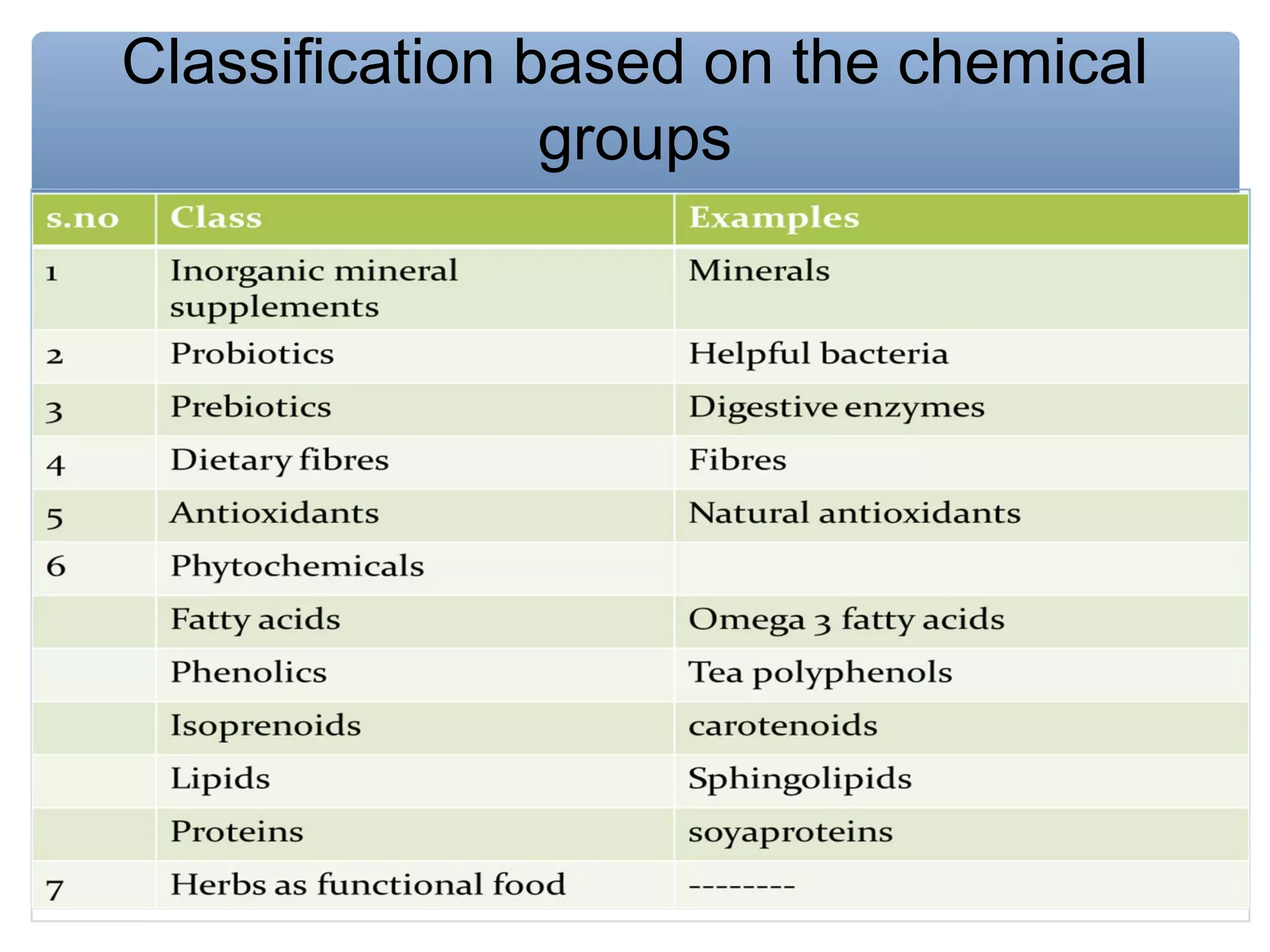
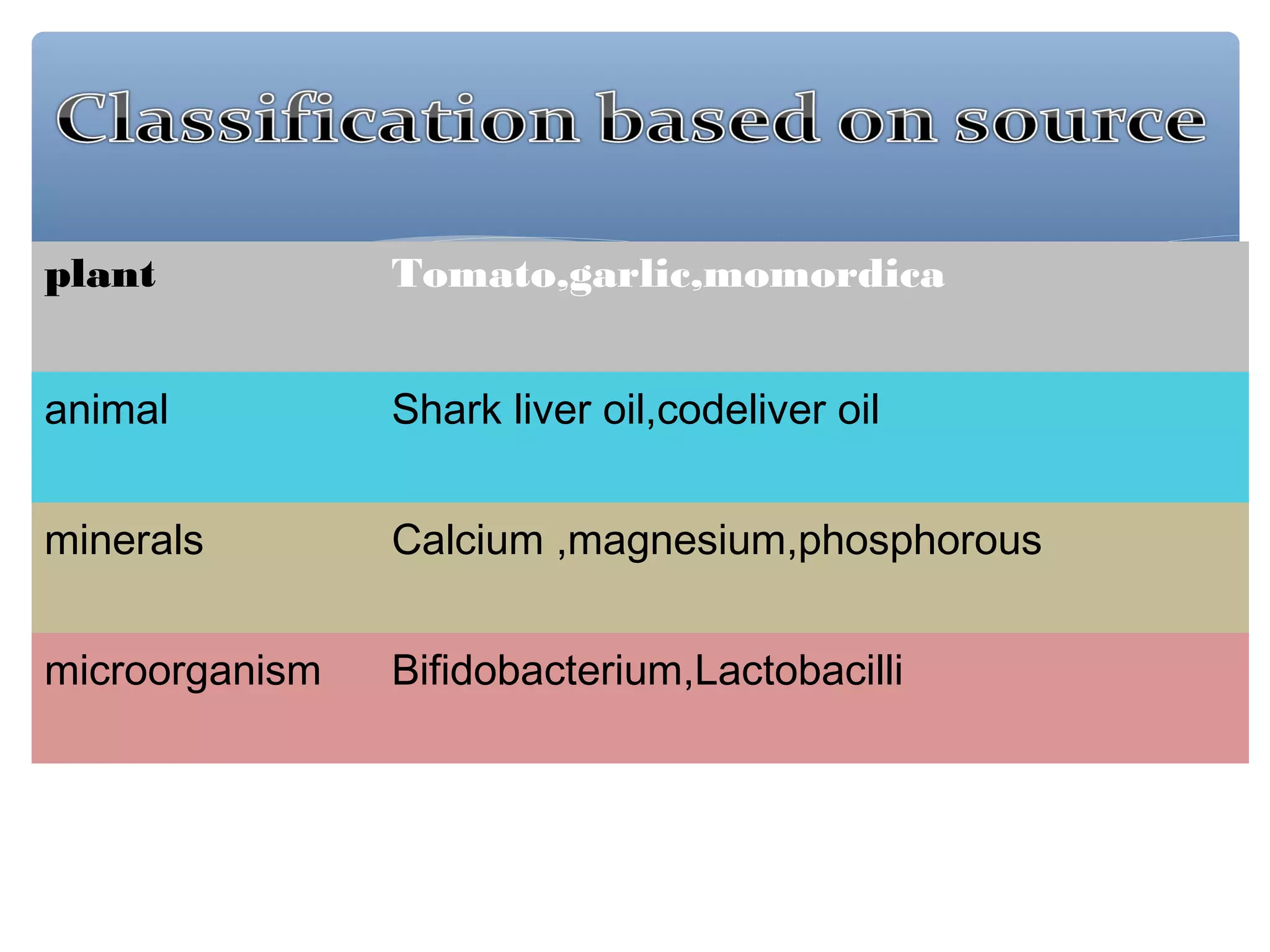
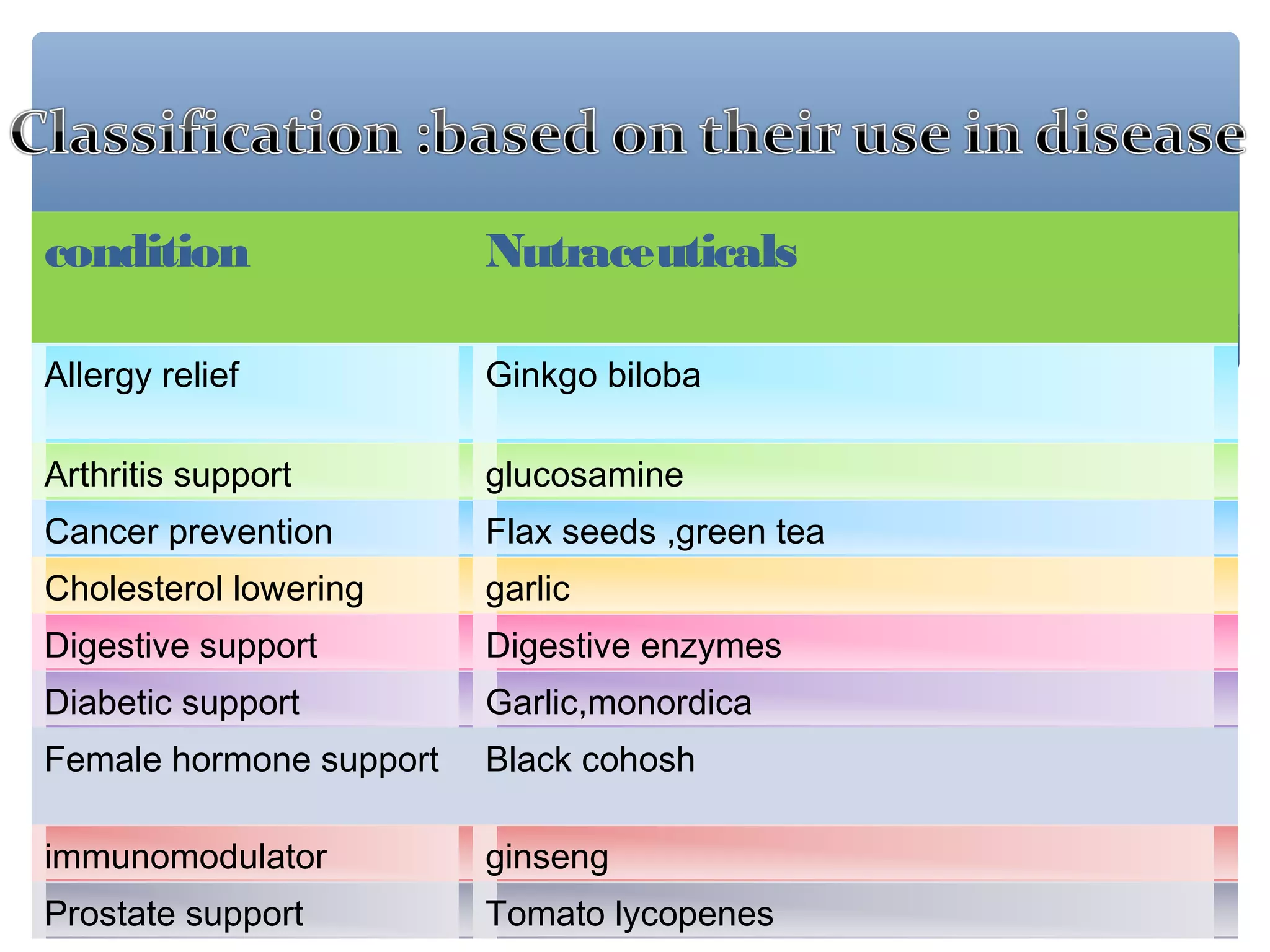
