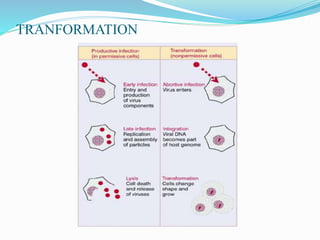
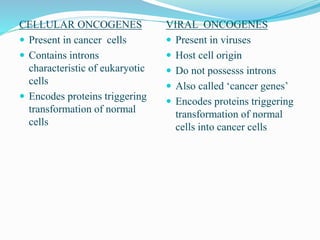
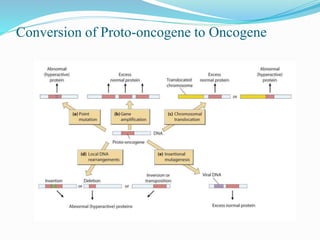
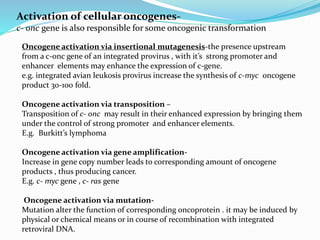
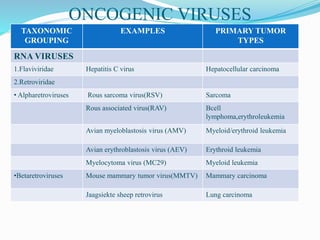
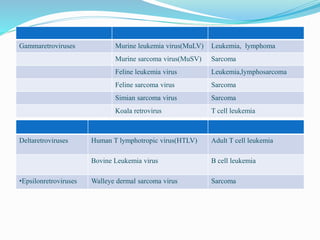
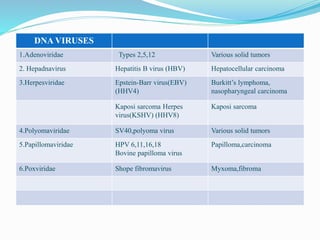
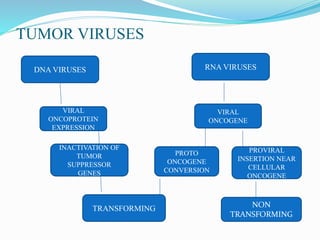
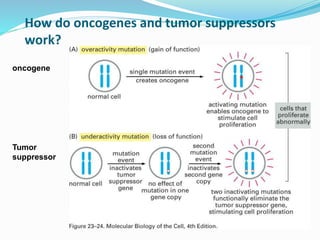
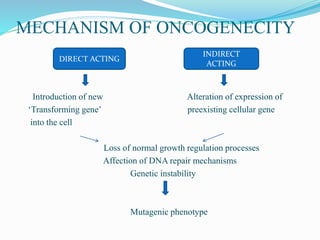
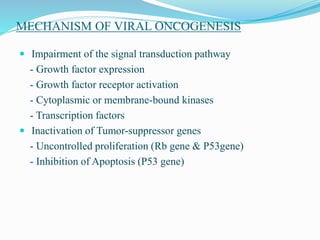
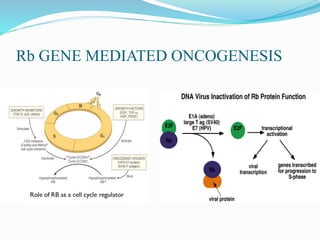
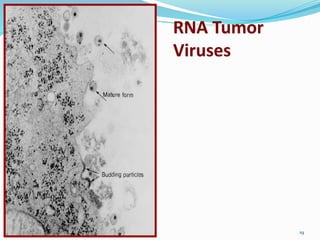
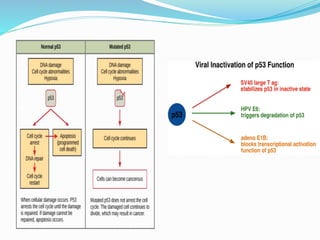
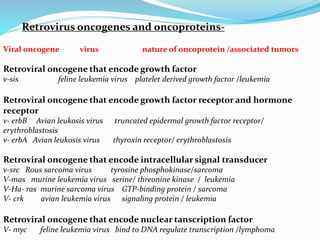
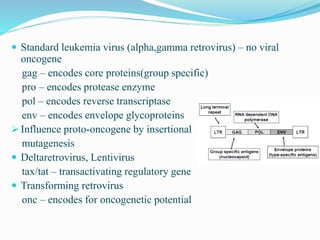
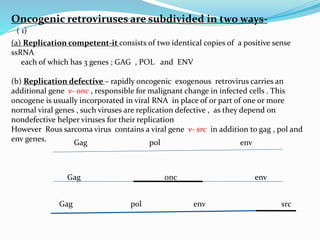
The document discusses viral oncogenesis, describing oncogenic viruses that can induce tumors in hosts and the mechanisms by which they cause cancer, including mutations in proto-oncogenes, activation of oncogenes, and inactivation of tumor suppressor genes. It highlights the characteristics of viral oncogenesis and distinguishes between different types of transforming viruses, as well as the role of oncogene activation through various means such as insertional mutagenesis and gene amplification. Additionally, the document provides examples of oncogenic viruses from both RNA and DNA families and their associated tumor types.