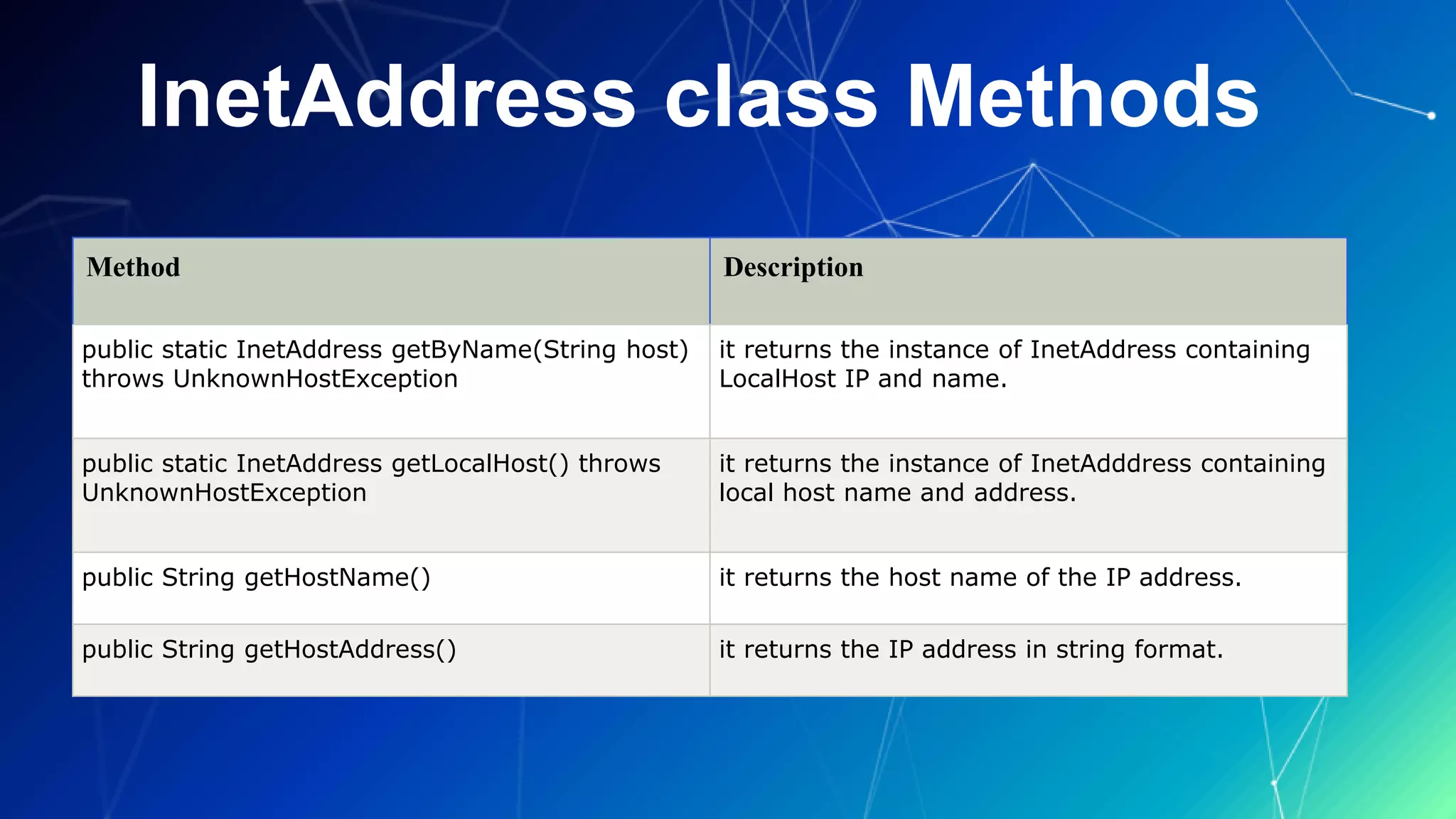
This document introduces key concepts in Java networking. It defines Java networking as connecting computing devices to share resources using socket programming. The advantages are sharing resources and centralized software management. Key terminology includes IP address, protocol, port number, MAC address, connection-oriented and connection-less protocols, and sockets. IP addresses are unique identifiers for network nodes. Protocols define communication rules, and port numbers identify applications. MAC addresses uniquely identify network interfaces. Connection-oriented protocols use acknowledgements reliably but slowly, while connection-less protocols do not use acknowledgements but are faster. Sockets provide two-way communication between applications on different Java runtime environments.