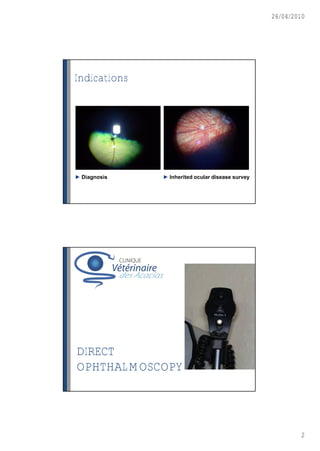
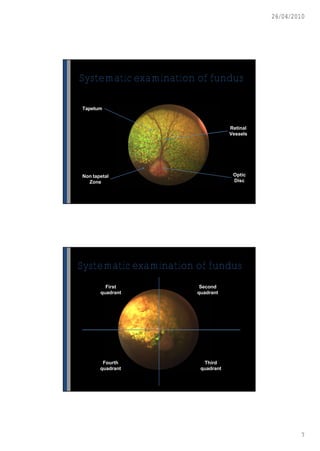
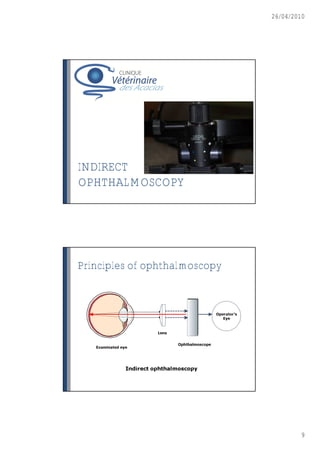
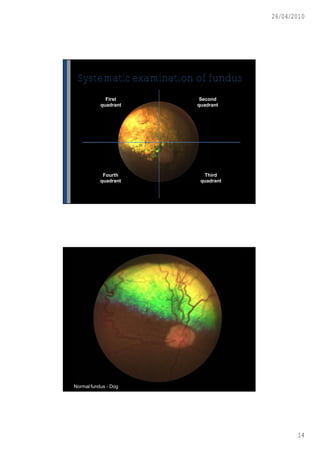
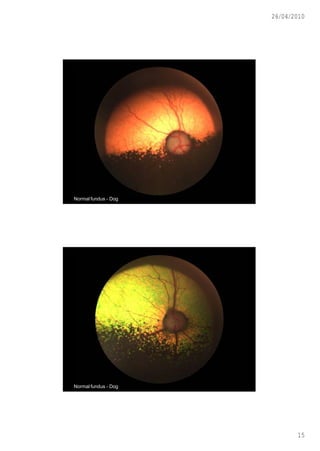
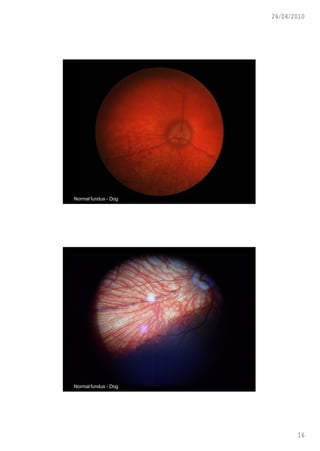
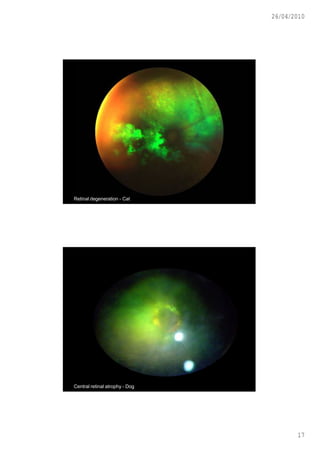
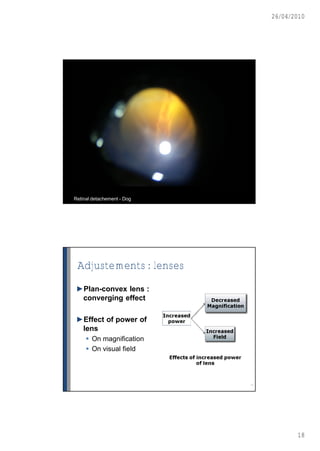
This document discusses ophthalmoscopy techniques for examining the fundus of animal eyes. It describes direct ophthalmoscopy, where a handheld device is placed against the examiner's eye, and indirect ophthalmoscopy, which uses a light source and lenses. Both techniques allow viewing of the retina and optic disc but have different advantages - direct provides higher magnification while indirect allows a wider field of view. Proper animal restraint, pupil dilation, and examination procedure are emphasized. Examples of normal and abnormal fundus findings are also presented.