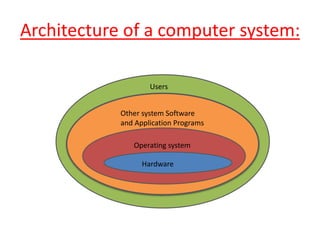
An operating system is software that controls computer resources like the CPU, memory and I/O devices, and provides common services to allow applications to execute efficiently. It acts as an interface between hardware and users, managing resources and processes. Key functions of an operating system include process management, memory management, file management, device management, and security. Operating system performance is measured by throughput, turnaround time and response time.