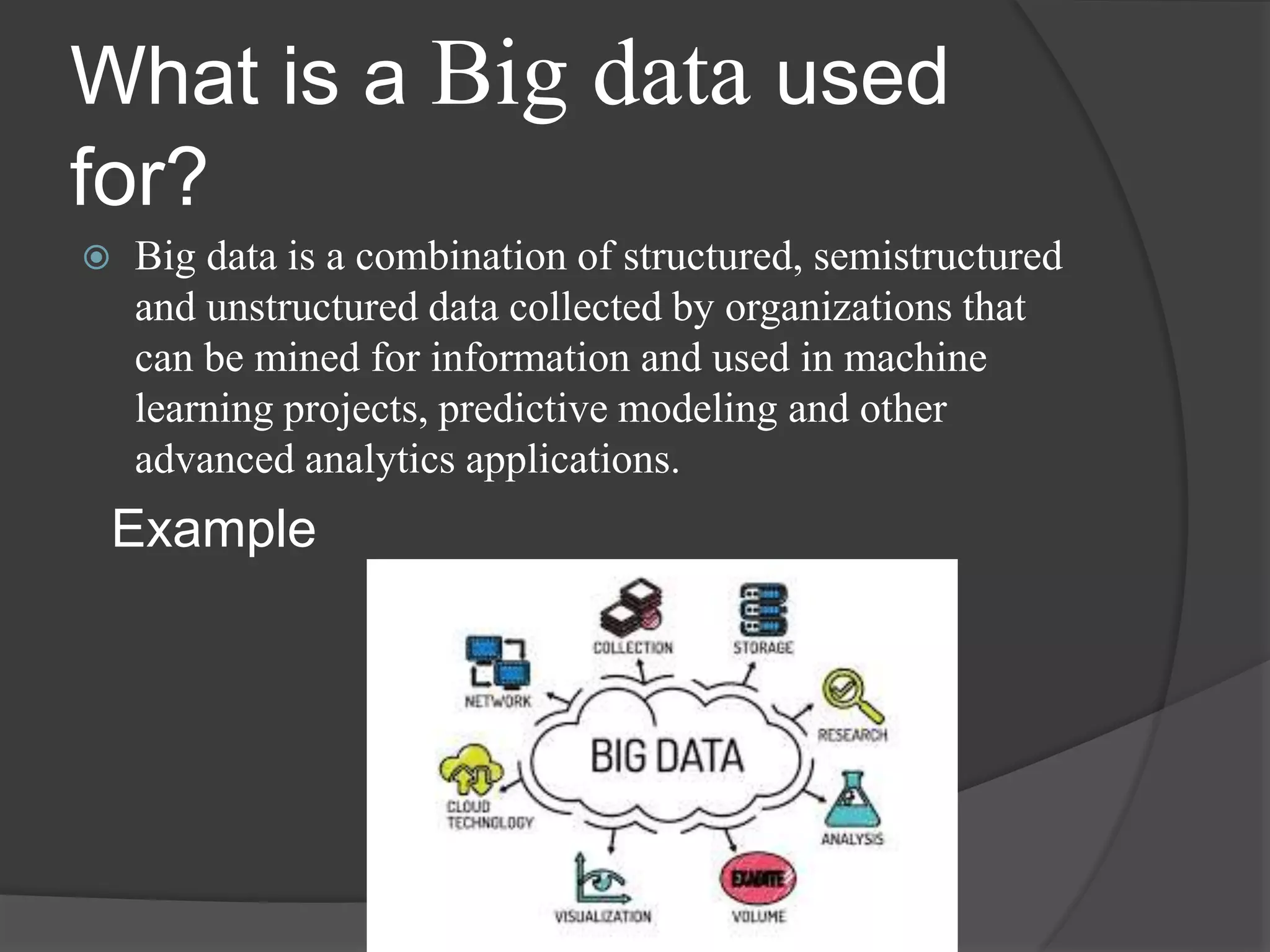
Big data is a huge collection of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data that grows exponentially over time. It is too large and complex for traditional data management tools to process efficiently. Big data comes from a variety of sources and is characterized by its volume, variety, velocity, and variability. Tools like Hadoop, Spark, and Cassandra are used to analyze big data to provide businesses insights for improved decision making, customer service, and operational efficiency.