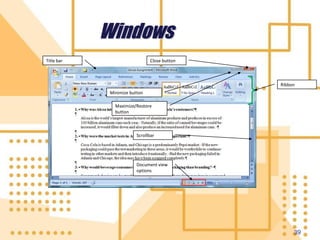
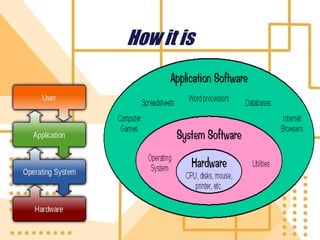
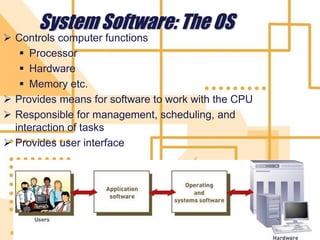
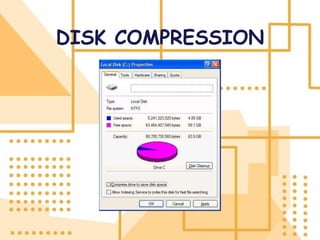
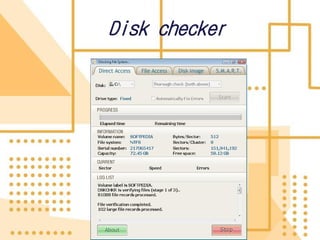
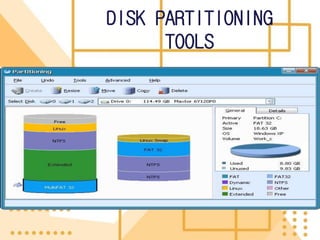
Software is a collection of programs that tells a computer what to do. There are three main types of software: system software, programming software, and application software. The first software program was written in 1948 by Tom Kilburn for the first stored-program electronic computer. System software includes operating systems, utility programs, and device drivers. Operating systems manage computer resources and provide services for other programs. Utility programs perform specific computer management tasks. Device drivers allow operating systems to communicate with hardware devices like printers.



















![28
Operating System Categories
• Four categories:
• Real-time (RTOS)
• Single-user, single-task (e.g. 1 student 1
teacher)
• Single-user, multitask [e.g. 1 teacher
multiple students]
• Multiuser](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jpp7zttseggvwlzynucq-ict-lecture-10-230221074303-1b706f03/85/ICT-Lecture_-_10-ppt-28-320.jpg)