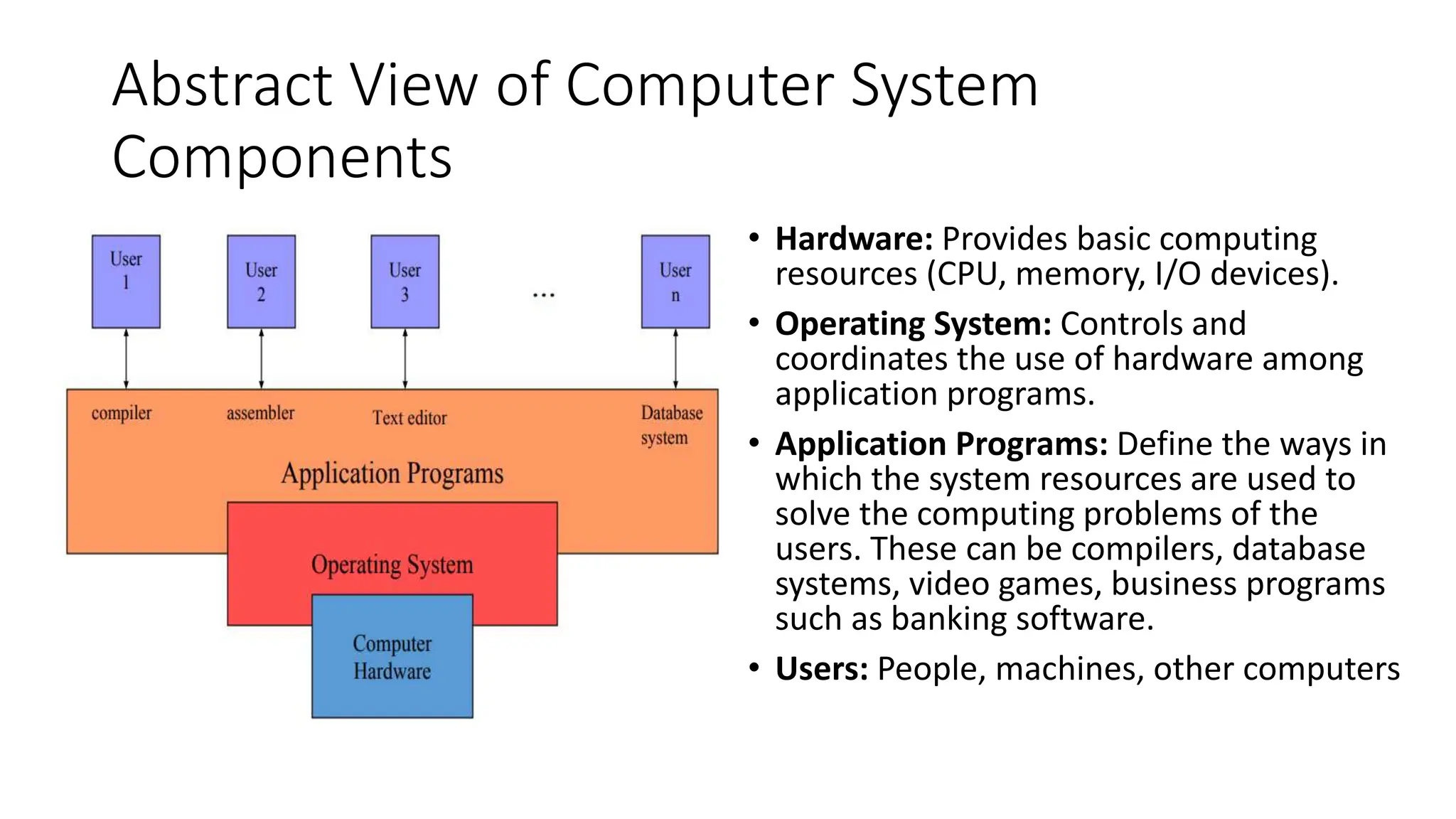
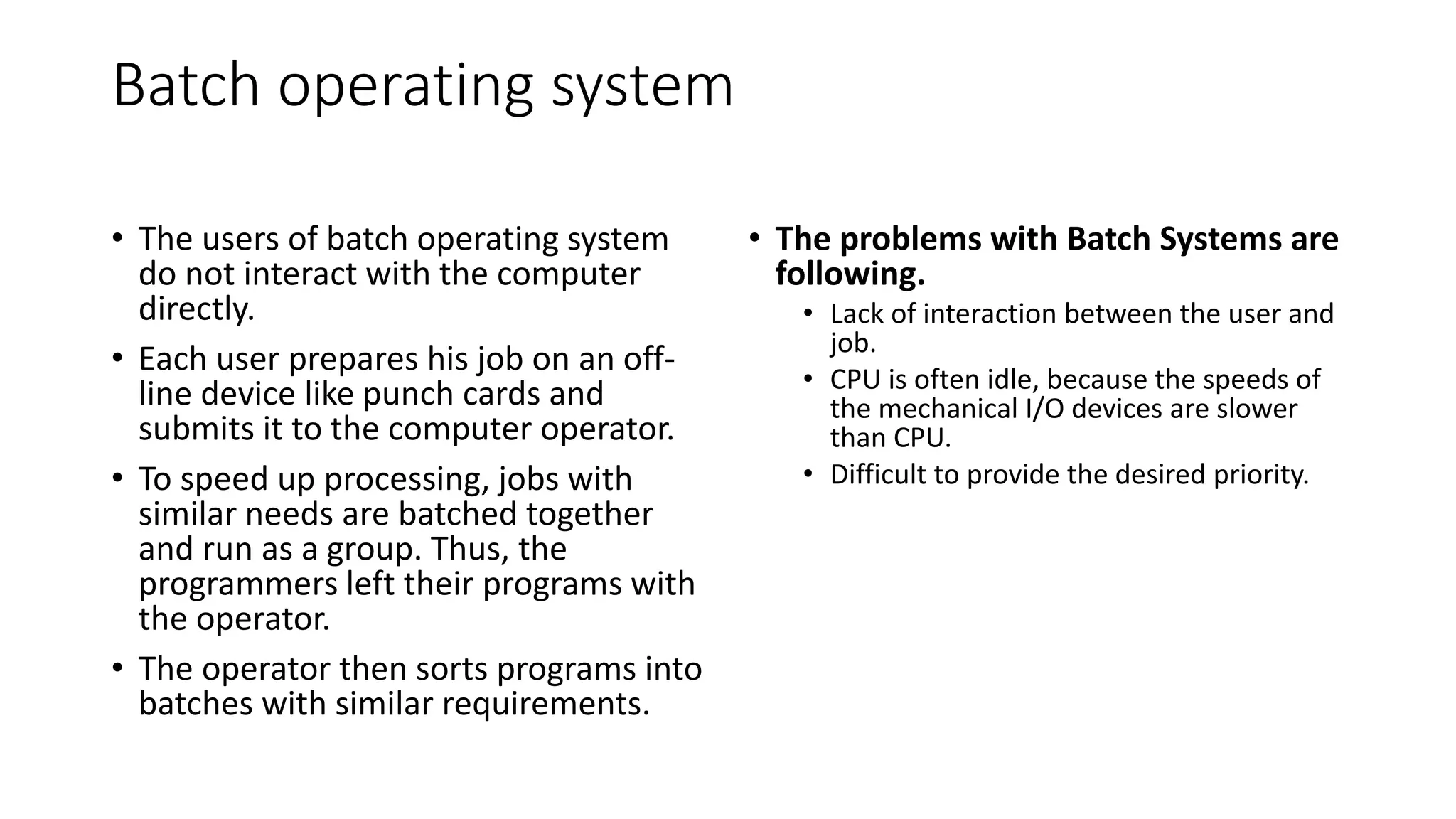
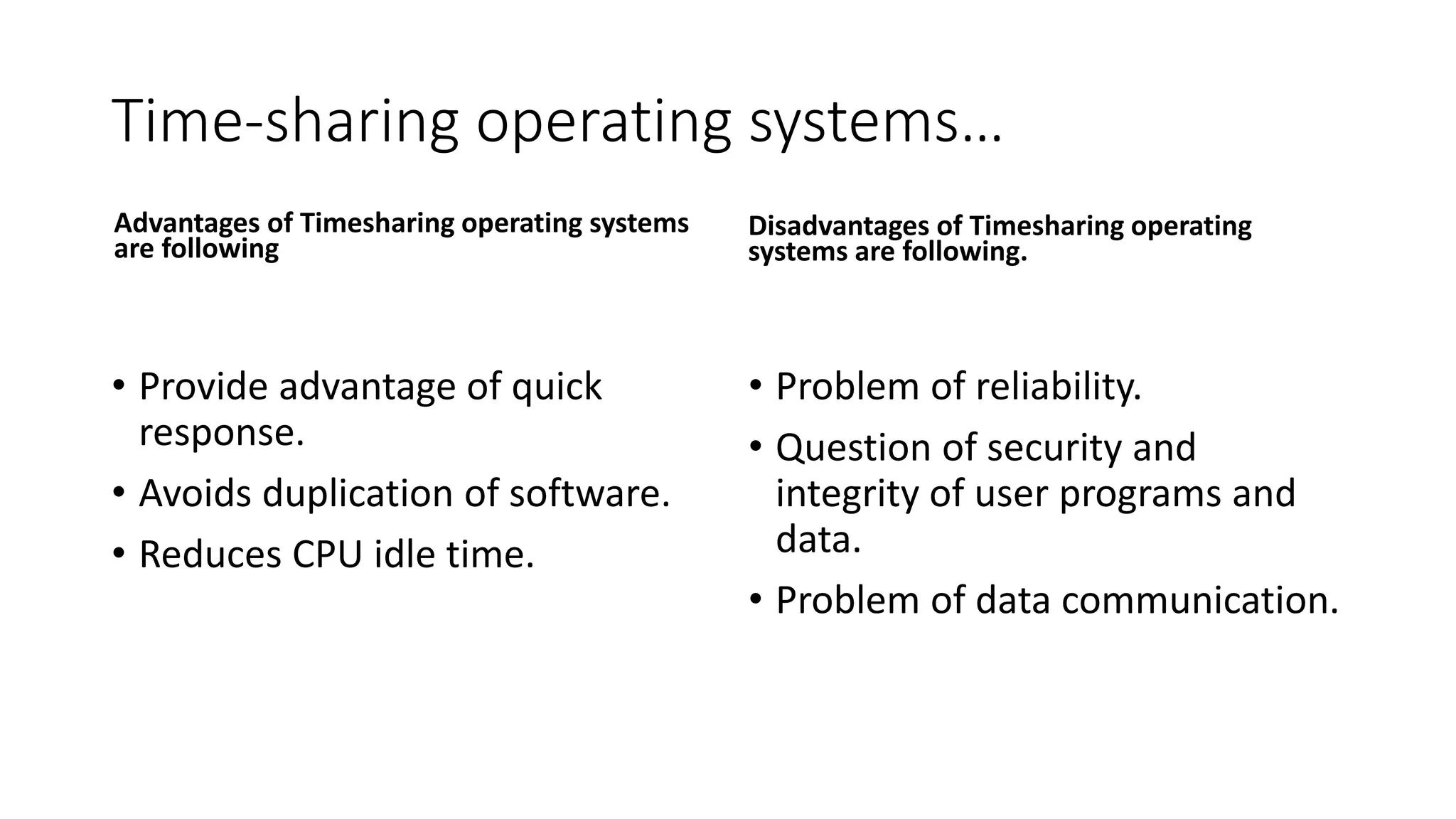
The document discusses different types of operating systems. It describes batch operating systems which run jobs in batches without user interaction. Time-sharing systems allow multiple users to access the system simultaneously through time-sharing of the CPU. Distributed systems distribute processing across networked computers. Network operating systems manage resources and functions on servers to enable file and printer sharing across local networks. Real-time systems have strict time constraints and are used for applications like industrial controls where response times must be very fast.