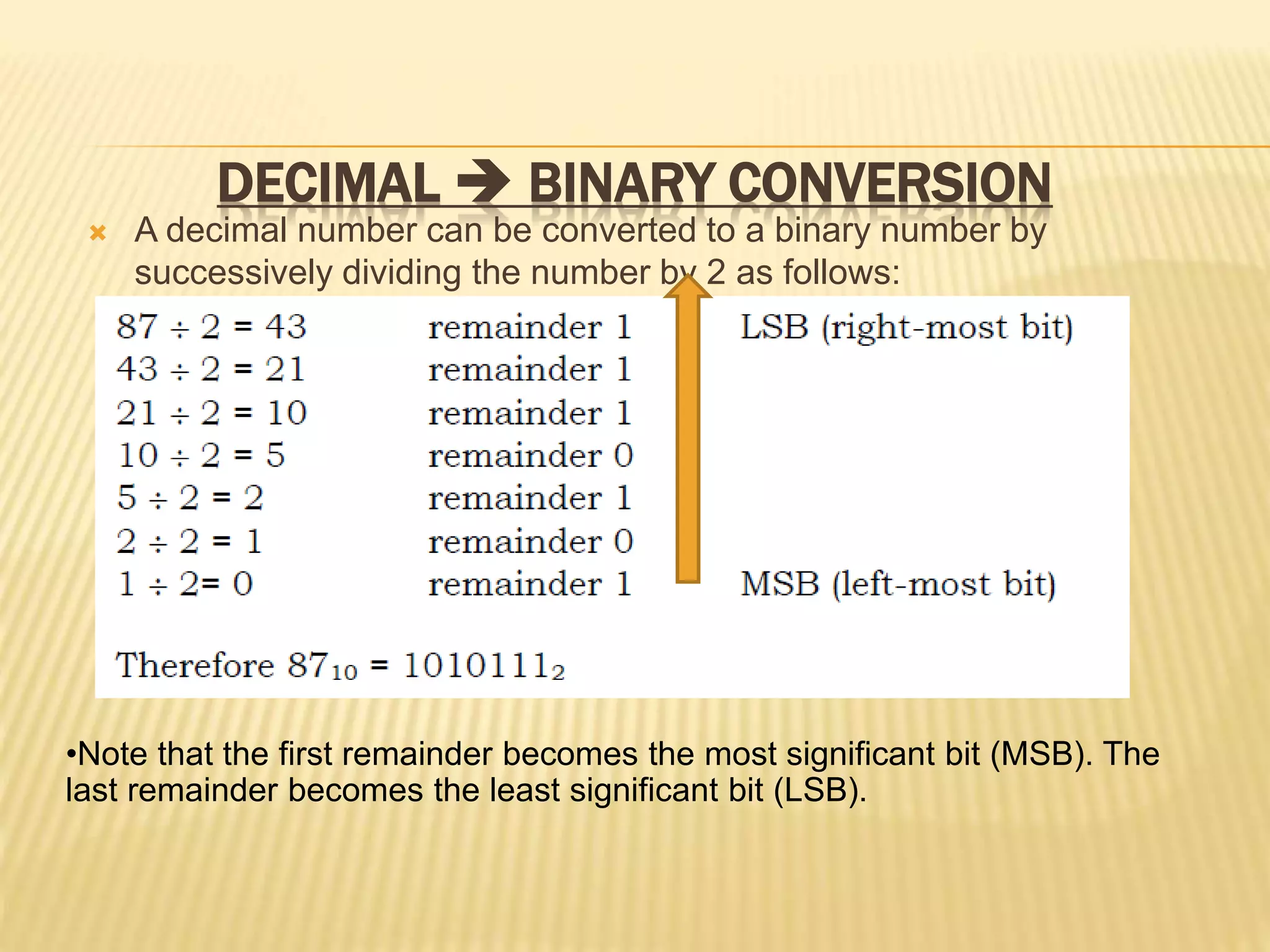
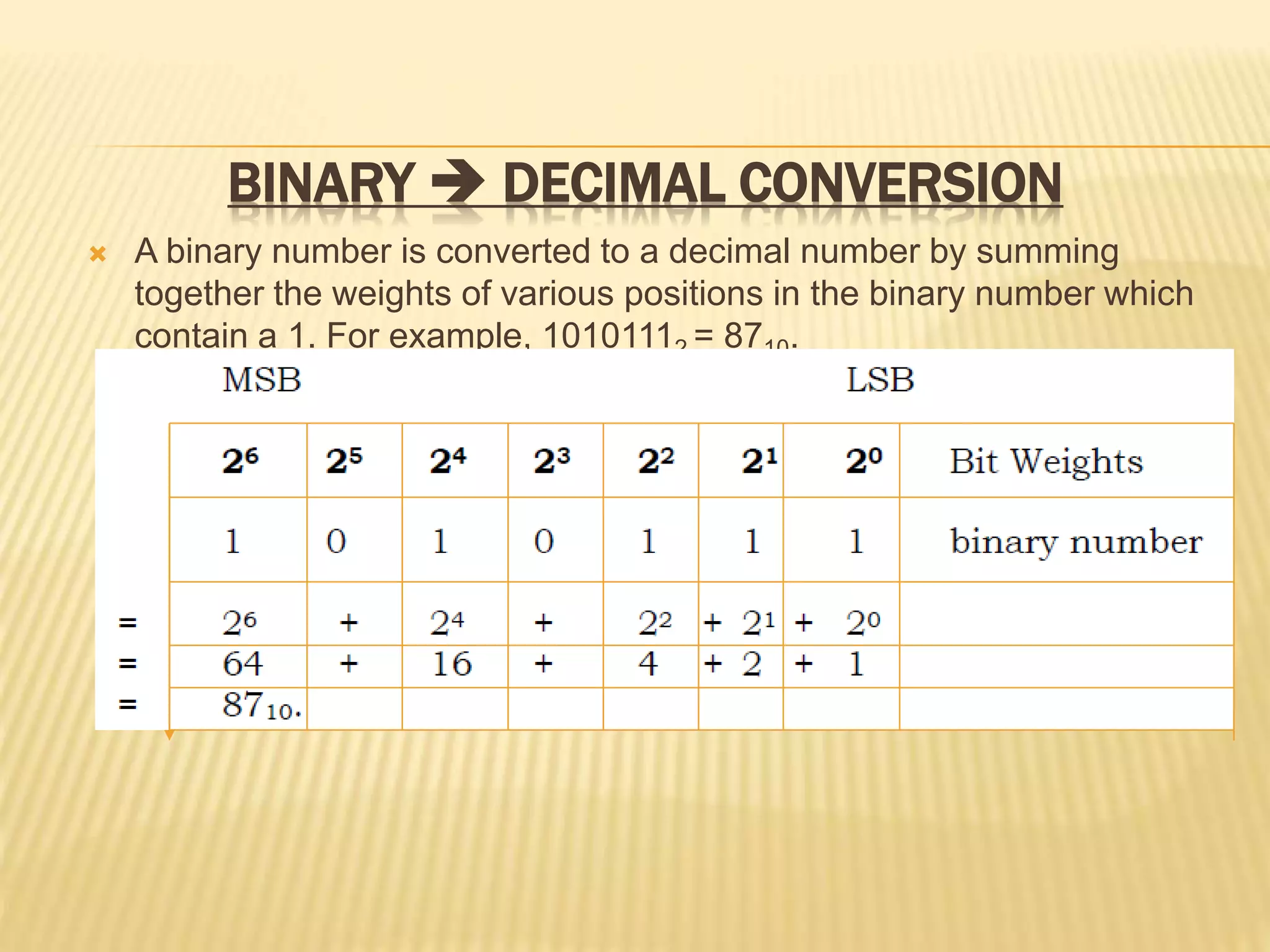
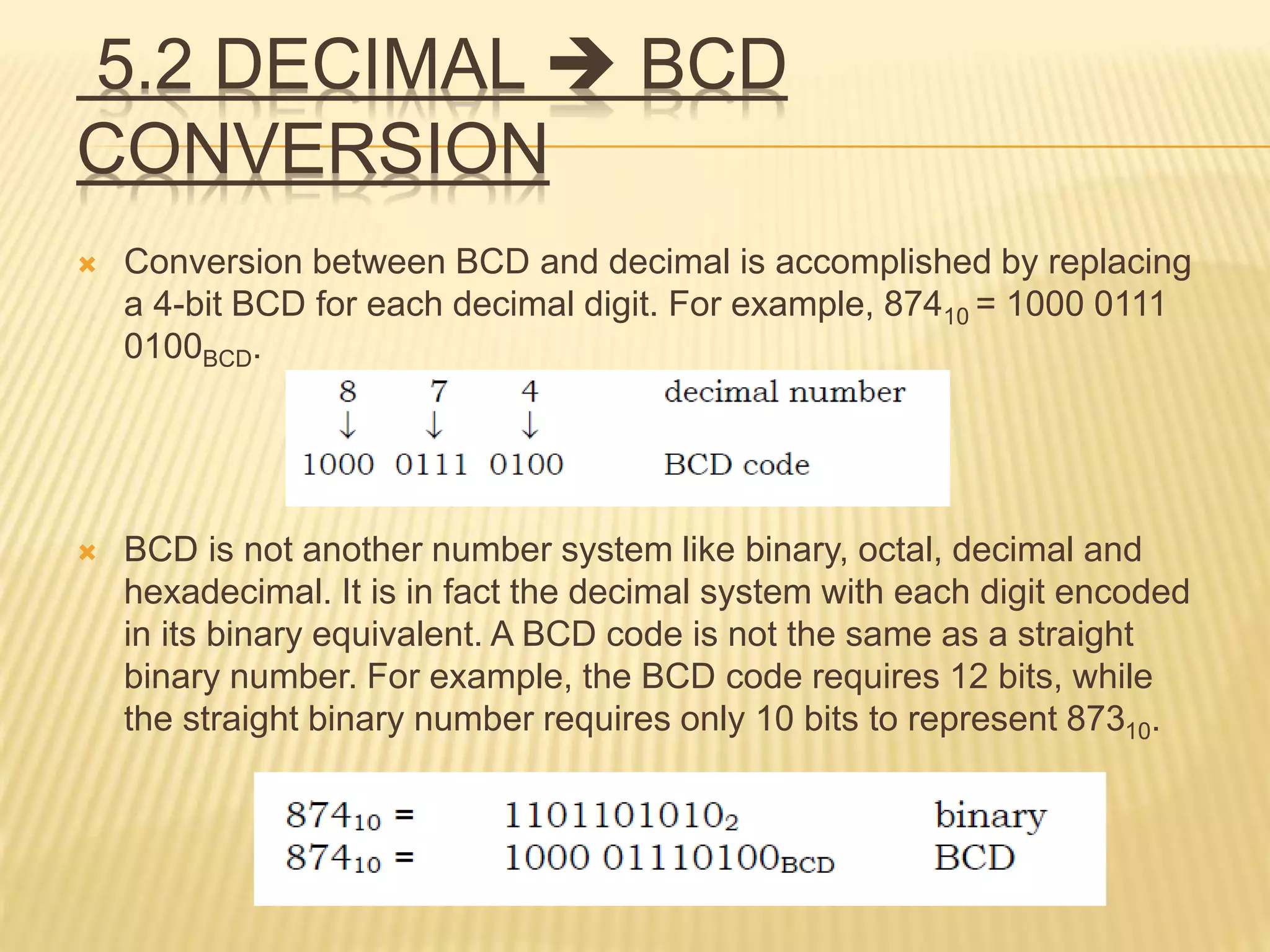
