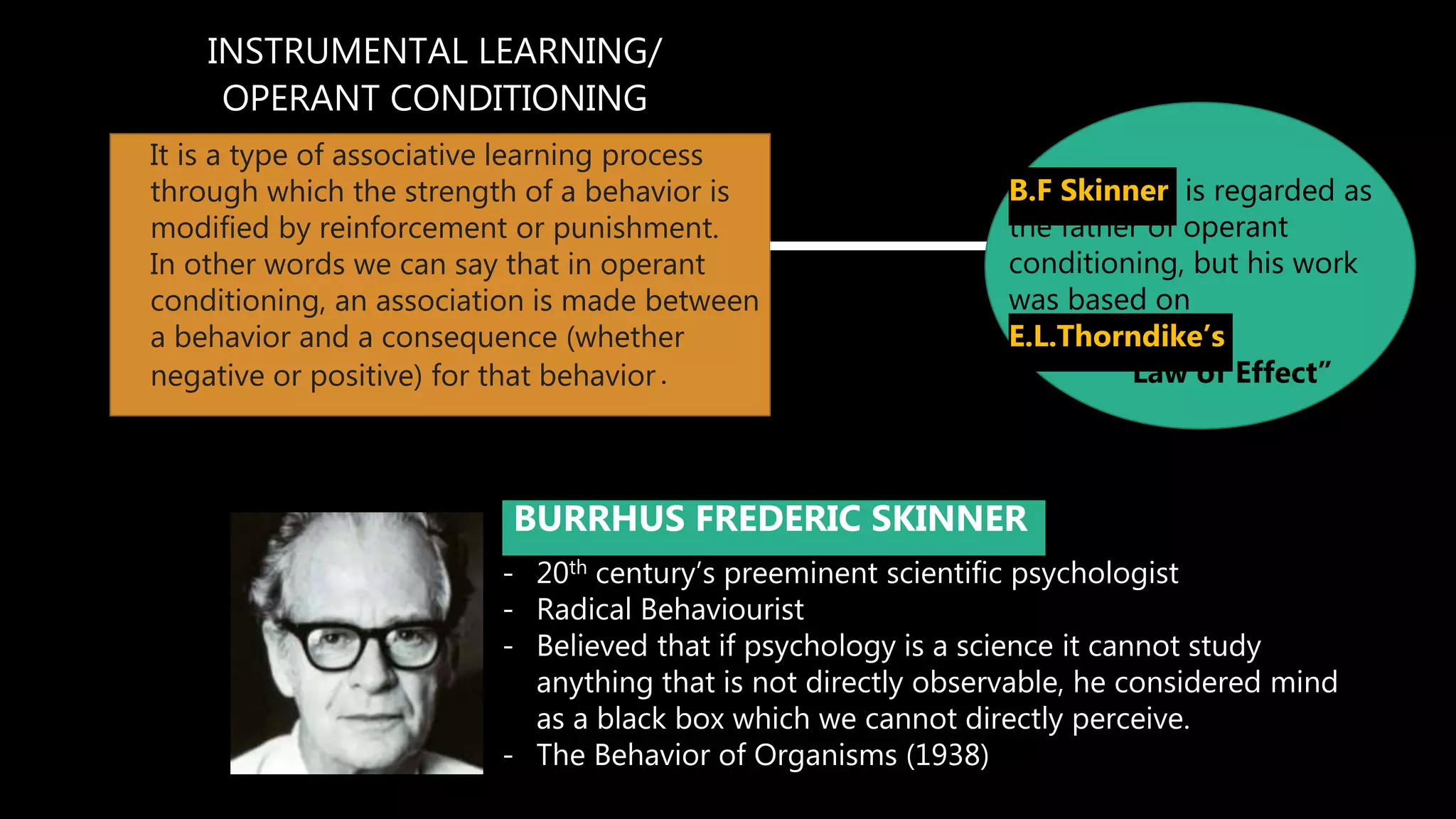
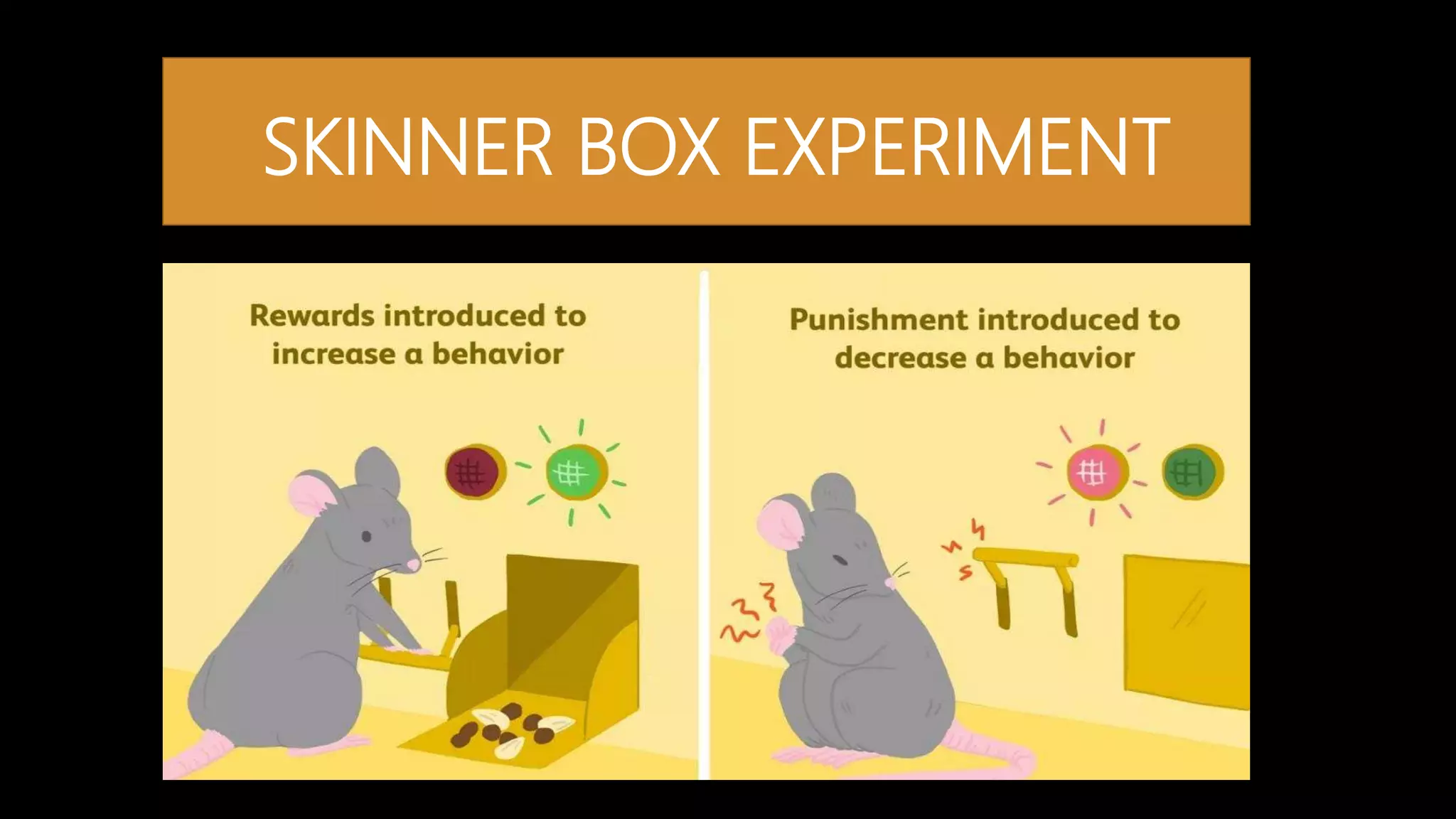
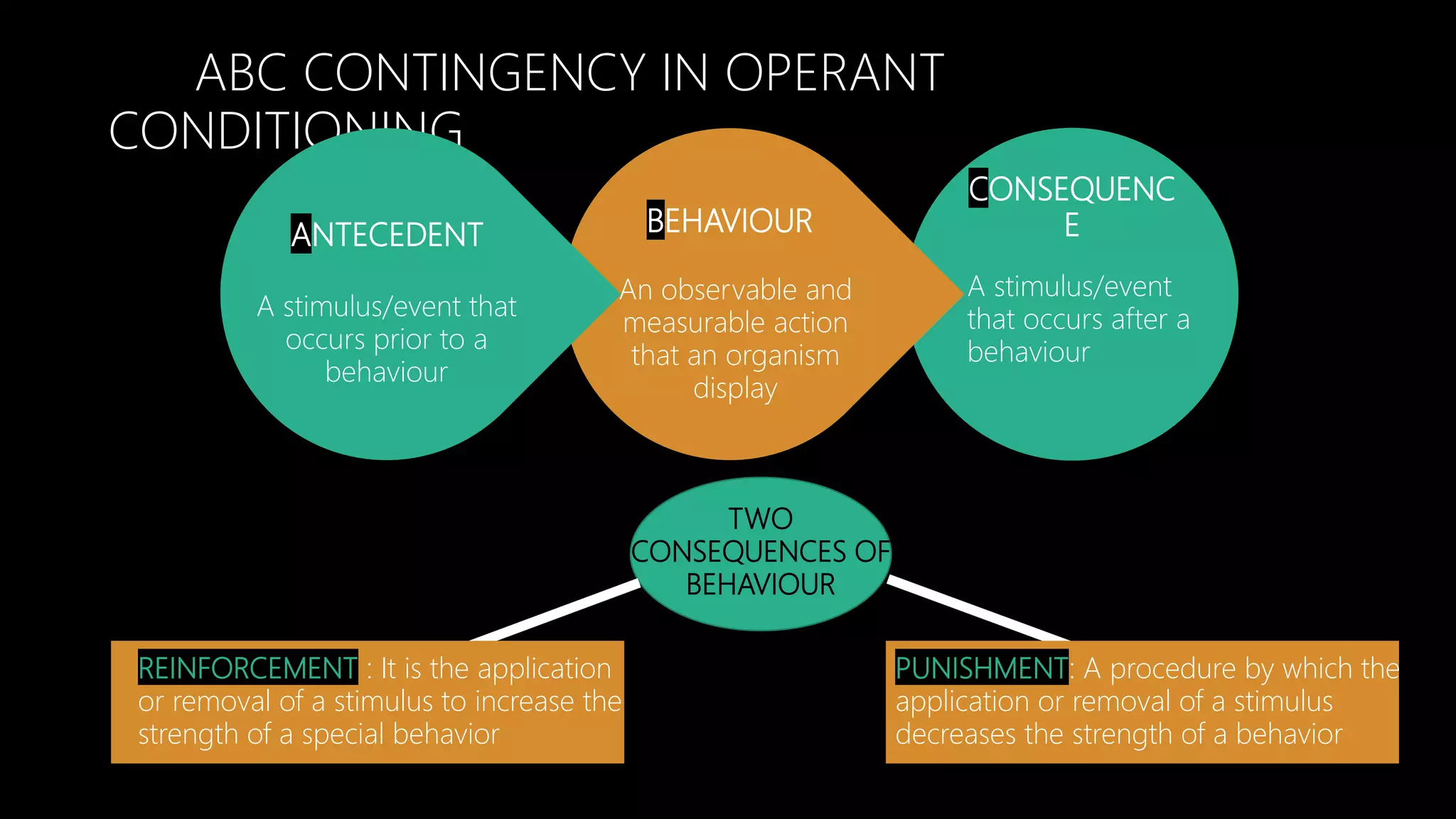
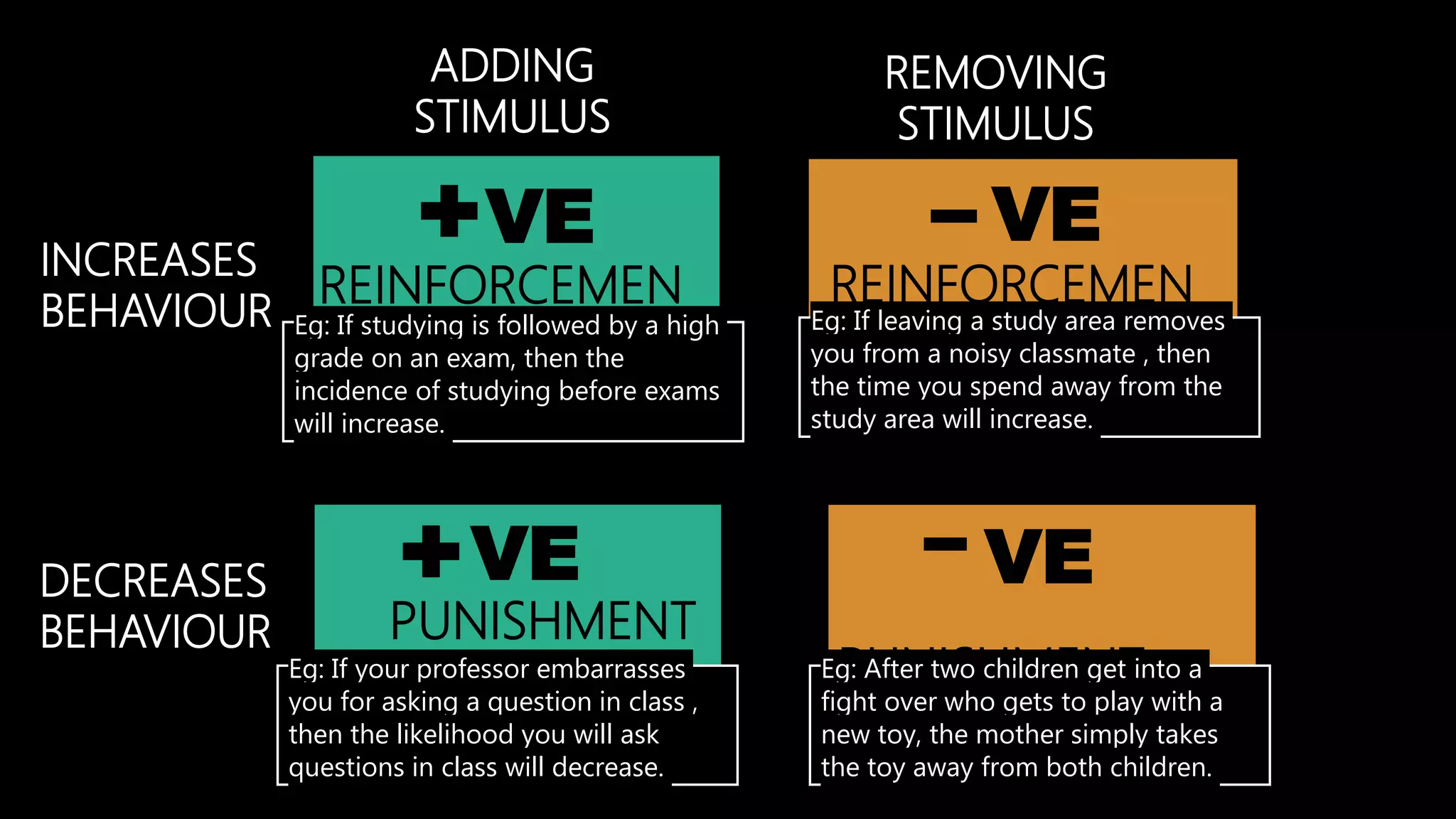
