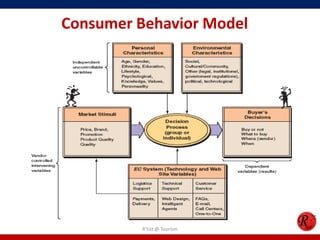
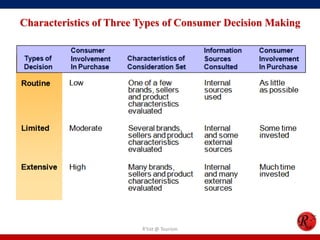
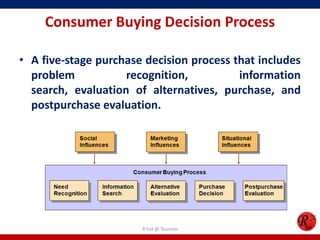
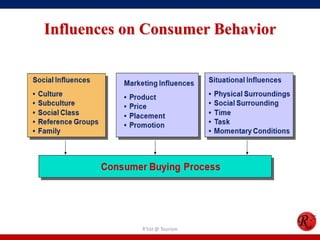
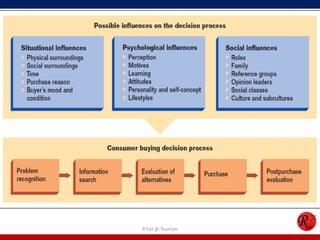
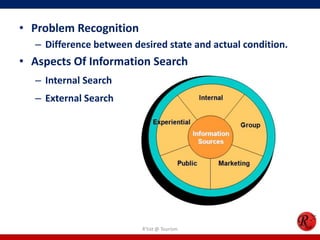
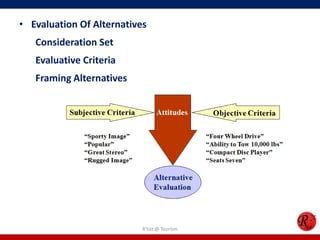
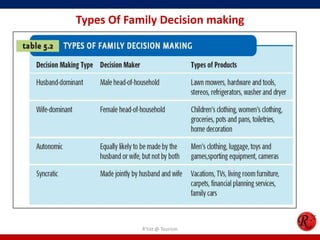
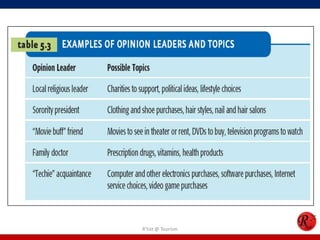
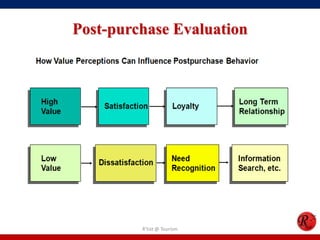
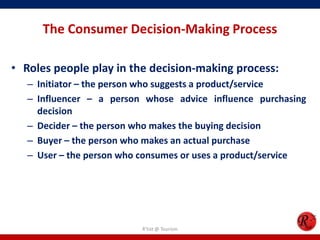
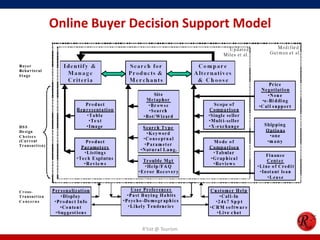
This document discusses consumer behavior in online marketing. It begins by defining consumer and business markets, and consumer buying behavior. It then covers the consumer decision-making process, which involves problem recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase, and post-purchase evaluation. Influences on consumer behavior include personal characteristics, psychological factors, and environmental influences. The document also discusses types of online shoppers and compares online versus traditional consumers in terms of technology adoption, convenience, loyalty and trust, products versus services, and site design.