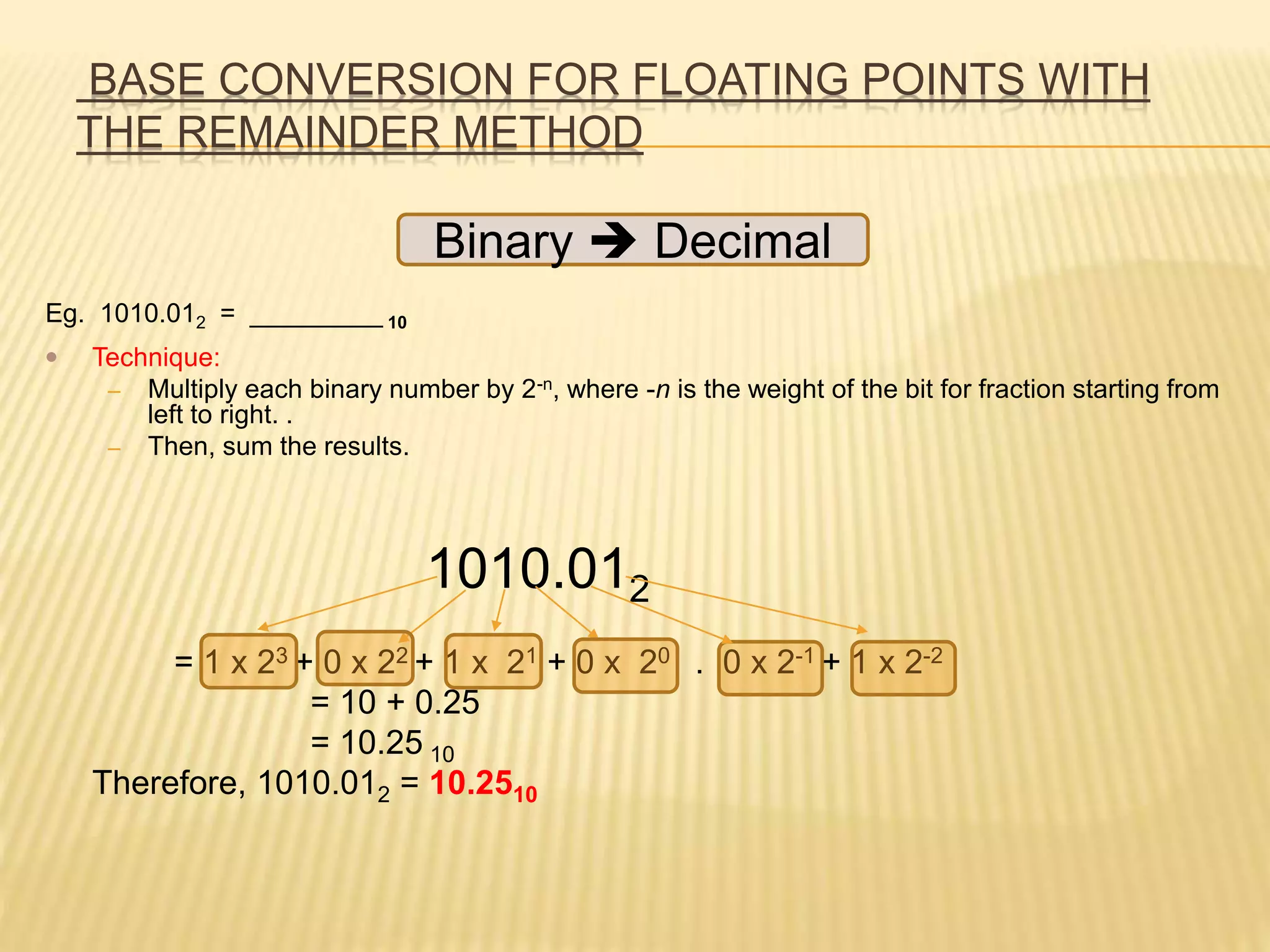
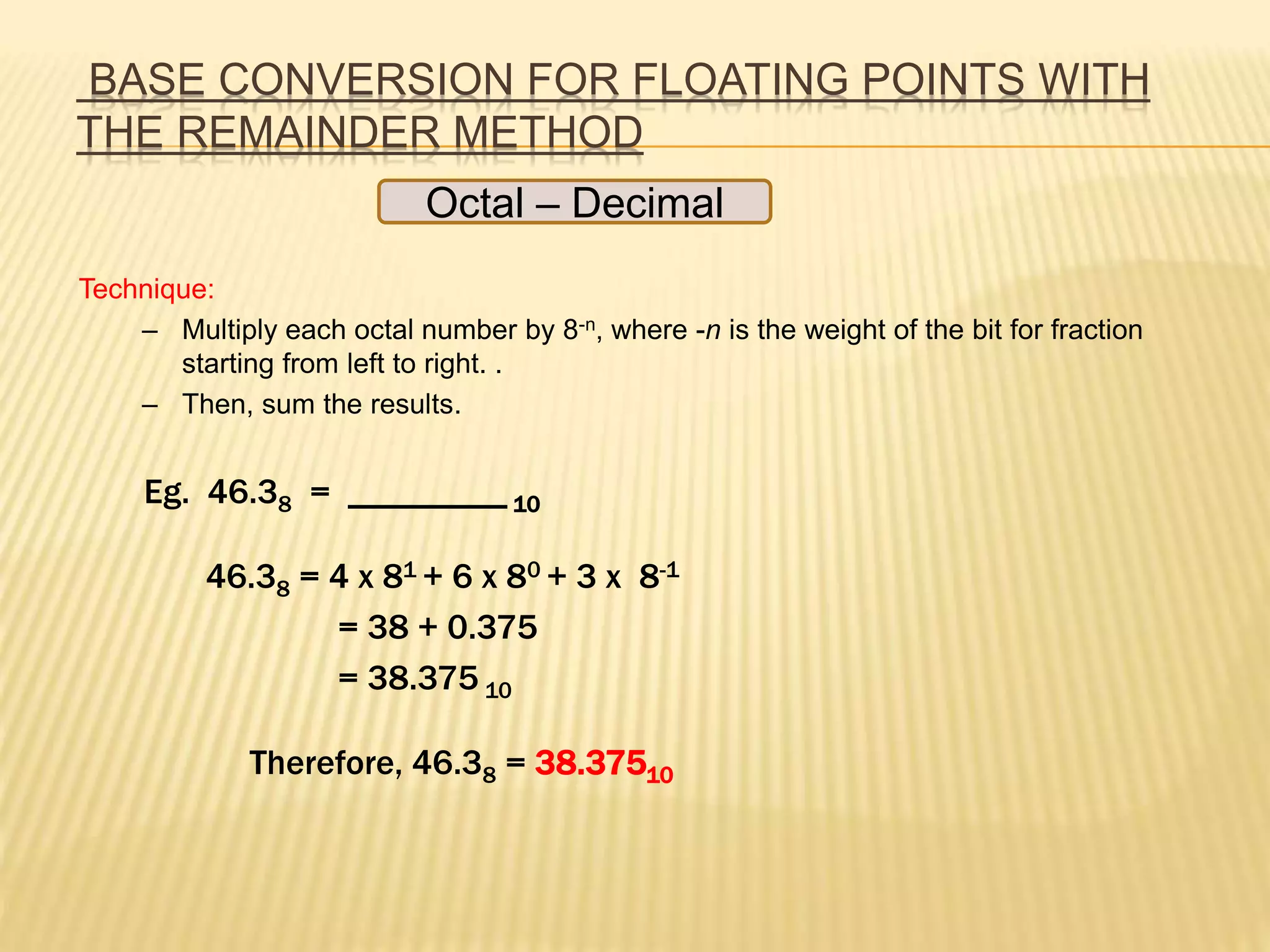
This document discusses different number systems including binary, decimal, octal, hexadecimal and binary-coded decimal (BCD). It explains how to convert between these number systems using techniques like successive division and multiplying by place values. Floating point numbers can be converted between bases by treating the integer and fractional parts separately and using the remainder method.