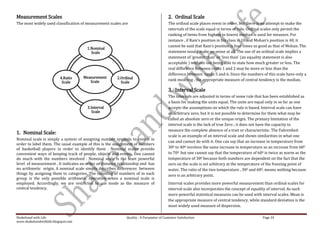
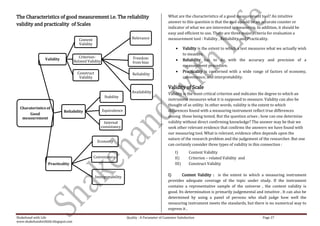
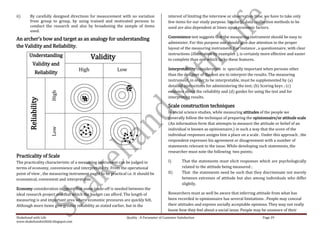
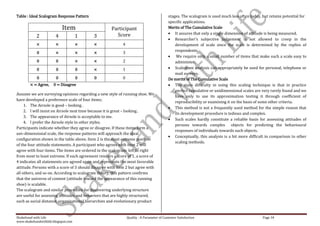
This document is a comprehensive set of notes prepared by Narender Sharma for MBA students focusing on research methodology, its significance in business decision-making, and the formulation of research problems. It covers various units including research designs, data collection methods, scaling techniques, and hypothesis testing, all aimed at enhancing students' understanding and application of research in real-world scenarios. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of continuous feedback for improvement and outlines several motivational insights for aspiring leaders in the field.




























![be indicated as ibid , followed by a comma and the page number. A single researcher should learn to recognize them as well as he should learn to use
page should be referred to as p., but more than one page be referred to as pp. them);
If there are several pages referred to at a stretch, the practice is to use often Abbreviations Meaning
the page number, for example , pp. 190ff , which means page number 190 and anon., anonymous
the following pages; but only for page 190 and the following page ‘190f’. ante., before
Roman numerical is generally used to indicate the number of the volume of a art., article
book. Op. cit.( opera citato, in the work cited ) or Loc. cit. ( loco citato, in the aug., augmented
place cited ) are two of the very convenient abbreviations used in the bk., book
footnotes. Op. cit. or Loc. cit. after the writer’s name would suggest that the bull., bulletin
reference is to work by the writer has been cited in detail in an earlier cf., compare
footnote but intervened by some other references. ch., chapter
7. Punctuation and abbreviations in footnotes col., column
The first item after the number in the footnotes is the author’s name, given in diss., dissertation
the normal signature order. This is followed by a comma. After the comma, ed., editor, edition, edited.
the title of the book is given : the article (such as “A” , “An” , “The” etc. ) is ed. cit., edition cited
omitted and only the first word and proper nouns and adjective are e.g., exempli gratia; for example
capitalized. The title is followed by a comma. Information concerning the eng., enlarged
edition is given next. This entry is followed by a comma. The place of et. al., and others
publication is then stated; it may be mentioned in an abbreviated form, if the et seq., and the following
place happens to be a famous one such as Lond. for London, N.Y. for New ex., example
York, N.D. for New Delhi and so on. This entry is followed by a comma. Then f., ff., and the following
the name of the publisher is mentioned and this entry is closed by a comma. fig(s)., figure(s)
It is followed by the date of publication if the date is given on the title page. If fn., footnote
the date appears in the copyright notice on the reverse side of the title page ibid., ibidem: in the same place (when two or more
or elsewhere in the volume, the comma should be omitted and the date successive footnotes refer to the same
enclosed in square brackets [ c 1978], [1978]. The entry is followed by a work, it is not necessary to repeat
comma. Then follow the volume and page references and are separated by a complete reference for the second
comma if both are given. A period closes the complete documentary footnote. ibid. may be used. if different
reference. But one should remember that the documentation regarding pages are referred to, pagination must
acknowledgements from magazine articles and periodical literature follow a be shown).
different form as stated earlier while explaining the entries in the id., idem: the same
bibliography. ill., illus., or illust(s). illustrated, illustration(s)
Certain English and Latin abbreviations are quite often used in bibliographies Intro., intro., introduction
and footnotes to eliminate tedious repetition. The following is a partial list of l, or ll, line (s)
the most common abbreviations frequently used in report–writing ( the
Shakehand with Life Quality : A Parameter of Customer Satisfaction Page 42
www.shakehandwithlife.blogspot.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notesresearchmethodologymbasem-iiimdurohtakdde-110217190511-phpapp01/85/MBA-Notes-Research-Methodology-43-320.jpg)




