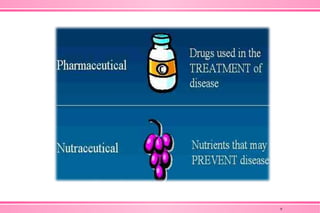
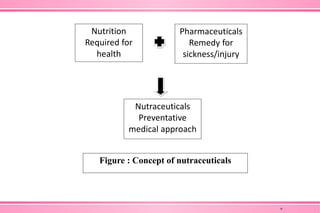
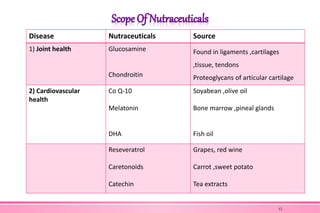
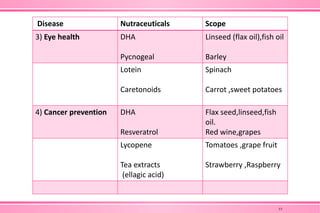
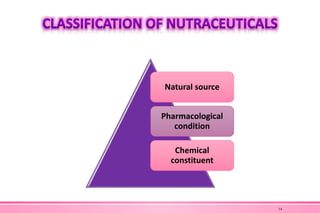
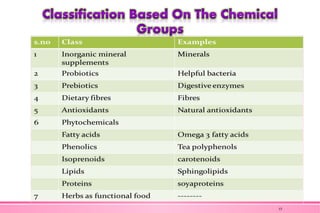
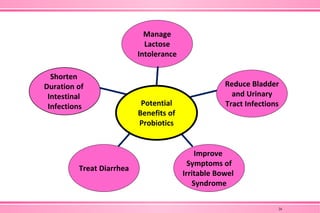
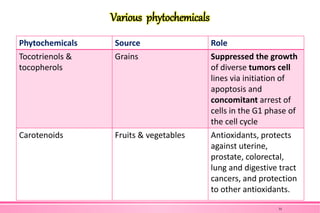
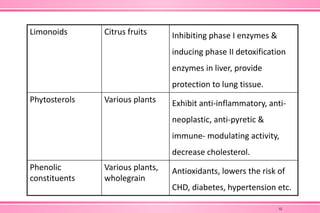
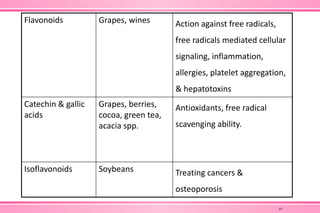
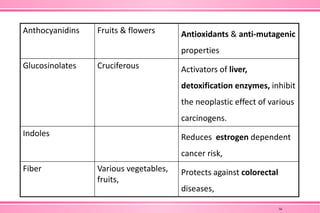
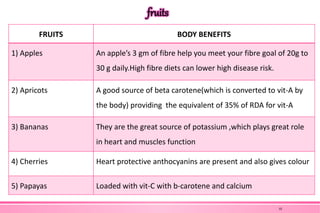
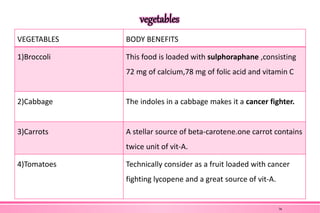
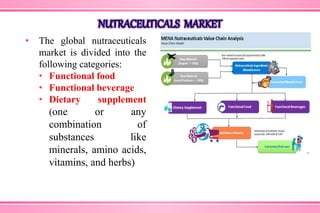
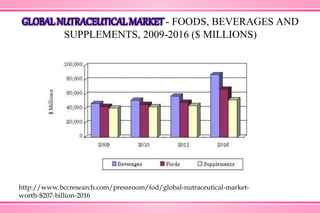
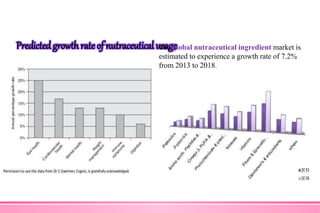
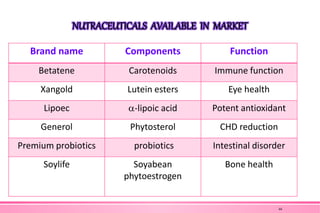
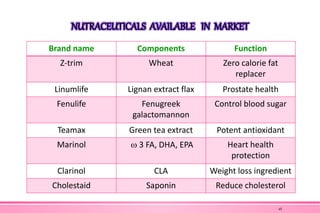
The document provides an overview of nutraceuticals. It defines nutraceuticals as food or food components that provide health benefits, including the prevention and treatment of disease. Nutraceuticals are classified into nutrients, herbals/phytochemicals, and dietary supplements. Common examples of disease areas that nutraceuticals can benefit include joint health, cardiovascular health, eye health, and cancer prevention. The global nutraceutical market is growing and includes functional foods, functional beverages, and dietary supplements. Some popular marketed nutraceutical products are also mentioned.