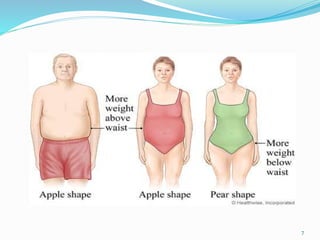
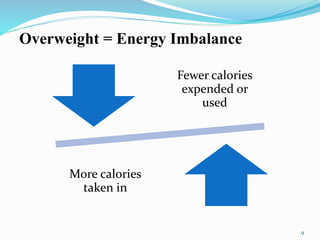
This document discusses body mass index and the causes and dangers of being overweight and underweight. It defines BMI and categories of underweight, normal weight, overweight, and obese. Being overweight increases the risk of health issues like diabetes and hypertension due to consuming more calories than expended. Treatments for overweight include reducing portion sizes, choosing low-calorie foods, exercising, and making long-term lifestyle changes. Underweight can be dangerous as well and may require a high-calorie diet and counseling to address physical or psychological causes. Maintaining a healthy weight requires energy balance through diet and exercise.