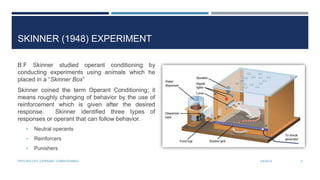
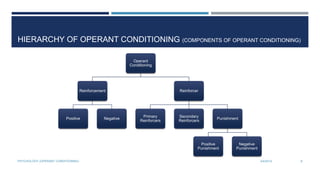
Operant conditioning is a method of learning through reinforcement and punishment of behaviors. B.F. Skinner coined the term and conducted experiments using animals in a Skinner Box. He found that behaviors followed by reinforcement are more likely to be repeated, while behaviors followed by punishment are less likely to be repeated. There are different types of reinforcement and punishment that can strengthen or weaken behaviors according to operant conditioning principles.