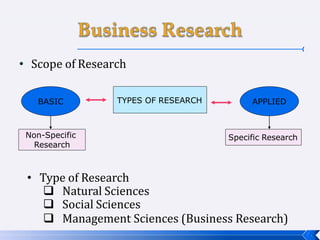
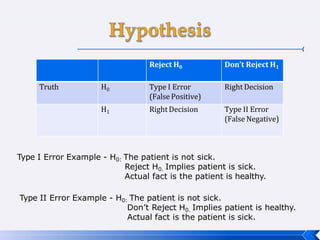
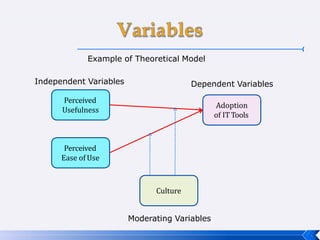
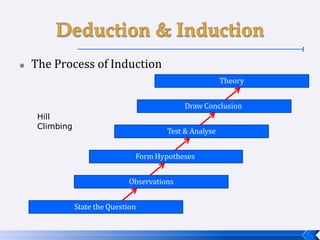
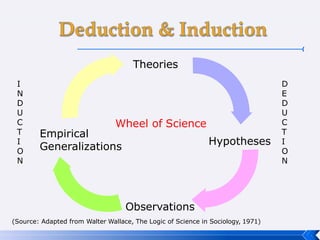
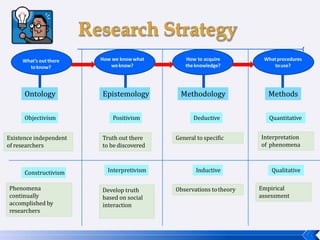
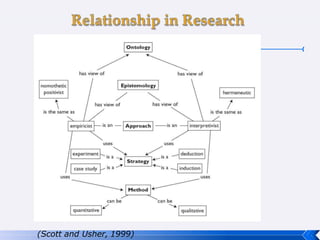
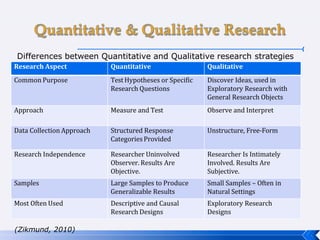
The document provides an introduction to business research methods. It discusses key concepts such as the definition of business research, the role of theory and hypotheses, deductive and inductive approaches, quantitative and qualitative research strategies, and mixed methods. The document also outlines different research paradigms and the ontological and epistemological assumptions underlying various approaches to research.