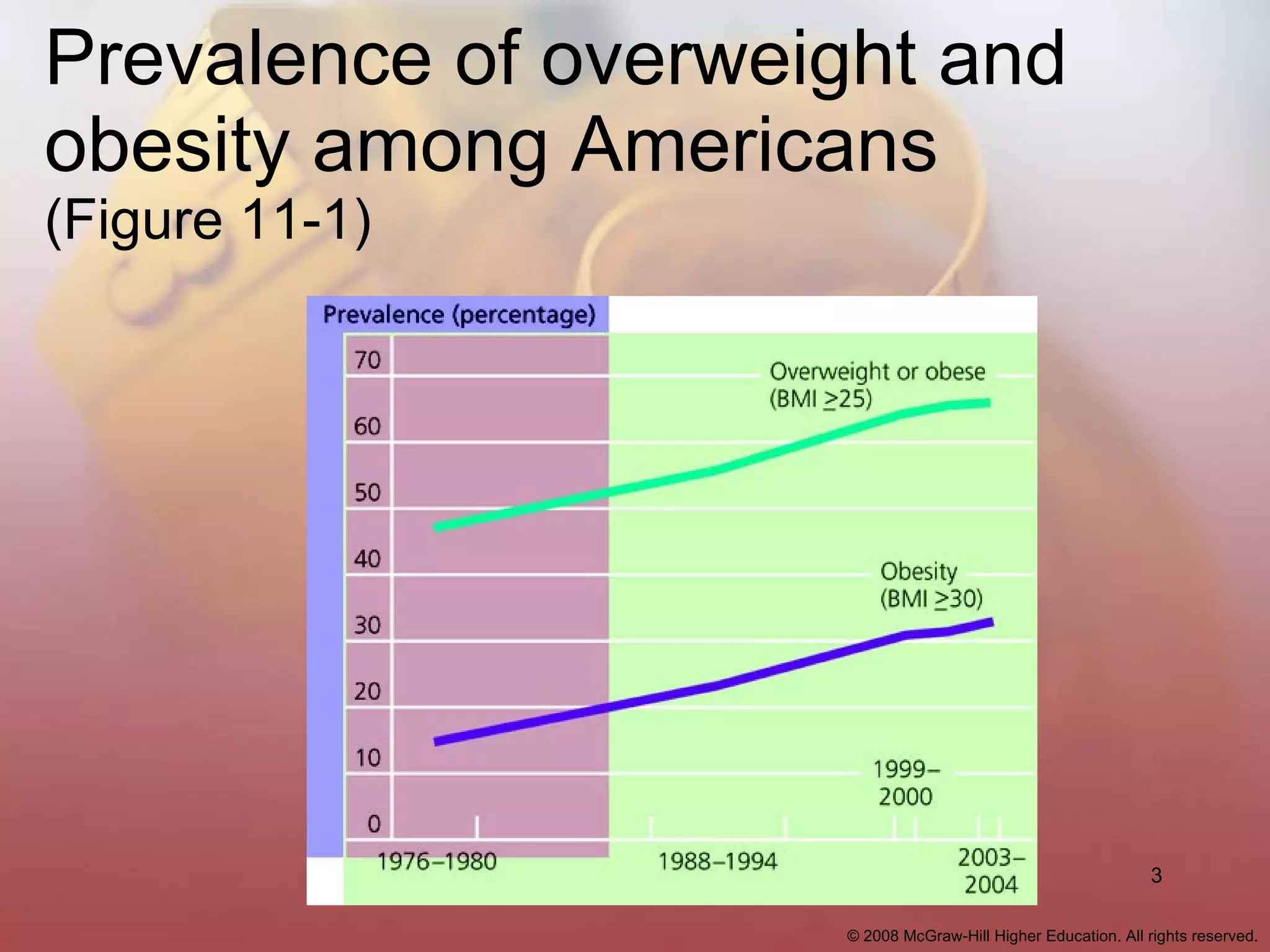
- 66% of American adults are overweight, including more than 32% who are obese. It is estimated that by 2030, the entire American adult population will be overweight or obese.
