Embed presentation

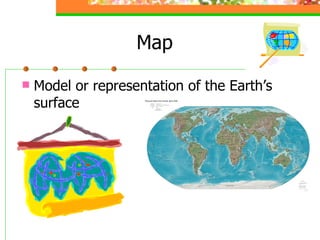
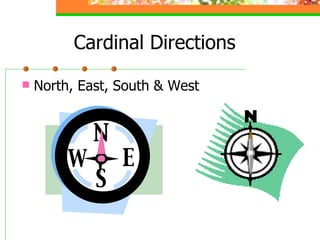


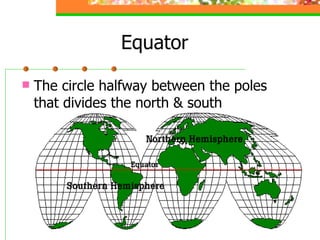

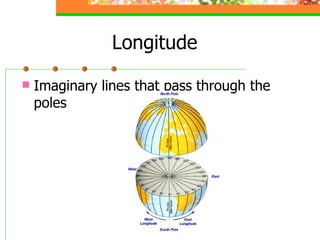
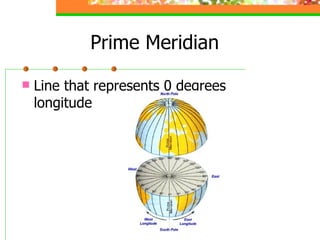

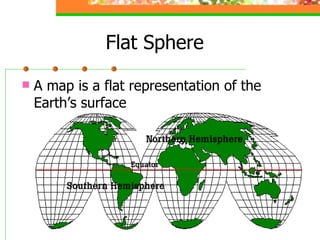
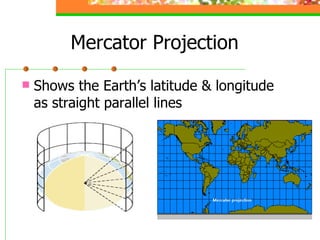
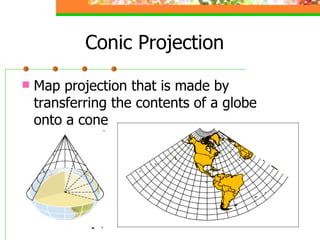
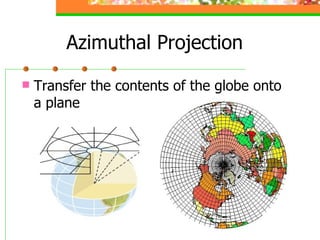








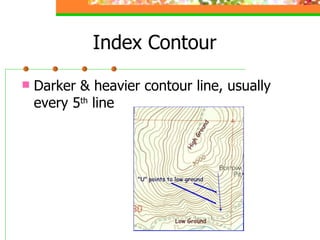
This document provides an overview of key concepts for understanding maps and models of the Earth, including cardinal directions, latitude and longitude, map projections, and topographic maps. It defines common geographic terms like the prime meridian, equator, and magnetic declination. It also explains how maps represent the spherical Earth on a flat surface using different projections, and how topographic maps indicate elevation, contours, relief, and index contours.






















