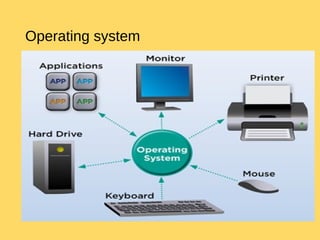
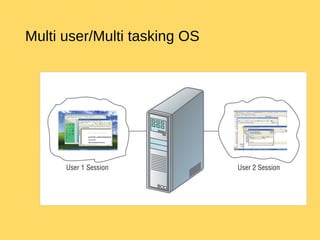
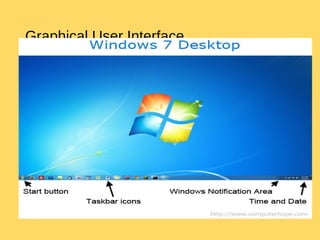
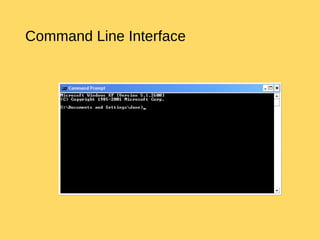
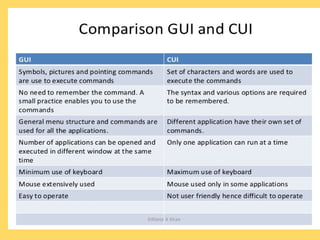
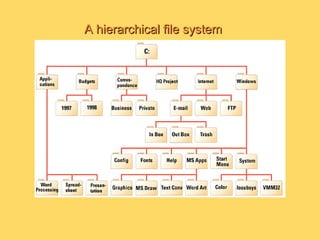
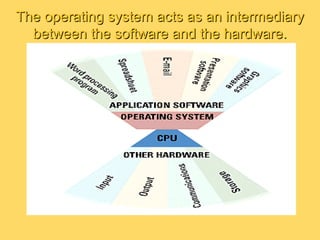
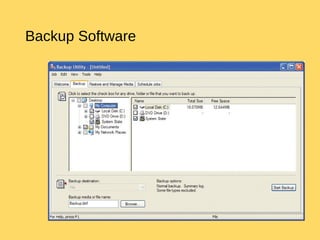
The operating system is the most important program that runs on a computer and allows other programs to run. It performs basic tasks like managing input/output, files and directories, and peripheral devices. For large systems, the operating system also ensures different programs and users do not interfere with each other and is responsible for security. Operating systems provide a user interface, run programs, manage hardware devices, and organize file storage. Common types include real-time, single-tasking, multitasking, and multi-user systems.