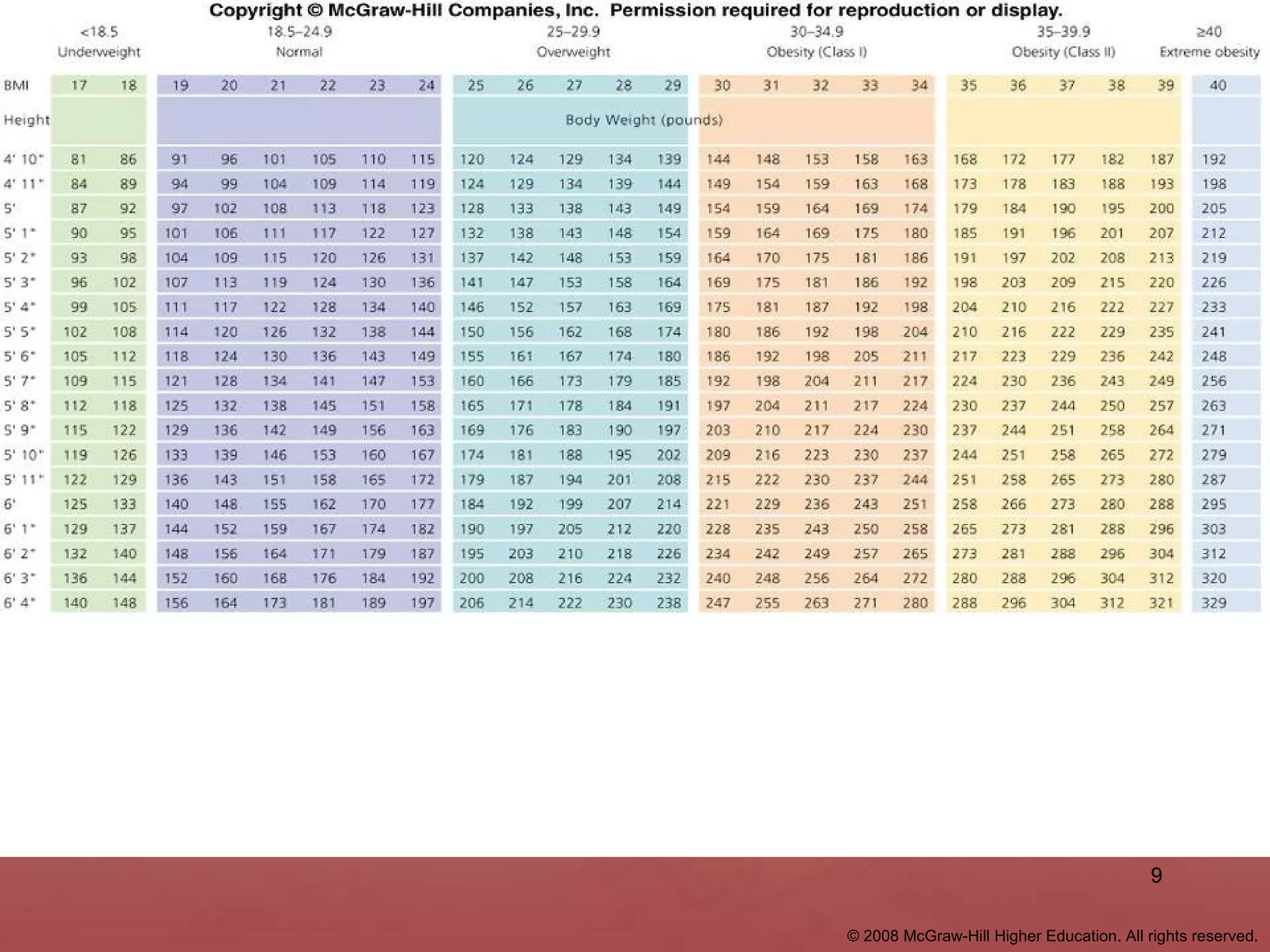
- Body mass index (BMI) is used to evaluate body weight and composition. A BMI over 25 is considered overweight and over 30 is obese. Factors like gender, age, heredity, and metabolism impact body composition and fat distribution.
- Excess body fat, especially around the waist, increases health risks like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and some cancers. Very low body fat can also cause problems with reproductive, circulatory and immune systems. Genetics, lifestyle, and psychological factors all contribute to weight issues.