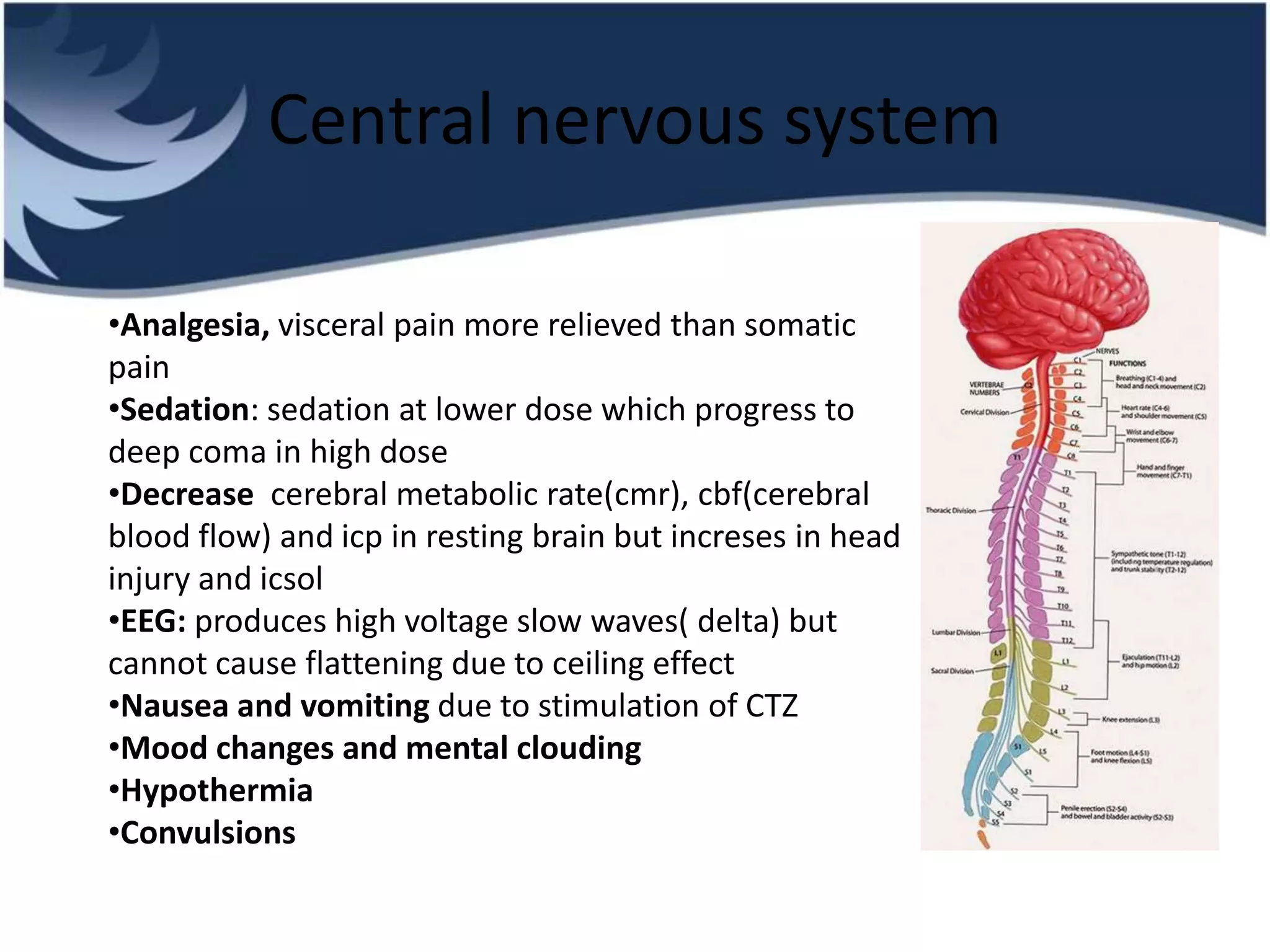
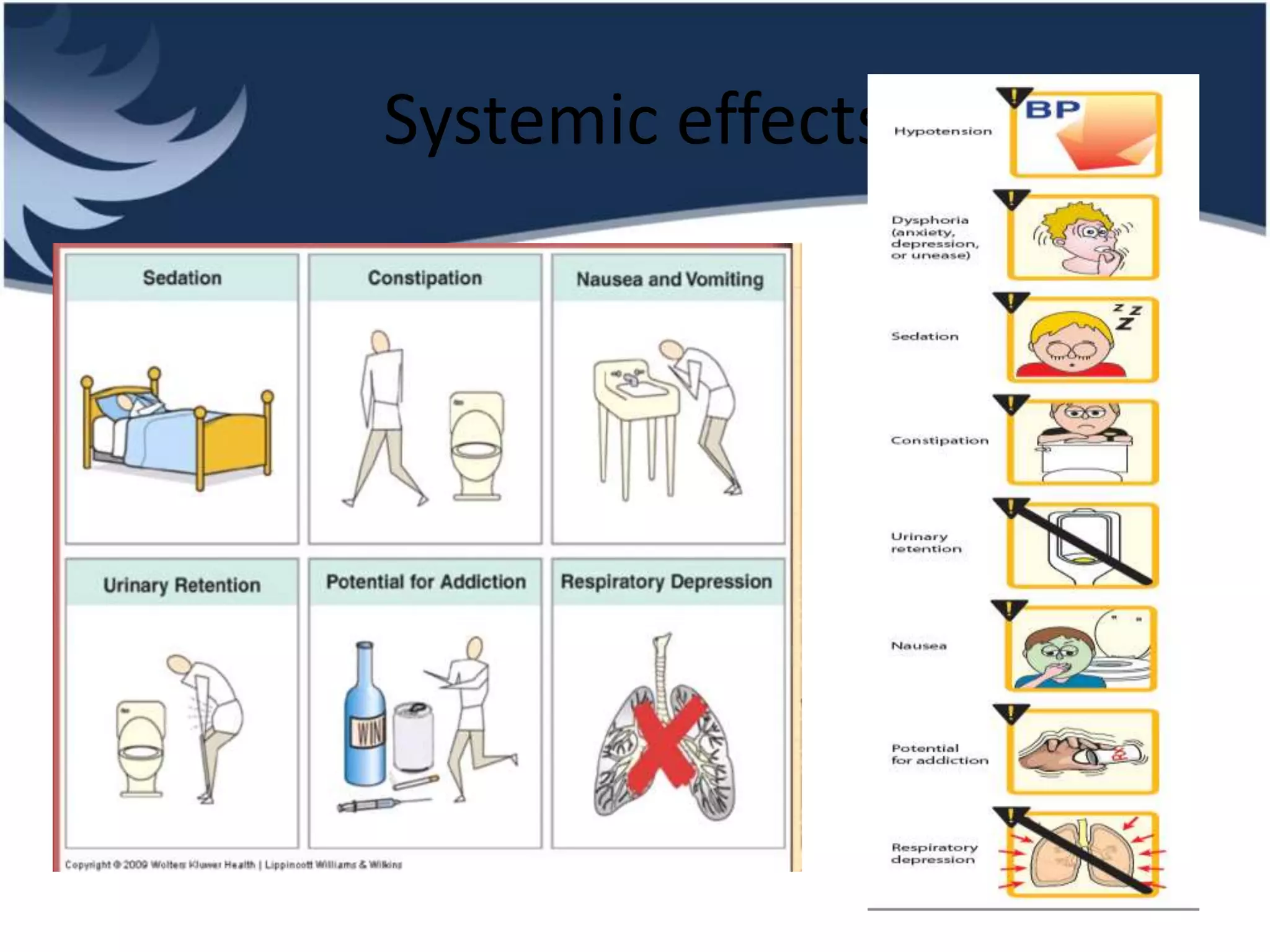
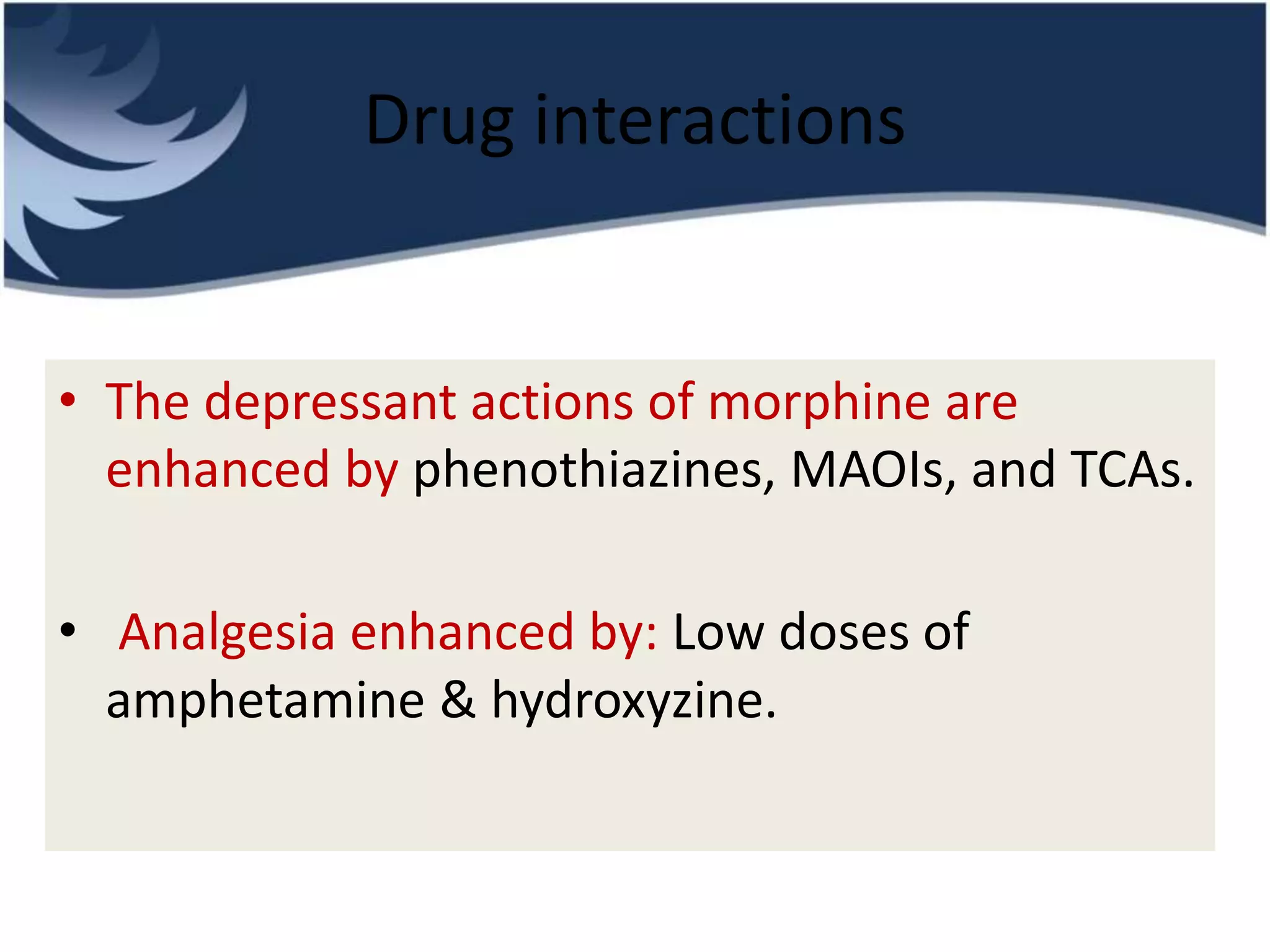
Opioids are powerful pain relievers that work by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and body. Friedrich Sertürner first isolated morphine from opium in 1803. Opioids include natural opiates derived from the opium poppy like morphine and codeine, semi-synthetic drugs like heroin, and fully synthetic drugs like fentanyl. They act primarily on mu, kappa, and delta opioid receptors and their effects include analgesia, sedation, respiratory depression, and constipation. Common opioids used in anesthesia include morphine, fentanyl, pethidine, and tramadol. While opioids are effective analgesics, their use can cause side effects and risks of dependence, addiction,