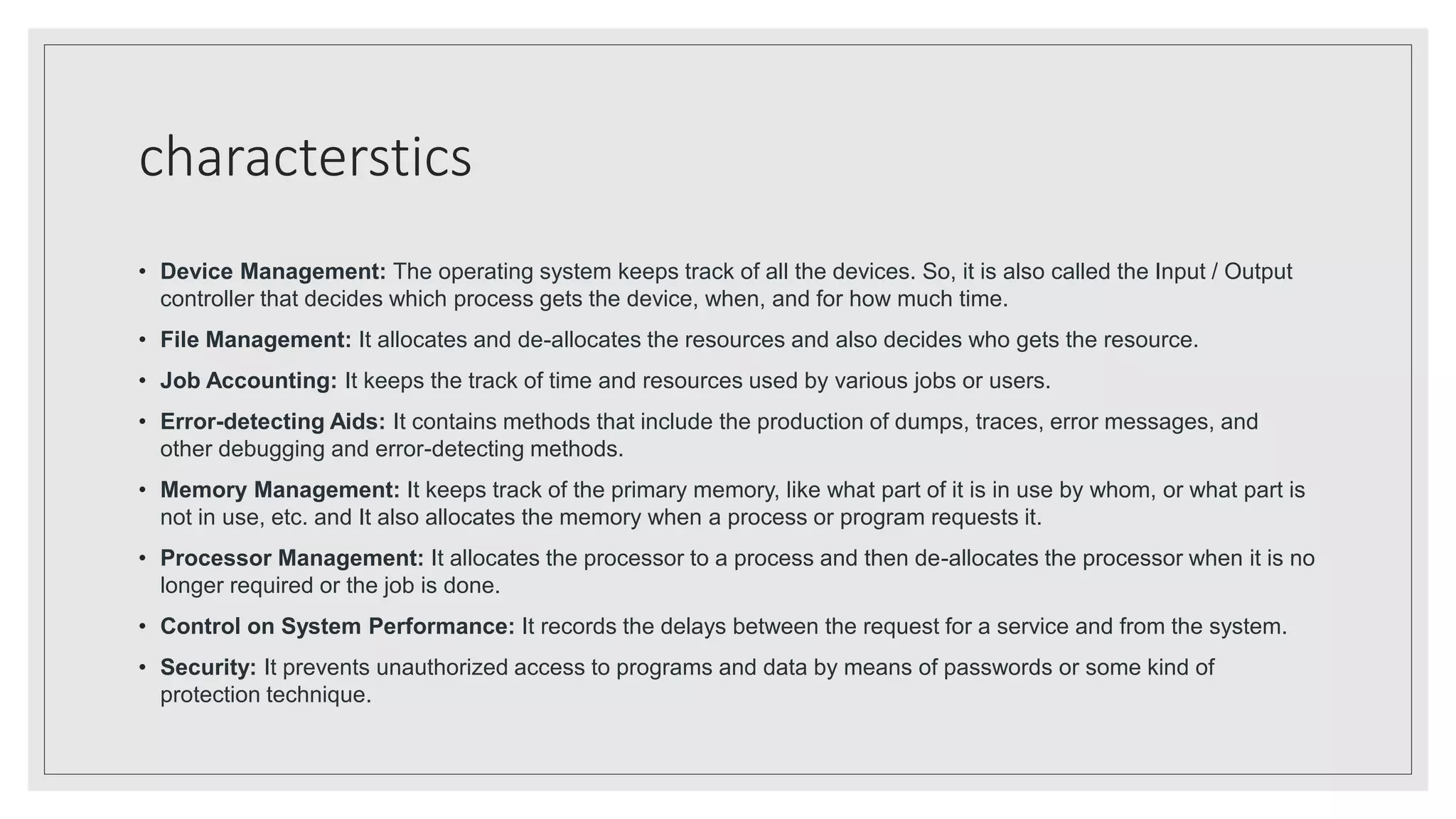
The operating system manages computer resources and acts as an interface between hardware and software. It controls and monitors the execution of all programs, including applications and other system software. Key objectives of an operating system include making the computer convenient and easy to use, managing resources, and providing fair sharing of resources between users and programs. Operating systems have characteristics like device management, file management, job accounting, error detection, memory management, processor management, and security controls. There are different types of operating systems including batch, time-sharing, distributed, network, and real-time operating systems.