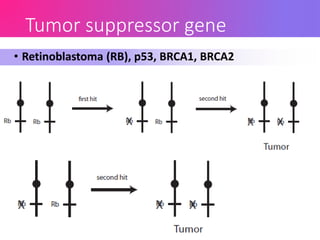
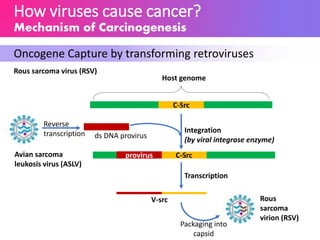
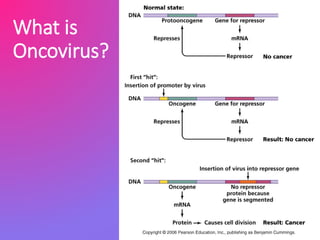
Oncoviruses are viruses that can lead to cancer by causing genetic changes, either through oncogene capture or insertional activation during viral replication, resulting in uncontrolled cell proliferation. Cancer can develop from mutations in proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, leading to benign or malignant tumors. Approximately 17.8% of global cancer cases in 2002 were attributed to infectious diseases, with certain viruses, such as HPV and hepatitis B, being notable contributors.