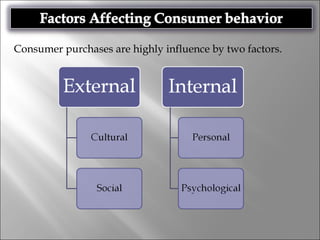
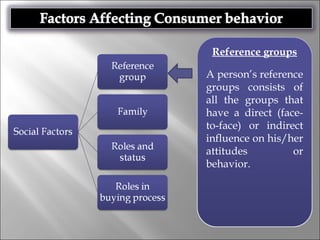
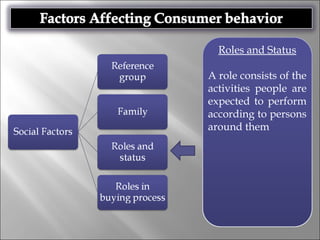
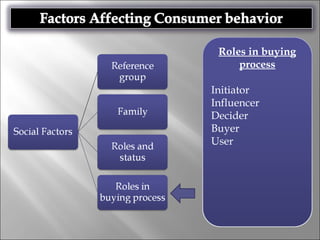
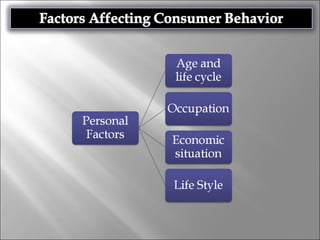
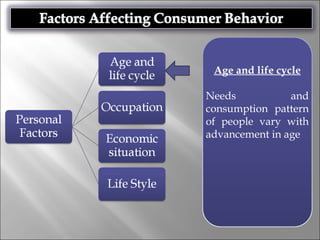
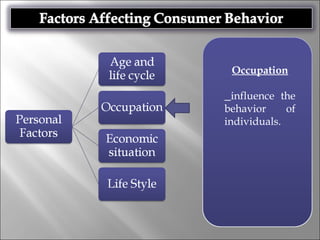
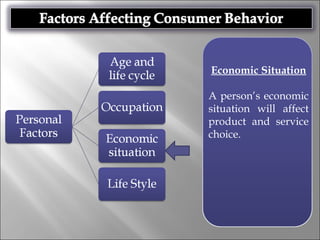
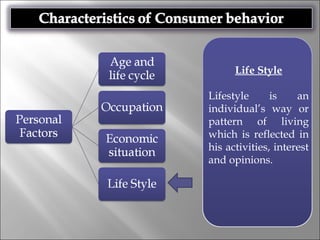
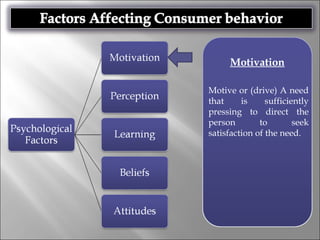
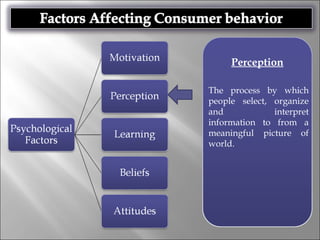
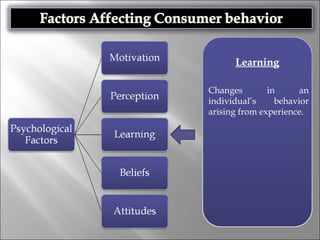
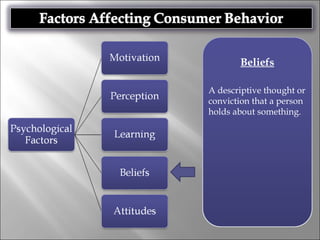
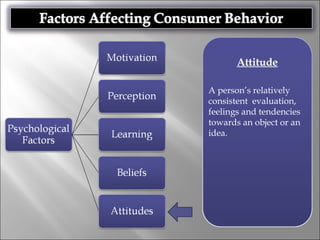
Consumer behavior involves the processes individuals use in evaluating, acquiring, and using services and products, influenced by cultural, social, and personal factors. Key determinants include family roles, social class, lifestyle, motivation, and perception, which shape how consumers make purchasing decisions. The evaluation of services is notably distinct from goods, with consumers often perceiving greater risk and engaging more in post-purchase evaluations.