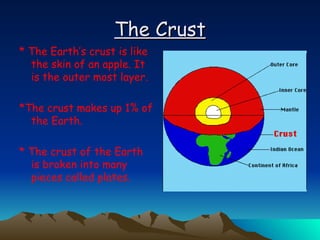
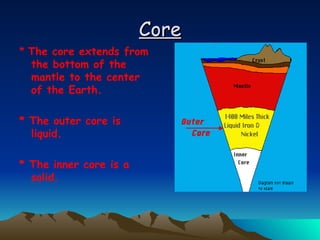
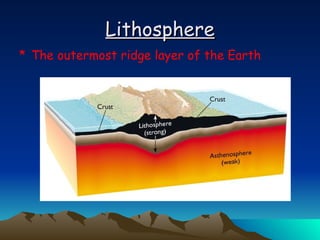
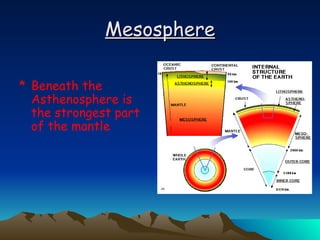
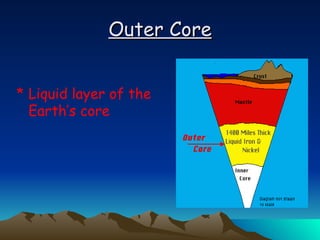
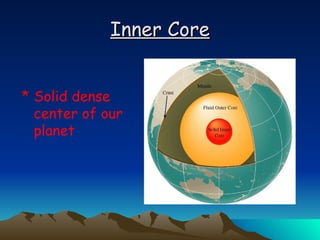
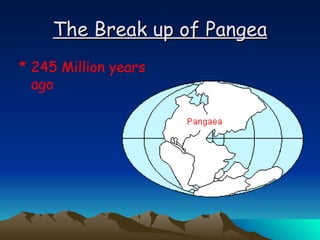
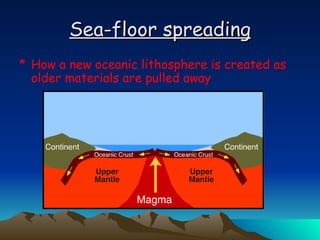
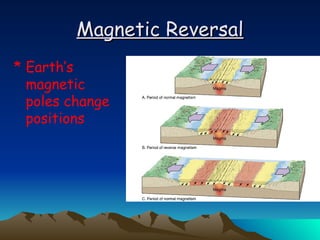
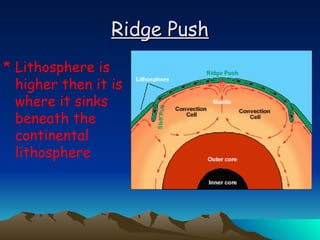
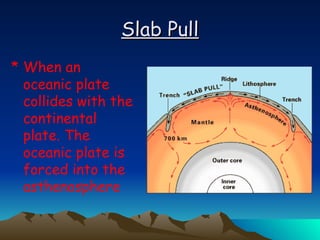
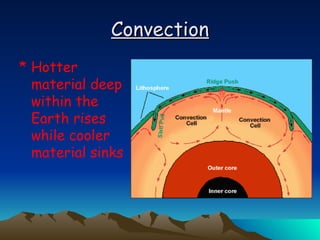
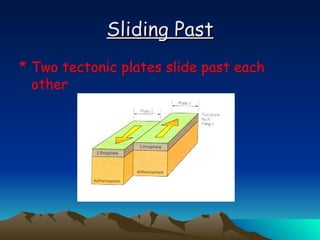
The document summarizes key concepts in plate tectonics. It describes how the Earth is divided into layers including the crust, mantle, and core. It explains that the crust is broken into plates that move around on the asthenosphere. There are three main types of plate boundaries: convergent where plates collide, divergent where they move apart, and transform where they slide past each other. Plate tectonics helps explain geological events like continental drift, mountain building, and volcanic activity.