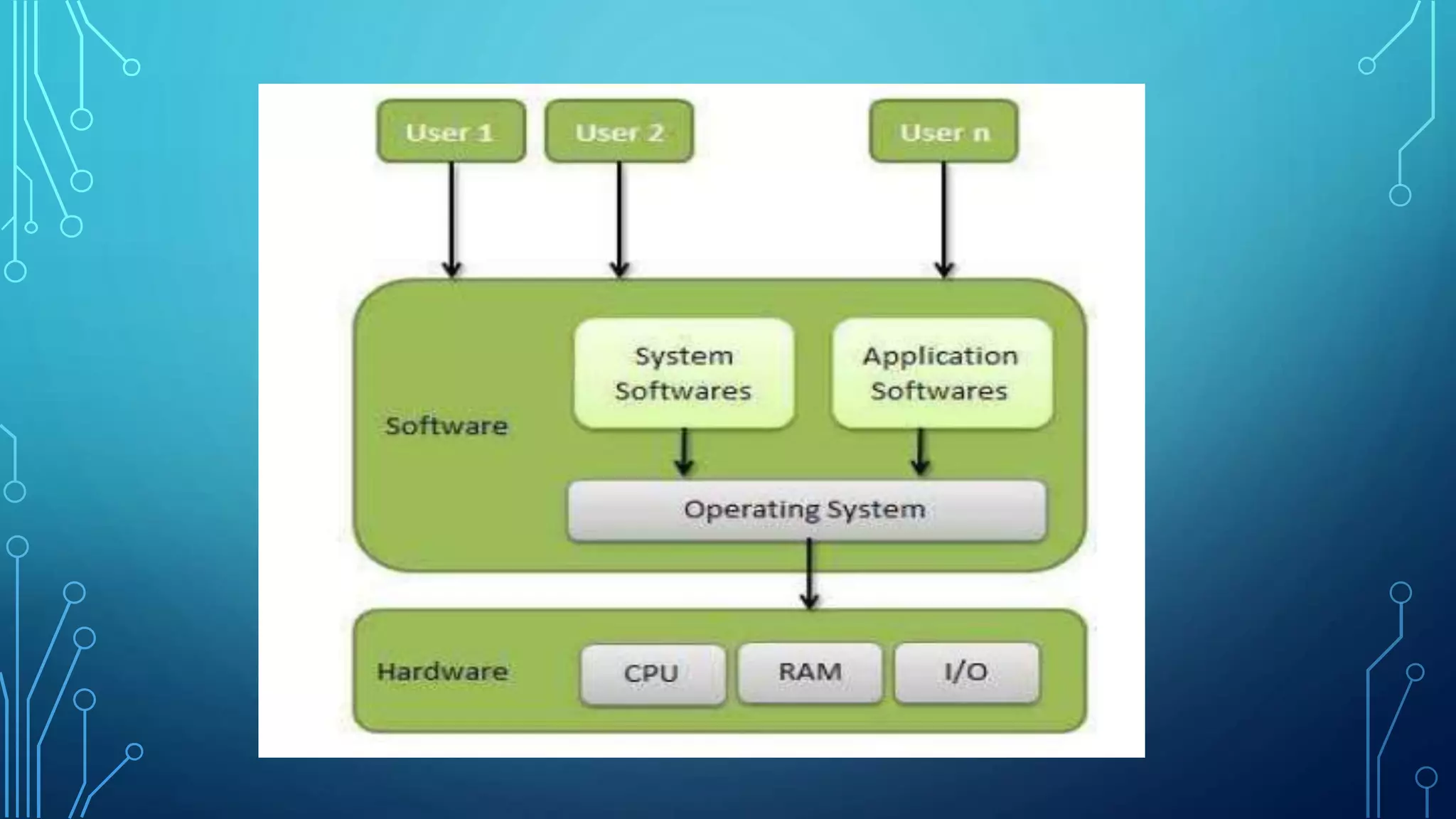
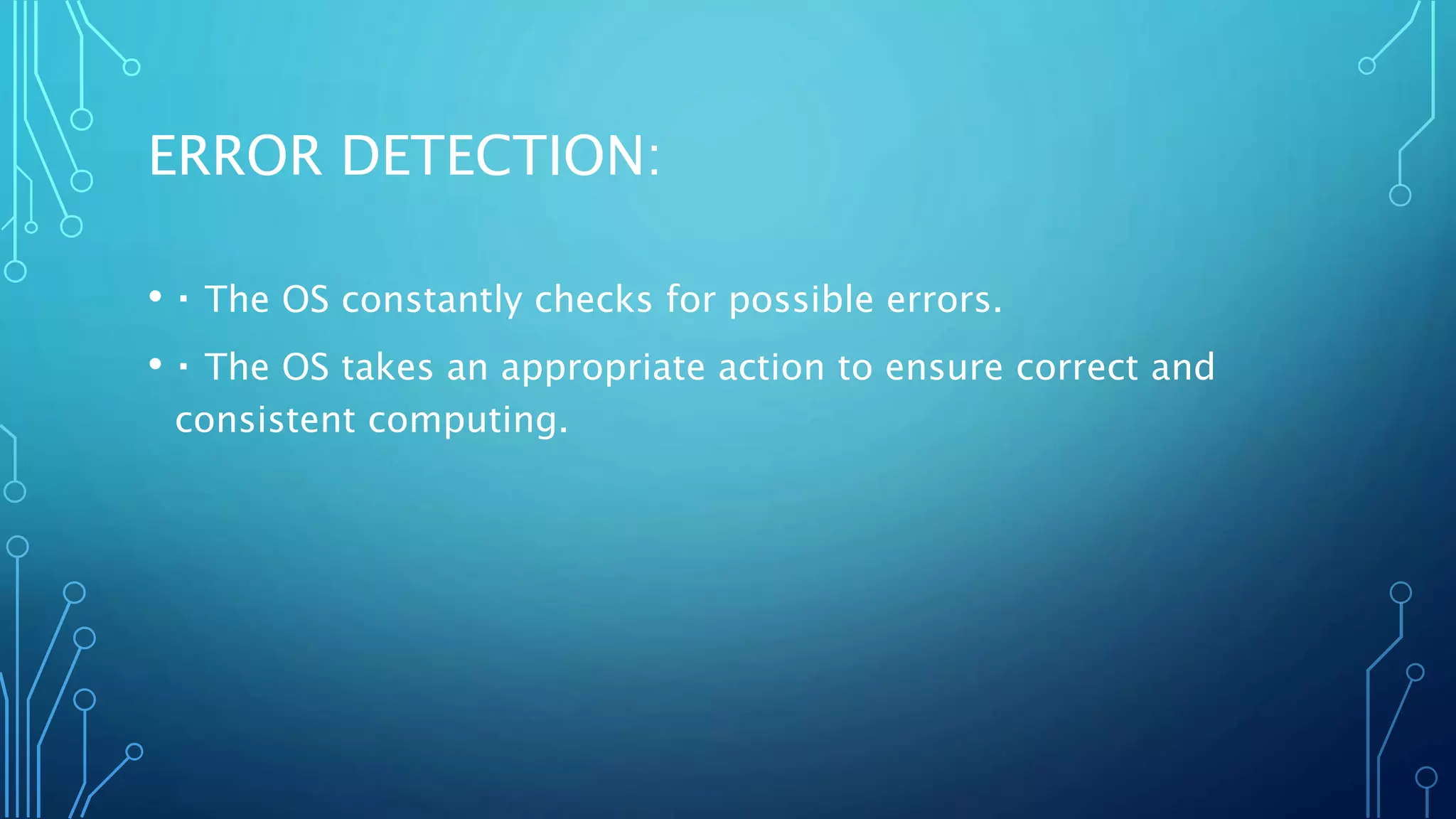
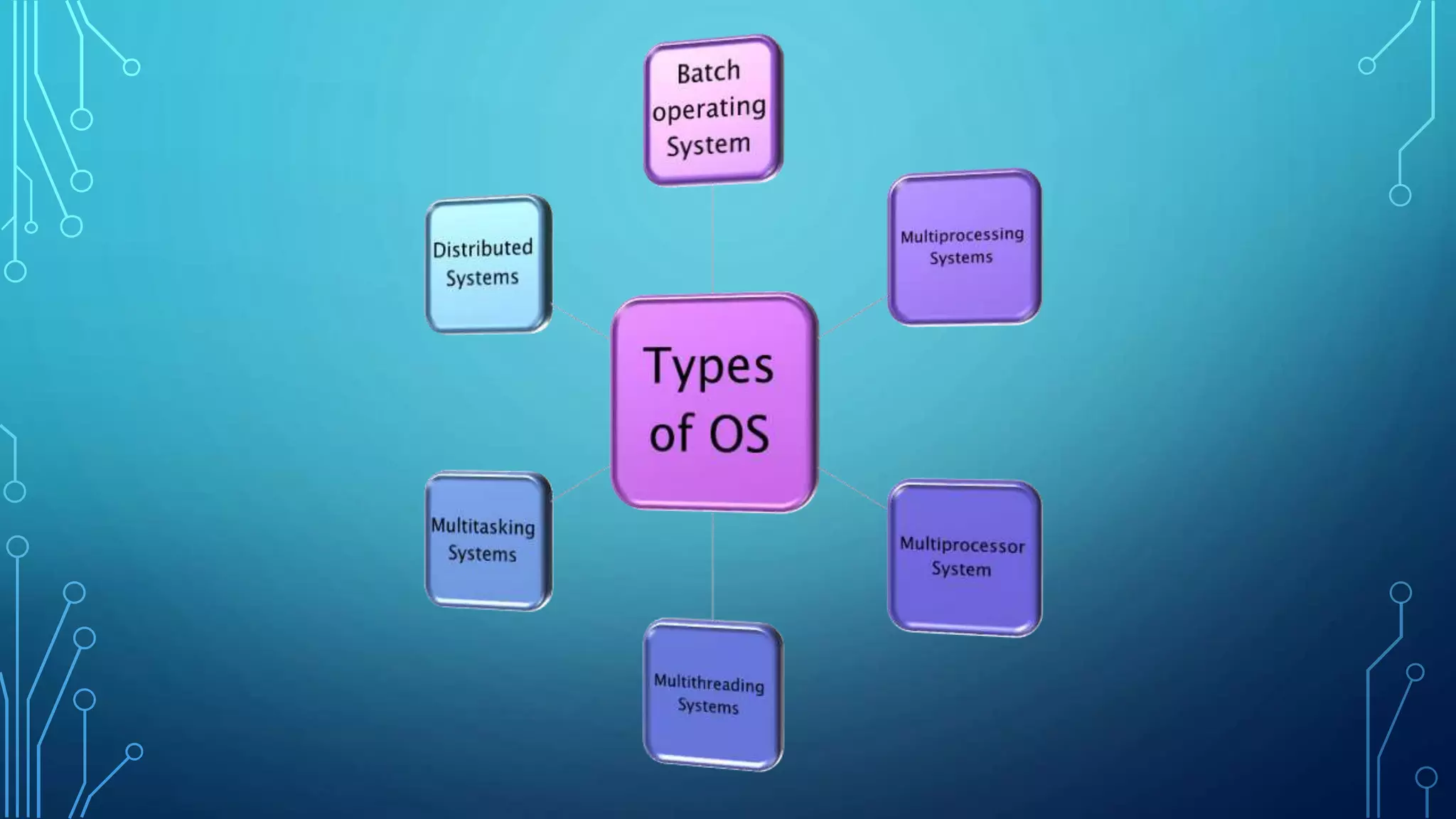
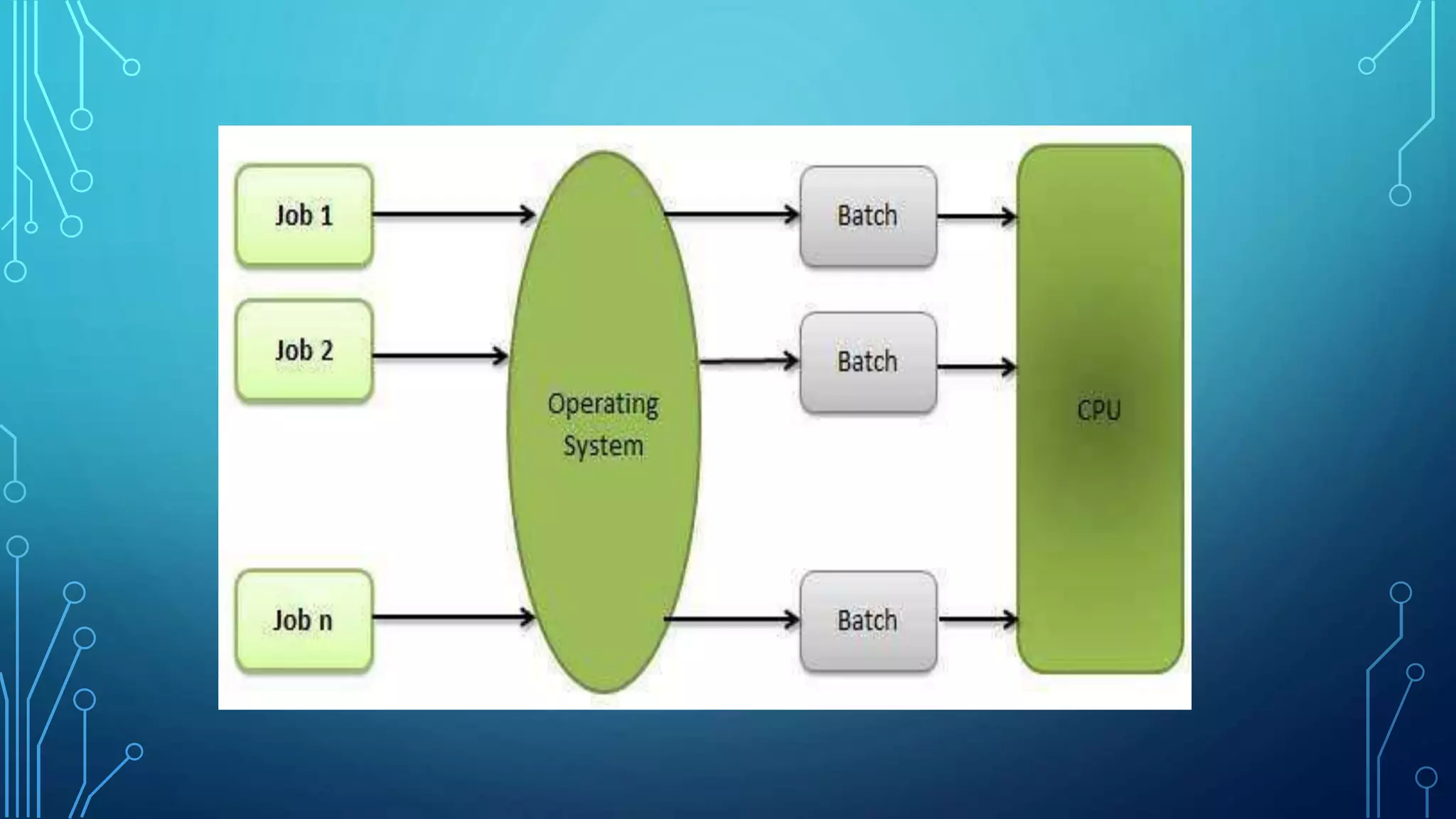
