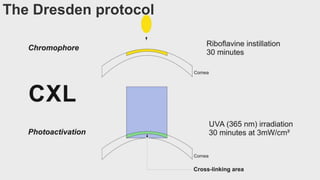
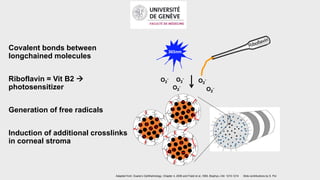
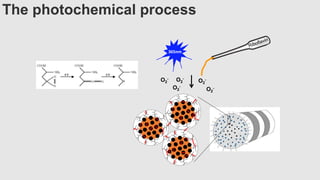
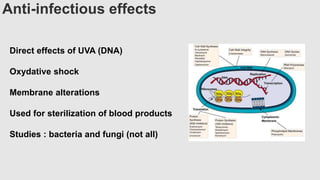
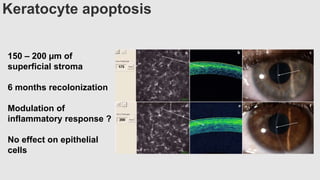
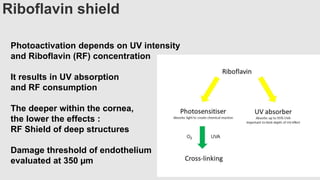
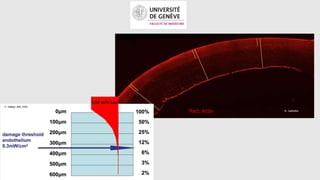
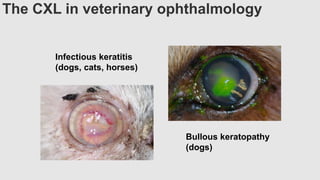
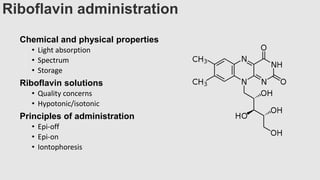
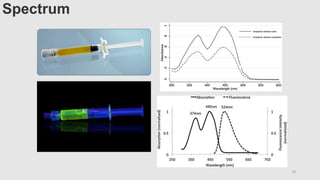
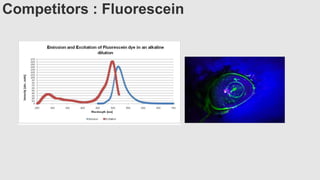
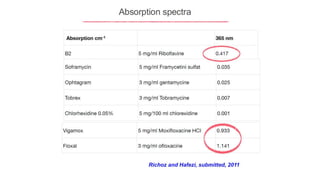
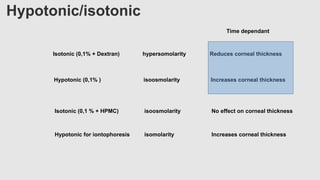
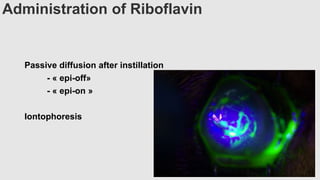
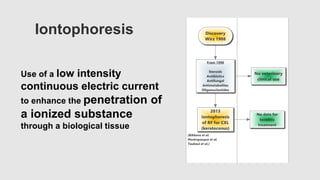
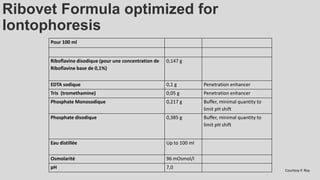
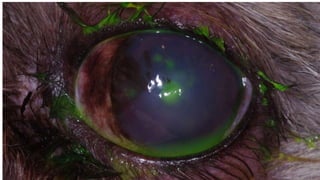
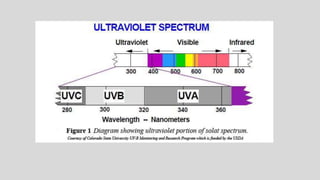
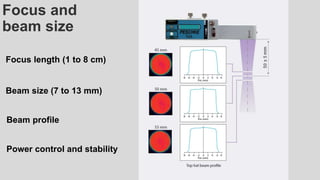
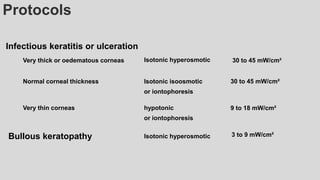
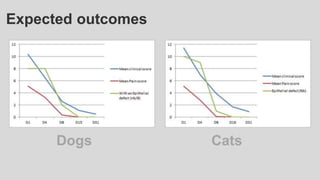
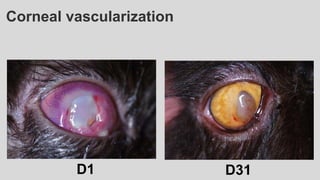
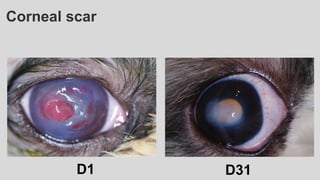
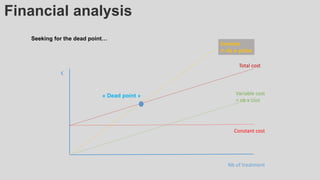
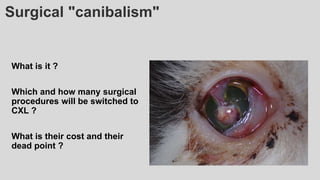
This document provides an overview of corneal collagen cross-linking (CXL) for veterinarians. It discusses the basic principles of CXL including riboflavin activation and its tissular effects. Guidelines are provided for riboflavin administration through both epi-off and epi-on methods as well as iontophoresis. The document also reviews UVA irradiation parameters and protocols for different corneal conditions. Expected outcomes from CXL are summarized for dogs and cats based on published studies. Financial considerations including cost analysis, pricing models and calculating the treatment "dead point" are also covered.