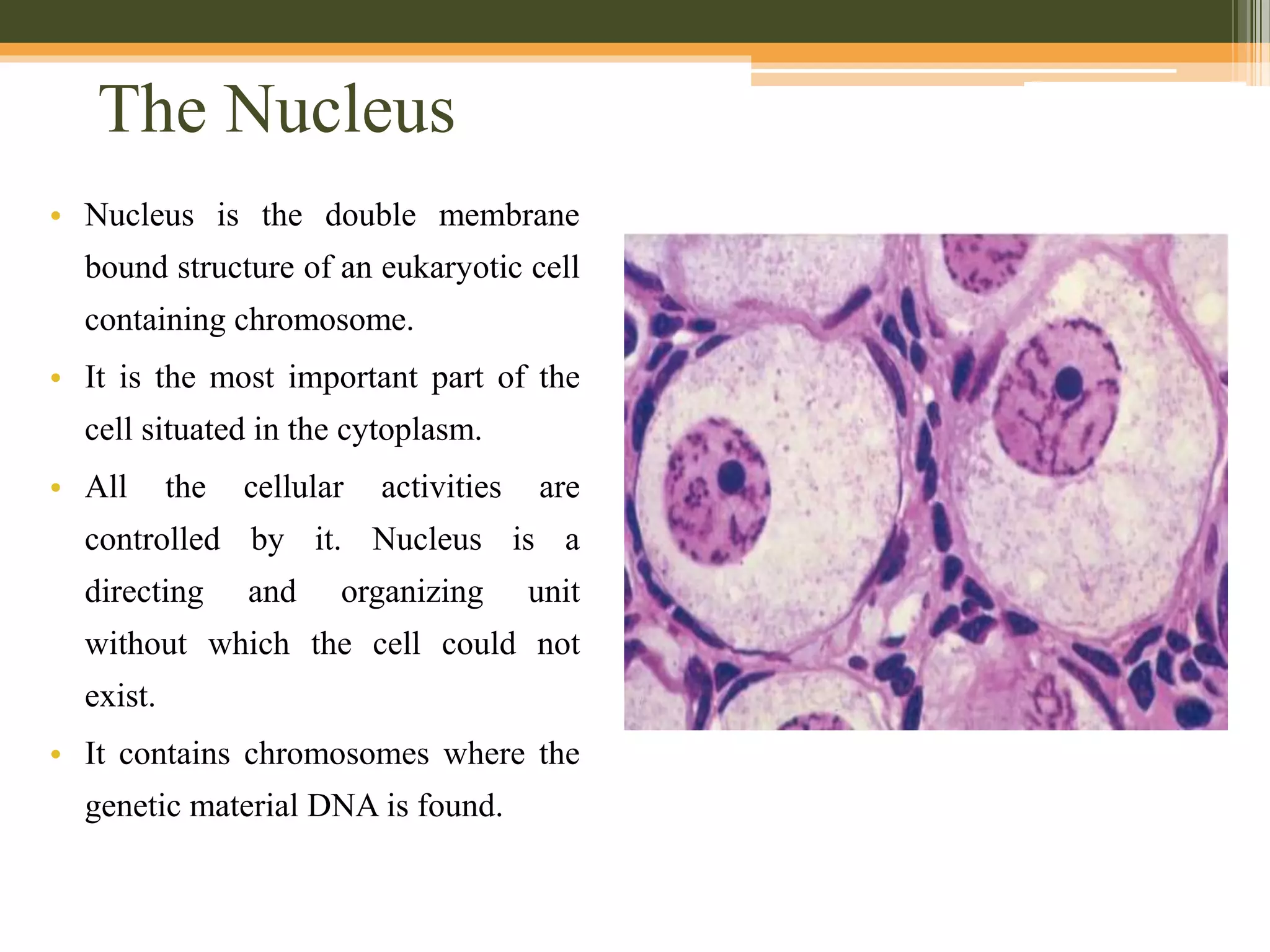
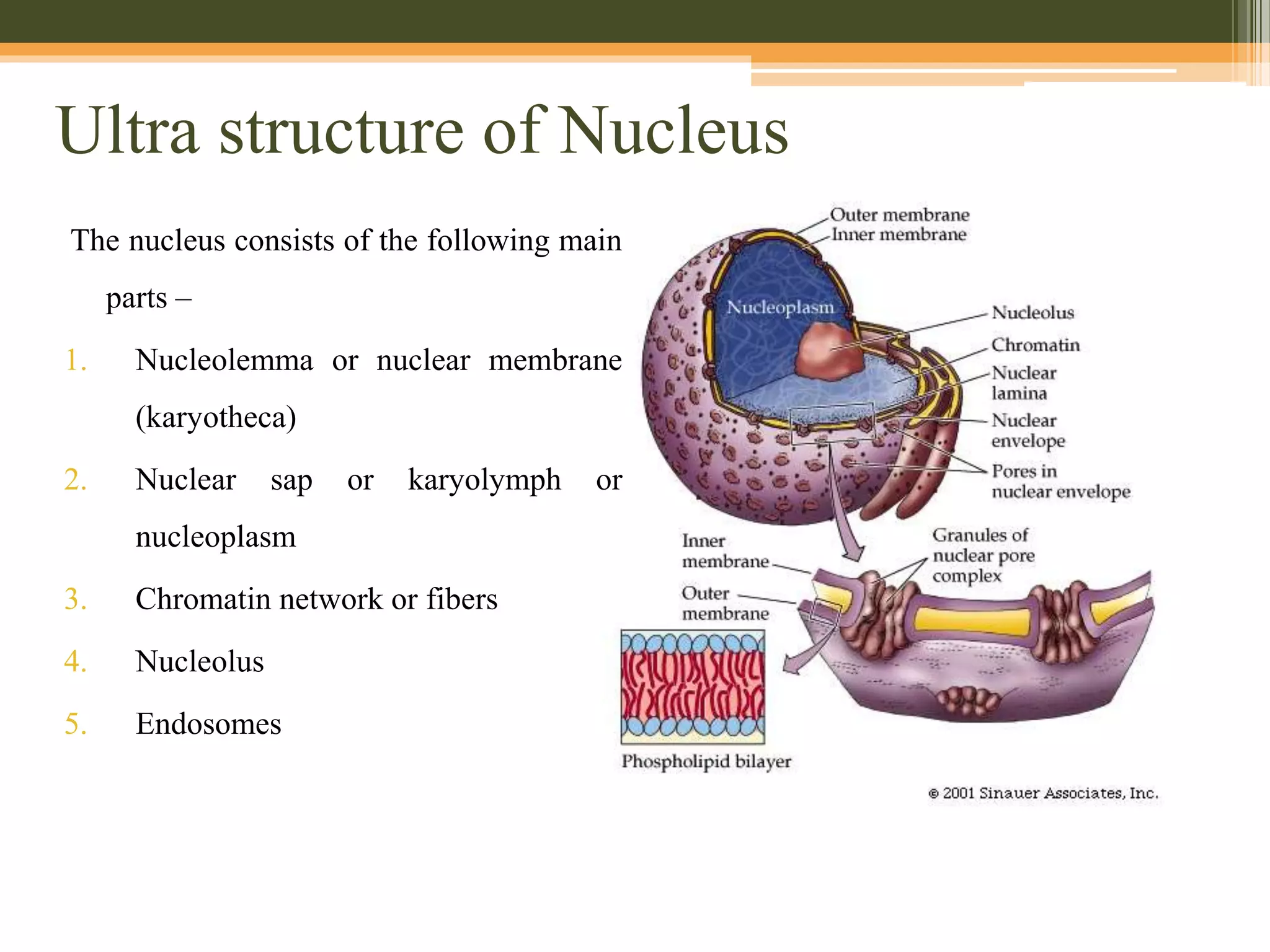
The nucleus is a double-membrane bound structure in eukaryotic cells that contains the genetic material DNA. During interphase, the nucleus contains a network of chromatin fibers in the nucleoplasm. The chromatin fibers are made up of nucleosomes, which consist of DNA wound around histone proteins. The nucleolus and endosomes are also found in the nucleoplasm. The nuclear membrane separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm, and contains nuclear pores that allow for transport between the two compartments.