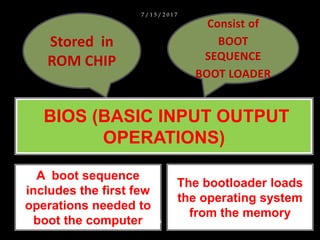
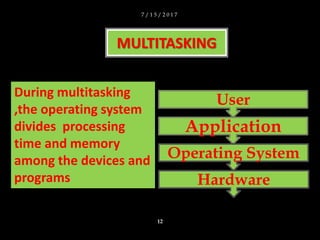
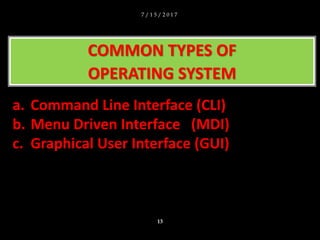
The document discusses operating systems and their functions. It describes how operating systems control computer systems by managing programs, files and directories, system devices, and allowing multitasking. It also discusses the different types of user interfaces that operating systems use including command line interfaces, menu driven interfaces, and graphical user interfaces.