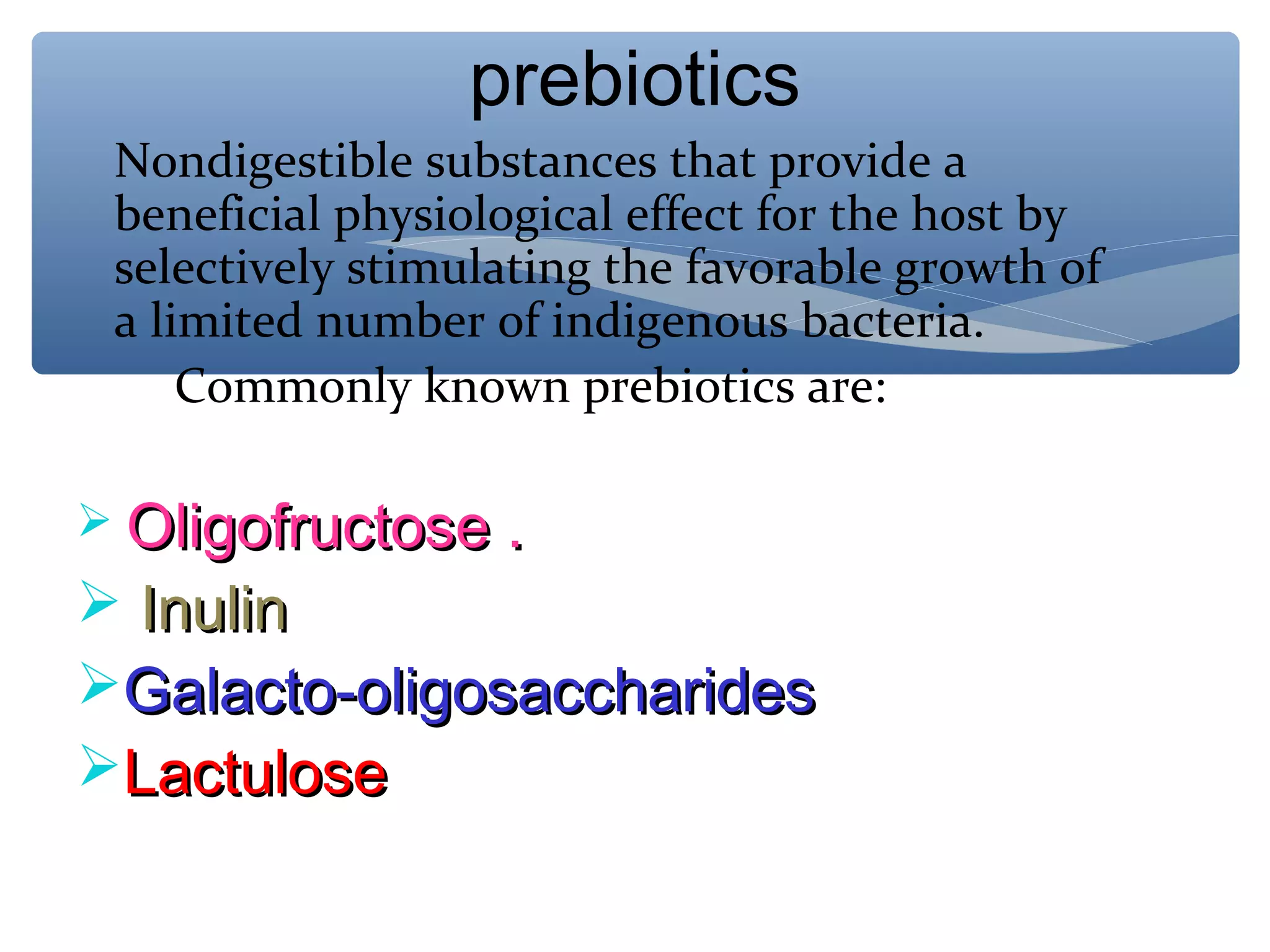
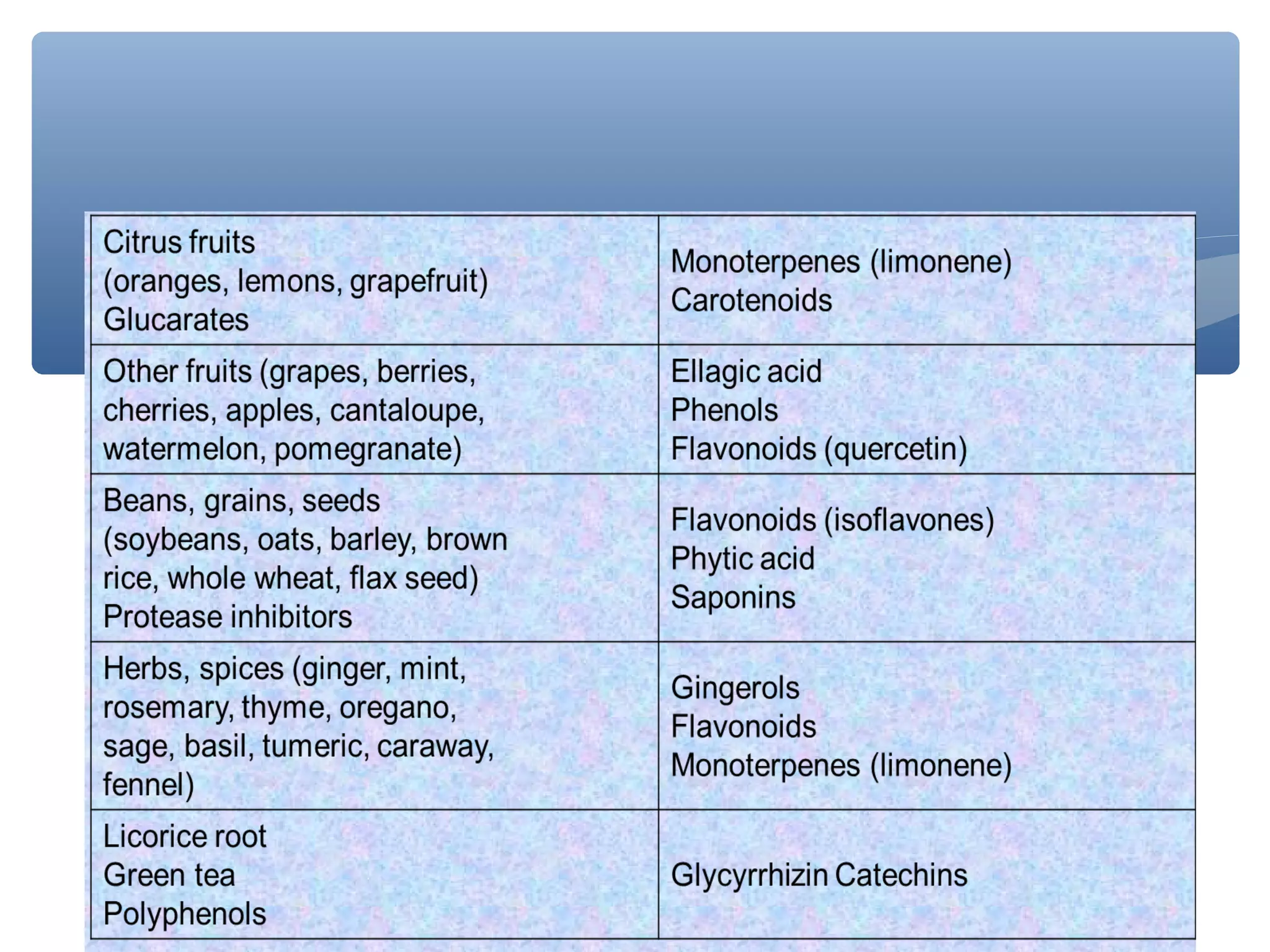
The document discusses nutraceuticals, defined as foods or parts of foods that provide health benefits, including disease prevention and treatment. It highlights various nutrients, vitamins, dietary supplements, and phytochemicals, explaining their roles in enhancing health and preventing diseases like cancer and diabetes. The importance of diet rich in nutraceuticals, combined with exercise and stress management, is emphasized for maximizing health and reducing disease risk.