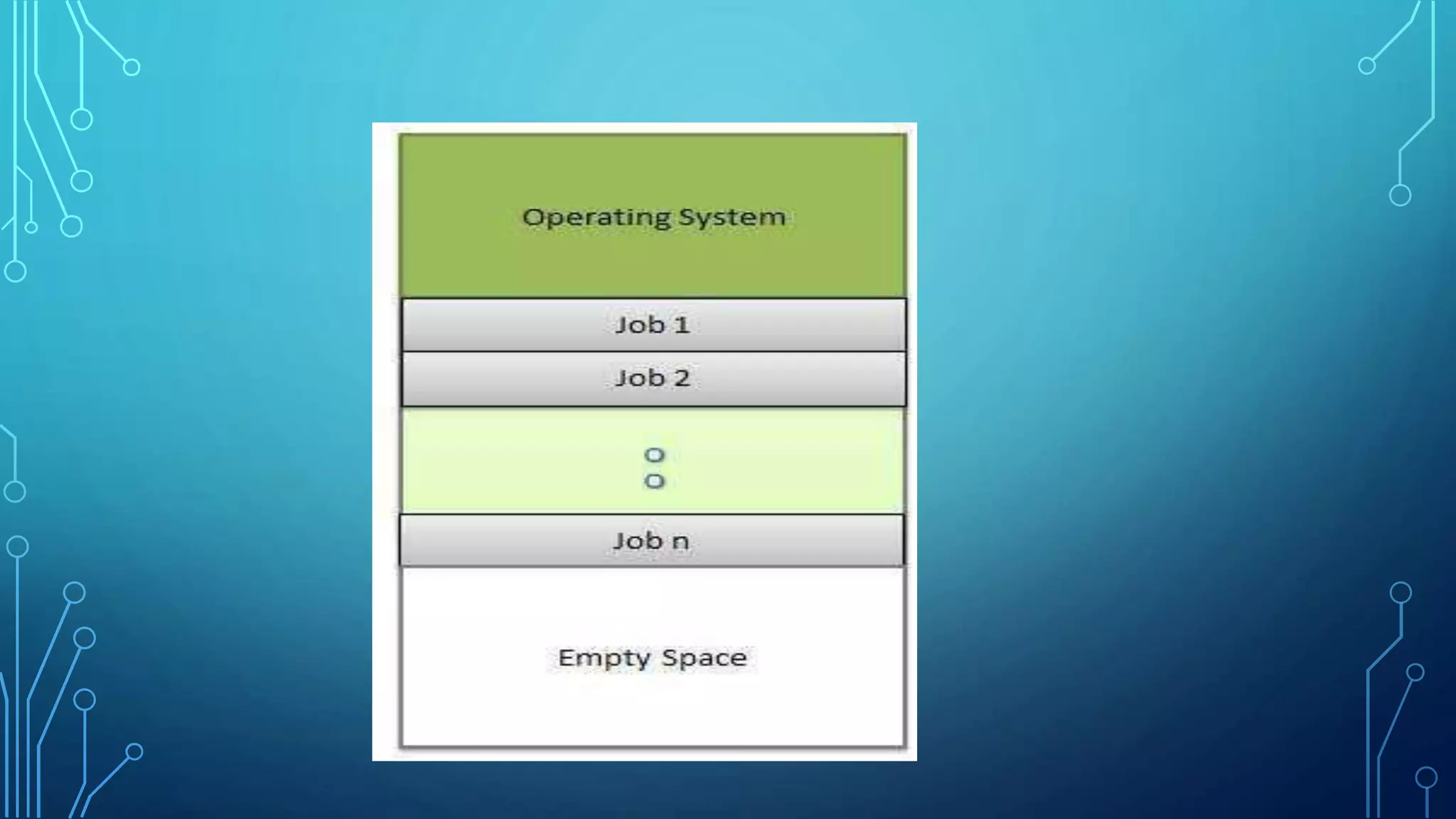
The document defines an operating system and describes the key services it provides, including managing hardware resources, executing programs, handling input/output, manipulating the file system, enabling communication, detecting and handling errors, and allocating resources. It then discusses different types of operating systems like batch, multiprogramming, multiprocessing, multithreading, and distributed systems. Real-time operating systems designed to control machinery and instruments are also mentioned.