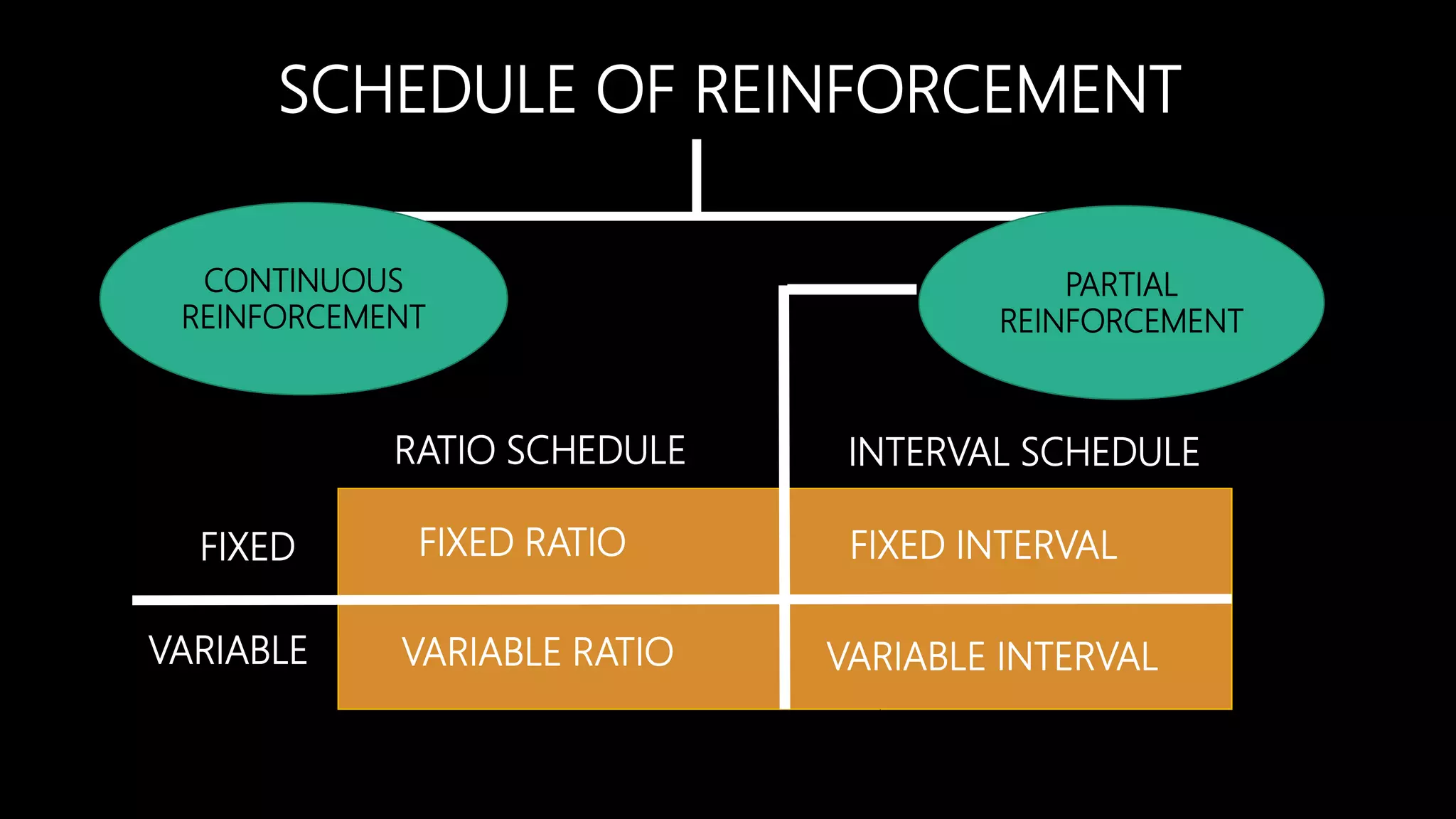
Instrumental learning, also known as operant conditioning, is a type of associative learning where behaviors are modified by reinforcement or punishment. B.F. Skinner developed operant conditioning based on Thorndike's "Law of Effect." Reinforcement increases behavior when a stimulus is added or removed after a behavior, while punishment decreases behavior. Skinner studied operant conditioning using a Skinner box and identified schedules of reinforcement like continuous, partial, fixed ratio, and variable interval reinforcement. While incomplete, operant conditioning explains a variety of behaviors and can be applied in different settings.