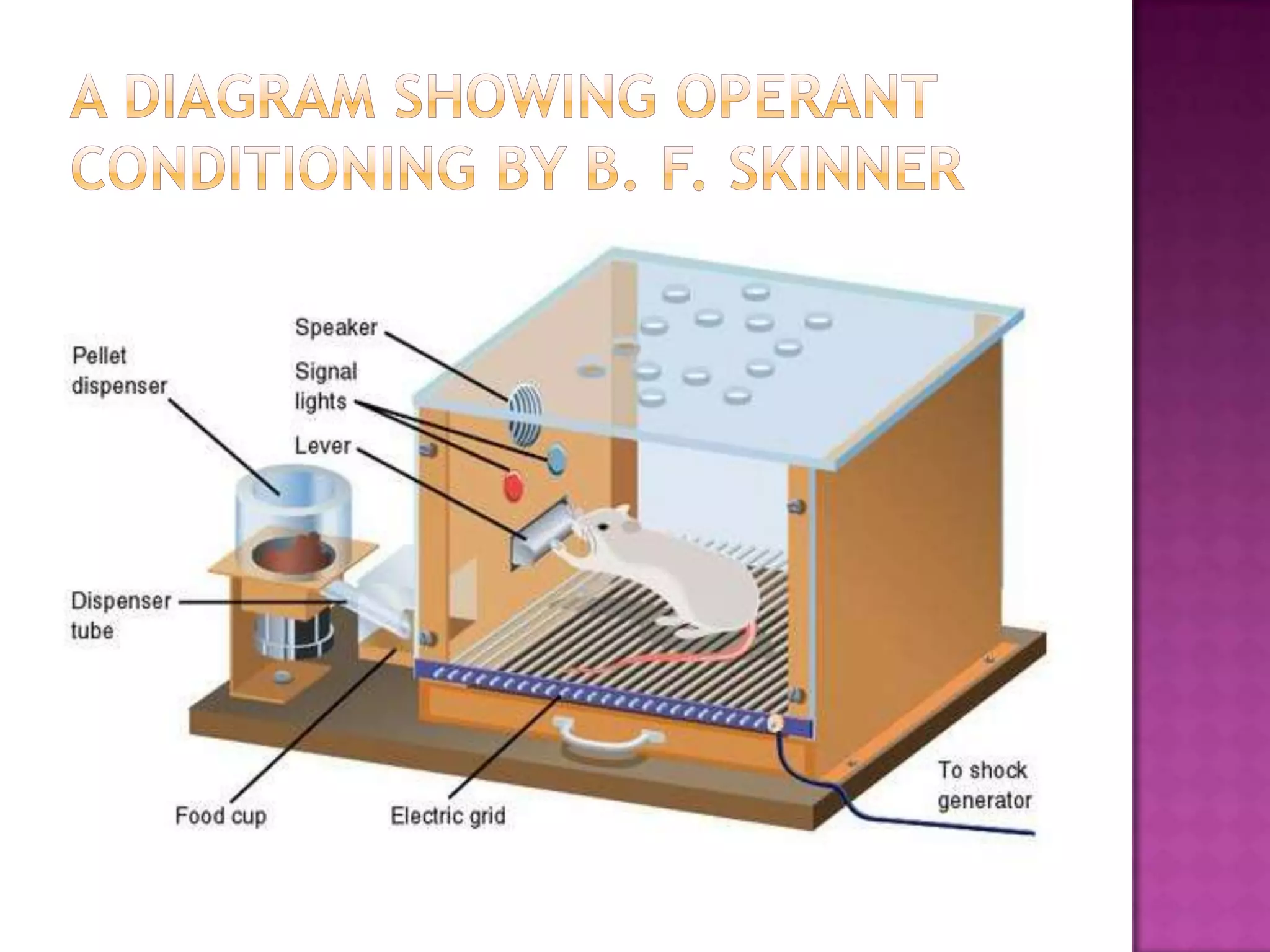
Group 3 presented on behaviorism on July 25th, 2013. Behaviorism is a theory that learning occurs through connections between stimuli and responses, and behavior can be explained through observable events rather than internal mental states. Key aspects of behaviorism include operant conditioning proposed by B.F. Skinner, which involves reinforcing desired behaviors through consequences to increase or decrease the likelihood of those behaviors reoccurring. Behaviorists view learning as a process of habit formation shaped by reinforcement or punishment from the environment.