Embed presentation
Downloaded 387 times


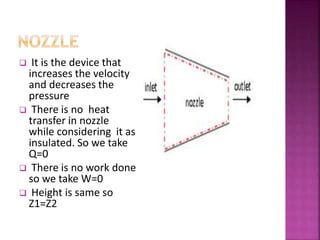
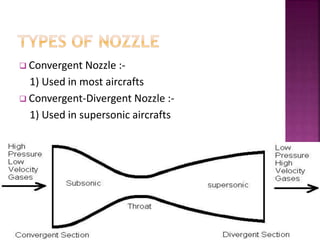

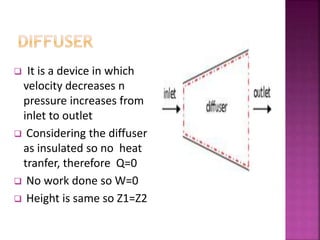









This document discusses nozzles and diffusers. It defines nozzles as devices that increase velocity and decrease pressure, and defines diffusers as devices that decrease velocity and increase pressure. Equations for steady flow through nozzles and diffusers using the energy equation are presented. Convergent nozzles are used in most aircrafts while convergent-divergent nozzles are used in supersonic aircraft. The Bernoulli principle is cited to explain how pressure decreases with decreasing area while velocity increases. The conclusion compares flow quality through different nozzle types.













