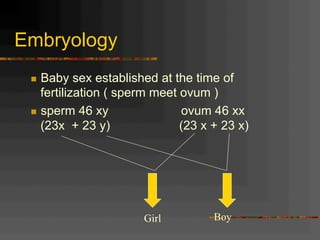
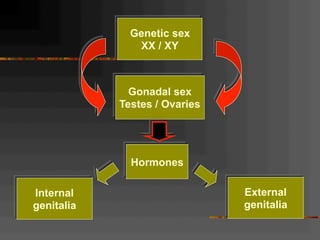
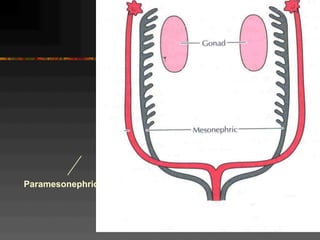
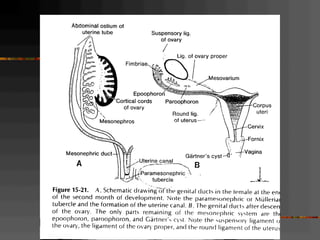
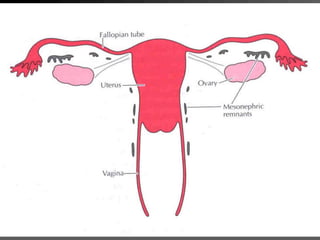
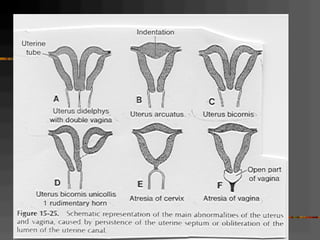
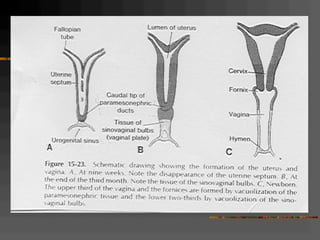
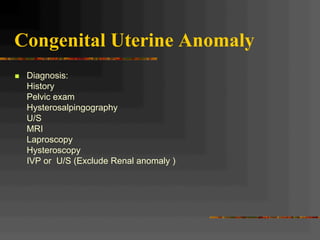
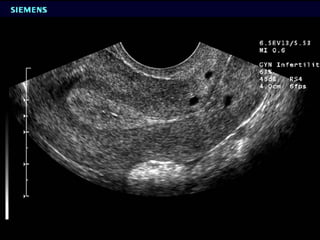
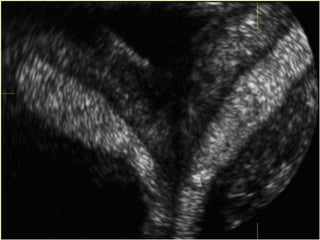
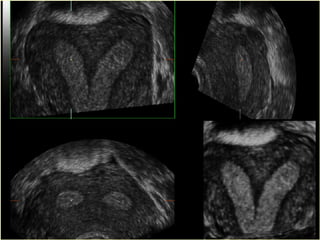
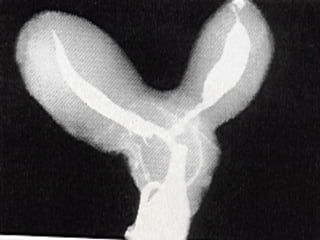
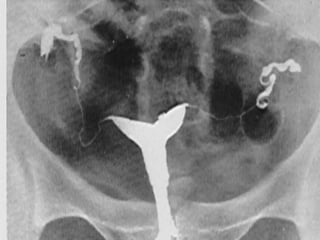
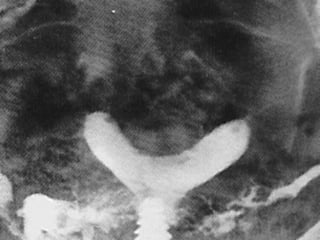
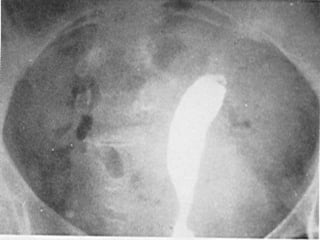
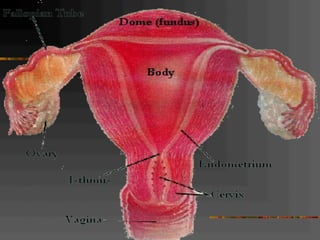
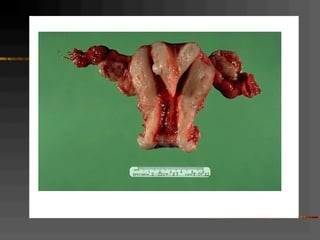
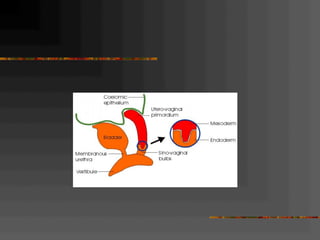
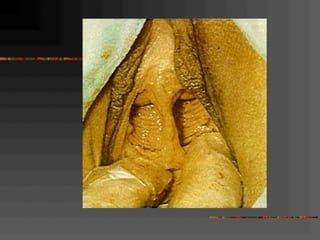
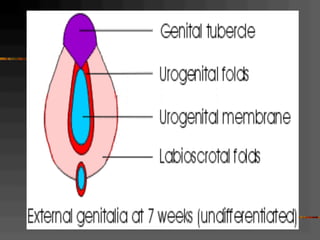
