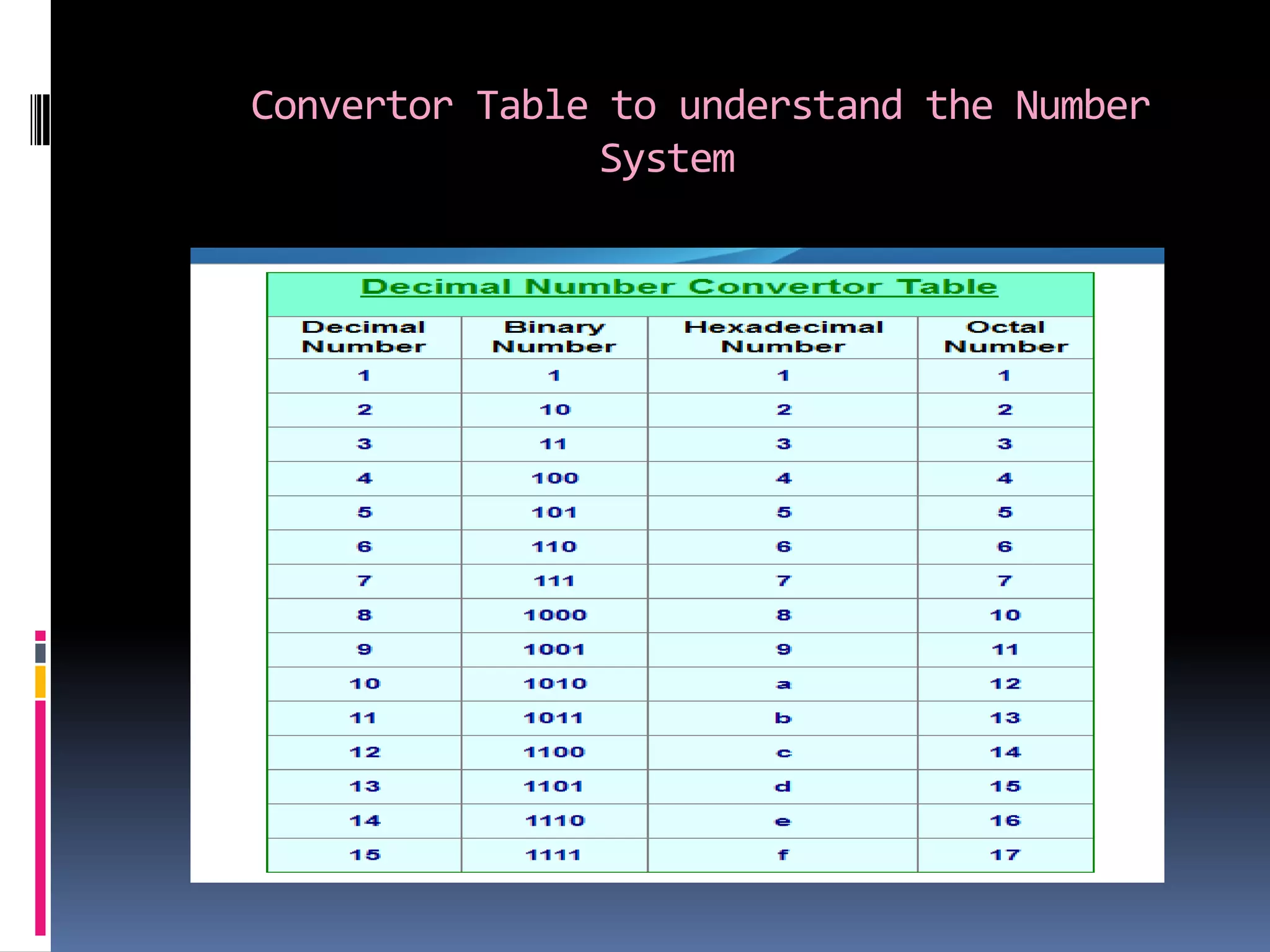
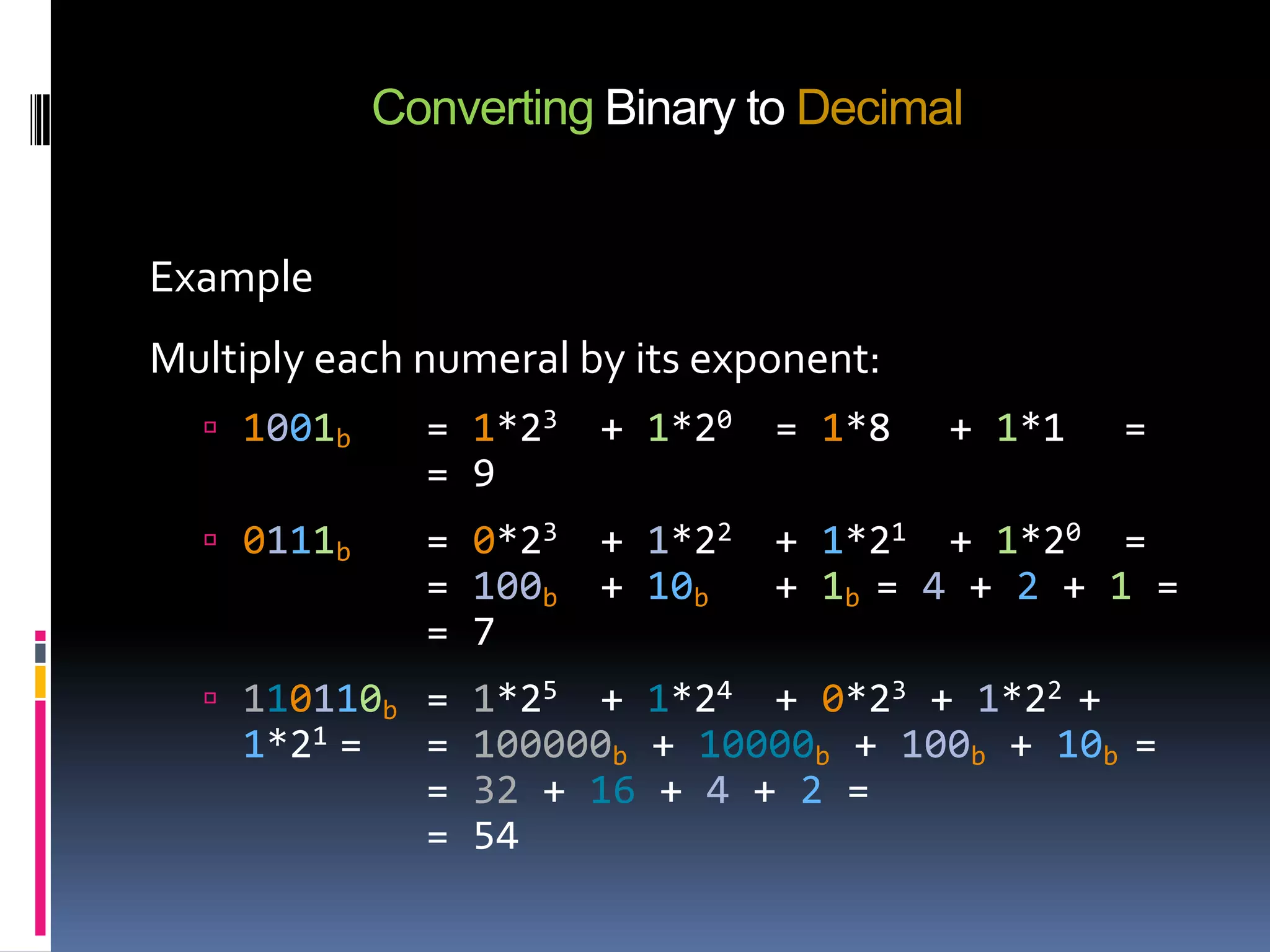
The document discusses different numeral systems used in computing including binary, decimal, octal and hexadecimal. It explains how each system uses a different base and symbol set. Binary uses base-2 with symbols 0-1. Decimal is base-10 with 0-9. Octal is base-8 with 0-7. Hexadecimal is base-16 with 0-9 and A-F. The document also provides examples and methods for converting between these different numeral systems that are commonly used for representing numbers, instructions and other data in computers.