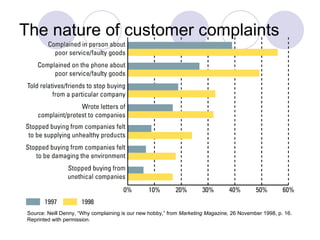
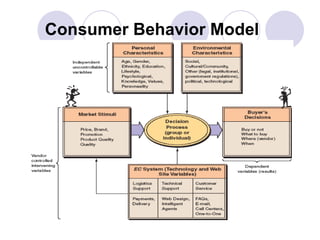
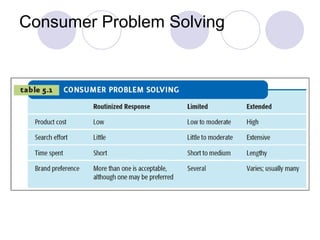
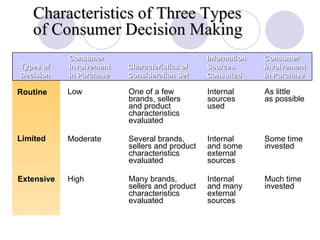
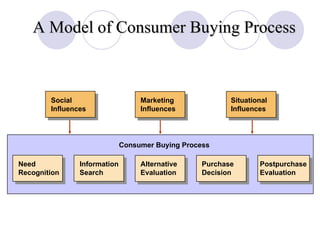
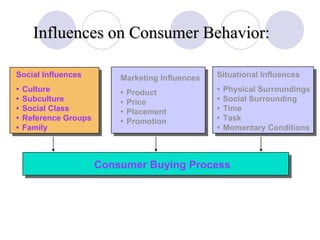
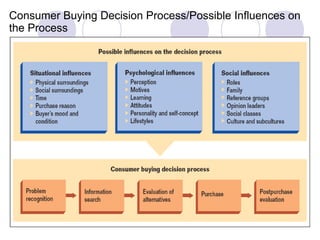
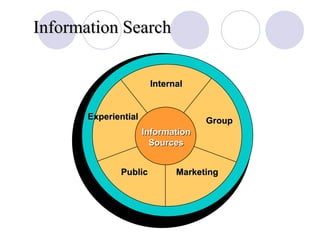
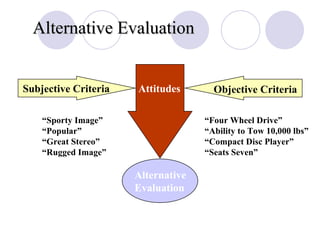
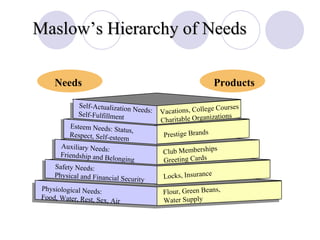
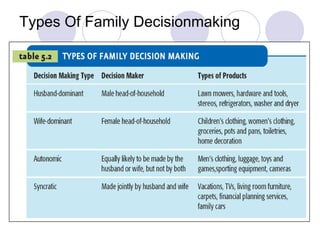
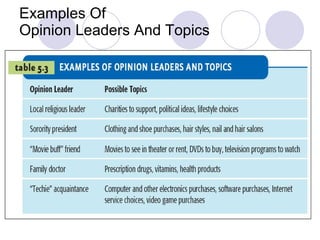
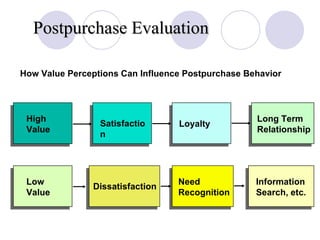
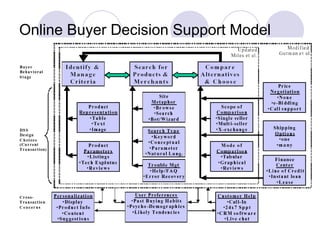
The document discusses factors that influence online consumer behavior and the consumer decision-making process online. It describes types of online shoppers and models of consumer behavior and decision-making online. The key differences between online and traditional consumers are that online consumers have more alternatives to consider, place less importance on price over time, and loyalty is easier to lose online due to lower switching costs.