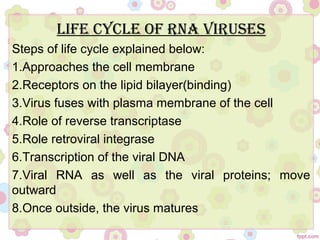
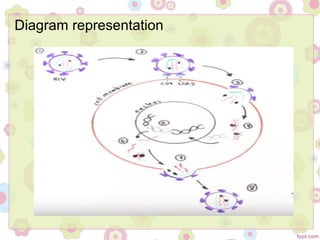
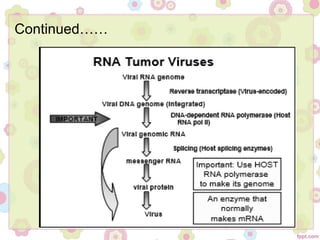
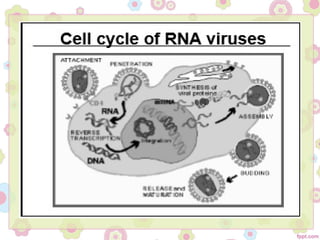
This document discusses viral oncogenesis, or how viruses can cause cancer. It defines oncogenes as viral genes that can cause tumors and proto-oncogenes as normal cellular genes that viruses can modify to become oncogenes. It describes the two main types of oncogenic viruses as DNA viruses and RNA viruses, listing some examples of each. For RNA viruses, it explains that all oncogenic viruses are retroviruses and describes the general life cycle of retroviruses, from entering the cell to replicating and exiting. The document concludes that while not all retroviruses contain viral oncogenes, they can integrate near proto-oncogenes and modulate host cell growth to cause cancer.