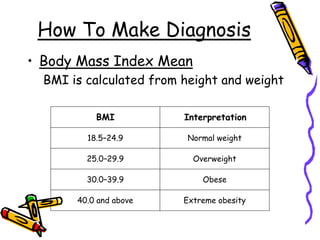
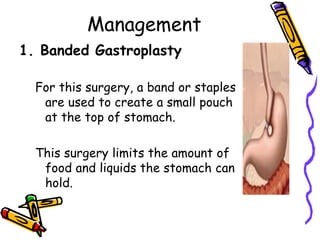
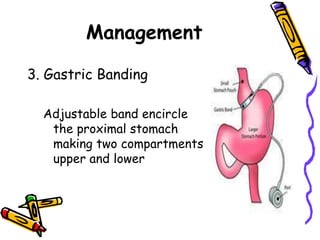
The document discusses obesity and overweight, defining them based on body mass index (BMI) and outlining their global prevalence according to the World Health Organization. It identifies various causes including energy balance, physical inactivity, genetic factors, certain health conditions, and emotional factors, and suggests management strategies such as lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, physical activity, and surgical options for severe cases. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of prevention through healthy eating and regular exercise.