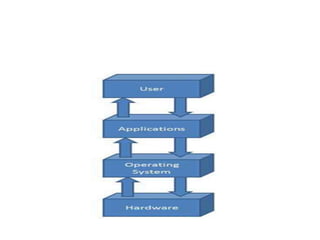
An operating system is a program that acts as an interface between the software and computer hardware. It manages the overall resources and operations of the computer by controlling and monitoring the execution of all other programs, including applications and other system software. The main objectives of an operating system are to make the computer system convenient to use efficiently, hide hardware details from users, and provide a convenient interface for users to access resources. Key characteristics of an operating system include memory management, processor management, device management, file management, security, job accounting, and coordination between software and users.