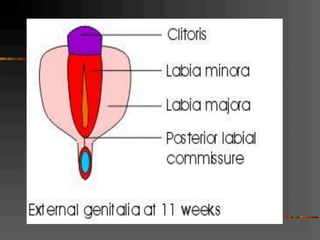
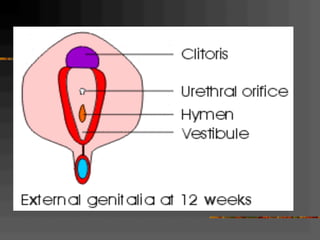
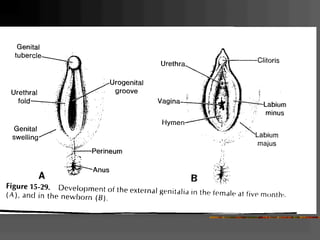
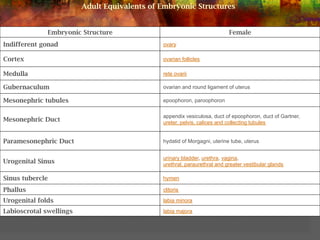
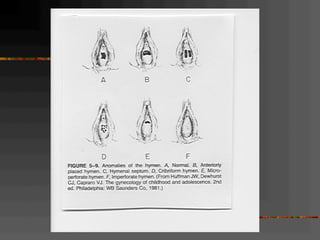
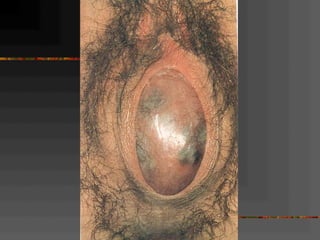
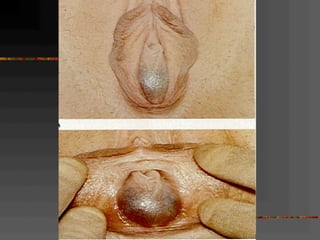
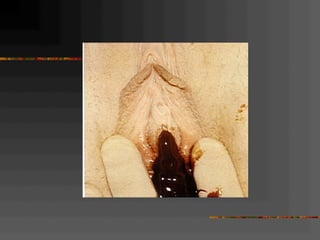
This document discusses normal and abnormal development of the female genital tract. It begins with an overview of embryology, including how genetic sex is determined at fertilization and how the indifferent gonad develops into either an ovary or testis. It then focuses on ovarian development and function. It describes several congenital uterine anomalies and their clinical presentations and treatment approaches. It also discusses Mullerian agenesis, vaginal agenesis, transverse vaginal septum, and imperforated hymen.